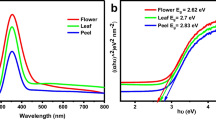
Abstract
Cyanidin 3,5-di-O-glucoside anthocyanin was extracted from red rose flower petals and used as reducing and capping agent for the green synthesis of anisotropic gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images indicated that the Au NPs have large number of small spheres of gold. Surface plasmon resonance band position strongly depended on the [HAuCl4] and [anthocyanin]. Cationic surfactant distinctly changed the shape, size, number of NPs, and size distribution of Au nanodisks at room temperature. Conventional techniques were used to the estimate the antiradical and antimicrobial activities of the cyanidin 3,5-di-O-glucoside anthocyanin and gold NPs. The 2,2-diphenyl-l-picrylhydrazyl nitrogen radical (DPPH·), two bacteria strains (Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli), and two yeast strains (Candida albicans ATCC 10231 and Candida parapsilosis ATCC 22019) were used to determine the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of CTAB-capped gold NPs. Eosin yellow photocatalytic degradation followed apparent first-order kinetics with activation energies of 54.4 kJ/mol and 39.5 kJ/mol, respectively, for oxidative and sunlight catalyzed paths. The photocatalytic rates drastically inhibited with scavengers, demonstrating that the reactive radical oxygen species (HO· and O2−·), holes (h+) and electrons (e−) played major role in the degradation.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.-C. Daniel, D. Astruc, Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 104, 293–346 (2004)
A. Henglein, D. Meisel, Radiolytic control of the size of colloidal gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 14, 7392–7394 (1998)
K. Esumi, K. Matsuhisa, K. Torigoe, Preparation of rodlike gold particles by UV irradiation using cationic micelles as a template. Langmuir 11, 3285–3287 (1995)
D.V. Goia, E. Matijevic, Tailoring the particle size of monodispersed colloidal gold. Coll. Surf. A 146, 139–152 (1999)
K. Jadhav, H.R. Rajeshwari, S. Deshpande, S. Jagwani, D. Dhamecha, S. Jalalpure, K. Subburayan, D. Baheti, Phytosynthesis of gold nanoparticles: characterization, biocompatibility, and evaluation of its osteoinductive potential for application in implant dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 93, 664–670 (2018)
M.S. Bakshi, F. Possmayer, N.O. Petersen, Role of different phospholipids in the synthesis of pearl-necklace-type gold-silver bimetallic nanoparticles as bioconjugate materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 14113–14124 (2007)
M.S. Bakshi, H. Kaur, T.S. Banipal, N. Singh, G. Kaur, Biomineralization of gold nanoparticles by lysozyme and cytochrome c and their applications in protein film formation. Langmuir 26, 13535–13544 (2010)
M.S. Bakshi, Colloidal micelles of block copolymers as nanoreactors, templates for gold nanoparticles, and vehicles for biomedical applications. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 213, 1–20 (2014)
B. Nikoobakht, M.A. El-Sayed, Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem. Mater. 15, 1957–1962 (2003)
S. Khademi, S. Sarkar, A. Shakeri-Zadeh, N. Attaran, S. Kharrazi, M. RezaAy, H. Ghadiri, Folic acid-cysteamine modified gold nanoparticle as a nanoprobe for targeted computed tomography imaging of cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 89, 182–193 (2018)
Z. Shervani, Y. Yamamoto, Carbohydrate-directed synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: effect of the structure of carbohydrates and reducing agents on the size and morphology of the composites. Carbohydr. Res. 346, 651–694 (2011)
P.C. Pandey, G. Pandey, A. Walcarius, 3-Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane mediated solvent induced synthesis of gold nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 79, 45–54 (2017)
Z. Khan, T. Singh, J.I. Hussain, A.A. Hashmi, Au(III)-CTAB reduction by ascorbic acid: preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles. Coll. Surf. B 104, 11–17 (2013)
M.N. Khan, T.A. Khan, S.A. Al-Thabaiti, Z. Khan, Spectrophotometric evidence to the formation of AuCl4-CTA complex and synthesis of gold nano-flowers with tailored surface textures. Spectrochim. Acta A 149, 889 (2015)
