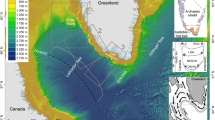
Abstract
Submarine fans and turbidite systems are important and sensitive features located offshore from river deltas that archive tectonic events, regional climate, sea level variations and erosional process. Very little is known about the sedimentary structure of the 1800 km long and 400 km wide Mozambique Fan, which is fed by the Zambezi and spreads out into the Mozambique Channel. New multichannel seismic profiles in the Mozambique Basin reveal multiple feeder systems of the upper fan that have been active concurrently or consecutively since Late Cretaceous. We identify two buried, ancient turbidite systems off Mozambique in addition to the previously known Zambezi-Channel system and another hypothesized active system. The oldest part of the upper fan, located north of the present-day mouth of the Zambezi, was active from Late Cretaceous to Eocene times. Regional uplift caused an increased sediment flux that continued until Eocene times, allowing the fan to migrate southwards under the influence of bottom currents. Following the mid-Oligocene marine regression, the Beira High Channel-levee complex fed the Mozambique Fan from the southwest until Miocene times, reworking sediments from the shelf and continental slope into the distal abyssal fan. Since the Miocene, sediments have bypassed the shelf and upper fan region through the Zambezi Valley system directly into the Zambezi Channel. The morphology of the turbidite system off Mozambique is strongly linked to onshore tectonic events and the variations in sea level and sediment flux.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beiersdorf H, Kudrass H-R, von Stackelberg U (1980) Placer Deposits of Ilmenite and Zircon on the Zambezi Shelf. Schweizerbart Science Publishers, Stuttgart
Brown R, Summerfield M, Gleadow A, Gallagher K, Carter A, Beucher R, Wildman M (2014) Intracontinental deformation in southern Africa during the Late Cretaceous. J Afr Earth Sci 100:20–41. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.05.014
Burke K (1996) The African Plate. South African. J Geol 99:341–409
Burke K, Gunnell Y (2008) The African erosion surface: a continental-scale synthesis of geomorphology, tectonics, and environmental change over the past 180 million years. Geol Soc Am Memoir 201:1–66. doi:10.1130/2008.1201
Castelino JA, Reichert C, Klingelhoefer F, Aslanian D, Jokat W (2015) Mesozoic and Early Cenozoic sediment influx and morphology of the Mozambique Basin. Mar Pet Geol 66:890–905. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.07.028
Castelino JA, Eagles G, Jokat W (2016) Anomalous bathymetry and palaeobathymetric models of the Mozambique Basin and Riiser Larsen Sea. Earth Planet Sci Lett. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.018
Coffin MF (1992) The East African and Madagascar margins: stratigraphy, structure and tectonics. In: First Indian Ocean Petroleum Seminar, Proceedings of the First Indian Ocean Petroleum Seminar on Petroleum Exploration, Seychelles, 10–15 Dec 1990, pp. 325–343.
Coleman JM, Prior DB, Lindsay JF (1983) Deltaic Influences on shelfedge instability processes, In: Stanley DJ, Moore GT (eds) The Shelfbreak, SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology), Tulsa, pp. 121–137. doi:10.2110/pec.83.06.0121
Curray JR, Emmel FJ, Moore DG (2003) The Bengal Fan: morphology, geometry, stratigraphy, history and processes. Mar Pet Geol 19:1191–1223. doi:10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00035-7
Daszinnies MC, Jacobs J, Wartho JA, Grantham GH (2009) Post Pan-African thermo-tectonic evolution of the north Mozambican basement and its implication for the Gondwana rifting. Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar hornblende, biotite and titanite fission-track dating. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 324