L. Longenberger, G. Mills, Formation of metal particles in aqueous solutions by reactions of metal complexes with polymers. J. Phys. Chem. 99, 475–478 (1995)
X. Liu, M. Atwater, J. Wang, Q. Huo, Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Coll. Surf. B 58, 3–7 (2007)
P.-L. Kuo, C.-C. Chen, M.-W. Jao, Effects of polymer micelles of alkylated polyethylenimines on generation of gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 9445–9450 (2005)
M.H. Mashhadizadeh, R.P. Talemi, Synergistic effect of magnetite and gold nanoparticles onto the response of a label-free impedimetric hepatitis B virus DNA biosensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 59, 773–781 (2016)
B. Kumar, K. Smita, L. Cumbal, J. Camacho, E. Hernández-Gallegos, M. G. Chavez-Lopez, M. Grijalva, K. Andrade, One pot phytosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Genipa americana fruit extract and its biological applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 62, 725–731 (2016)
S.P. Dubey, M. Lahtinen, M. Sillanpaa, Tansy fruit mediated greener synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Process Biochem. 45, 1065–1071 (2010)
R. Geetha, T. Ashokkumar, S. Tamilselvan, K. Govindaraju, M. Sadiq, G. Singaravelu, Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Cancer Nano 4, 91–98 (2013)
C.H. Eugster, E. Marki-Fischer, The chemistry of rose pigments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 30, 654–672 (1991)
M.H. Eikani, F. Golmohammad, S. Rowshanzamir, M. Mirza, Recovery of water-soluble constituents of rose oil using simultaneous distillation-extraction. Flavour Fragr. J. 20, 555–558 (2005)
R. Nowak, M. Olech, Ł. Pecio, W. Oleszek, R. Los, A. Malm, J. Rzymowska, Cytotoxic, antioxidant, antimicrobial properties and chemical composition of rose petals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 94, 560–567 (2014)
M.S. Bakshi, Nanoshape control tendency of phospholipids and proteins: Protein-nanoparticle composites, seeding, self-aggregation, and their applications in bionanotechnology and nanotoxicology. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 13947–13960 (2011)
S.S. Shankar, A. Rai, A. Ahmad, M. Sastry, Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 275, 496–502 (2004)
N.R. Jana, L. Gearheart, C.J. Murphy, Seed-mediated growth approach for shape-controlled synthesis of spheroidal and rod-like gold nanoparticles using a surfactant template. Adv. Mater. 13, 1386–1389 (2001)
V.L. Singleton, J.A. Jr Rossi, Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 16, 144–158 (1965)
J.B. Harbornem, Spectral methods of characterizing anthocyanins. Biochem. J. 70, 22–28 (1958)
T. Fulehi, F.J. Francis, Quantitative methods for anthocyanins. 1. Extraction and determination of total Anthocyanin in cranberries. J. Food Sci. 33, 72–77 (1968)
Z. Zaheer, Eco-friendly walnut shell powder based facile fabrication of Ag-nanodisks, and their interaction with bovine serum albumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 193, 8–17 (2019)
J. Xiao, L. Qi, Surfactant-assisted, shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanocrystals. Nanoscale 3, 1383–1396 (2011)
L. Li, Z. Wang, T. Huang, J. Xie, L. Qi, Porous gold nano belts templated by metal-surfactant complex nanobelts. Langmuir 26, 12330–12335 (2010)
F. Bodker, S. Morup, S. Linderoth, Surface effects in metallic iron nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 282–285 (1994)
M. Liu, P. Guyot-Sionnest, Mechanism of silver(I)-assisted growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 22192–22200 (2005)
T.K. Sau, C.J. Murphy, Room temperature, high-yield synthesis of multiple shapes of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 8648–8649 (2004)
J.H. Lee, H.-J. Lee, M.-G. Choung, Anthocyanin compositions and biological activities from the red petals of Korean edible rose (Rosa hybrida cv Noblered). Food Chem. 129, 272–278 (2011)
M. Noruzi, D. Zare, K. Khoshnevisan, D. Davoodi, Rapid green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using rosa hybrida petal extract at room temperature. Spectrochemica. Acta A 79, 1461–1465 (2011)
H.E. Khoo, A. Azlan, S.T. Tang, S.M. Lim, Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 61, 1361779 (2017)
A. Castaneda-Ovando, M.L. Pacheco-Hernandez, M.E. Paez-Hernandez, J.A. Rodriguez, C.A. Galan-Vidal, Chemical studies of anthocyanins: a review. Food Chem. 113, 859–871 (2009)
R.L. Scalzo, A. Genna, F. Branca, M. Chedin, H. Chassaigne, Anthocyanin composition of cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis) and cabbage (B. oleracea L. var. capitata) and its stability in relation to thermal treatments. Food Chem. 107, 136–144 (2008)
Y. Cai, M. Sun, H. Wu, R. Huang, H. Corke, Characterization and quantification of betacyanin pigments from diverse amaranthus species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 2063–2070 (1998)
N. Ahmadiani, R.J. Robbins, T.M. Collins, M.M. Giusti, Molar absorptivity (ε) and spectral characteristics of cyanidin-based anthocyanins from red cabbage. Food Chem. 197, 900–906 (2016)
A. Mahal, P. Khullar, H. Kumar, G. Kaur, N. Singh, M. Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.S. Bakshi, Green Chemistry of zein protein toward the synthesis of bioconjugated nanoparticles: understanding unfolding, fusogenic behavior, and hemolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 627–639 (2013)
B. Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P. Mulvaney, L.M. Liz-Marzan, An electrochemical model for gold colloid formation via citrate reduction. Z. Phys. Chem. 221, 415–426 (2007)
S. Mondal, M.E. De Anda Reyes, U. Pal, Plasmon induced enhanced photocatalytic activity of gold loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for methylene blue degradation under visible light. RSC Adv. 7, 8633–8645 (2017)
H. Zhu, X. Chen, Z. Zheng, X. Ke, E. Jaatinen, J. Zhao, C. Guo, T. Xie, D. Wang, Mechanism of supported gold nanoparticles as photocatalysts under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation. Chem. Commun. 48, 7524–7526 (2009)
B. Tian, Q. Lei, B. Tian, W. Zhang, Y. Cui, Y. Tian, UV-driven overall water splitting using unsupported gold nanoparticles as photocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 54, 1845–1848 (2018)
R. Nowak, M. Olech, L. Pecio, W. Oleszek, R. Los, A. Malmc, J. Rzymowska, Cytotoxic, antioxidant, antimicrobial properties and chemical composition of rose petals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 94, 560–567 (2014)
J.A. He, M.M. Giusti, Anthocyanins: Natural colorants with health promoting properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technolo. 1, 163–186 (2010)
P. Natarajan, P. Sukthankar, J. Changstrom, C.S. Holland, S. Barry, W.B. Hunter, C.M. Sorensen, J.M. Tomich, Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional branched amphiphilic peptide bilayer conjugated gold nanoparticles. ACS Omega 3, 11071–11083 (2018)
I. Sondi, B. Salopek-Sondi, Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 275, 177–182 (2004)
Rahisuddin, S.A. Al-Thabaiti, Z. Khan, N. Manzoor, Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial and antifungal activities towards gram-positive, gram-negative bacterial strains and different species of candida fungus. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 38, 1773–1781 (2015)
A.I. Lopez-Lorente, S. Cardenas, Z.I. Gonzalez-Sanchez, Effect of synthesis, purification and growth determination methods on the antibacterial and antifungal activity of gold nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 103, 109805 (2019)
T. Pal, S. De, N.R. Jana, N. Pradhan, R. Mandal, A. Pal, A.E. Beezer, J.C. Mitchel, Organized media as redox catalysts. Langmuir 14, 4724–4730 (1998)
N. Pradhan, A. Pal, T. Pal, Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Coll. Surf. A 196, 247–257 (2002)
G. Li, K.H. Wong, X. Zhang, C. Hu, J.C. Yu, R.C.Y. Chan, P.K. Wong, Degradation of acid orange 7 using magnetic AgBr under visible light: The roles of oxidizing species. Chemosphere 76, 1185–1191 (2009)
K. Yamada, K. Miyajima, F. Mafune, Thermionic emission of electrons from gold nanoparticles by nanosecond pulse-laser excitation of interband. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 11246–11251 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under Grant No. (D-178-274-1439). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aazam, E.S., Zaheer, Z. Rose cyanidin 3,5-di-O-glucoside-assisted gold nanoparticles, their antiradical and photocatalytic activities. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 8780–8795 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03413-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03413-8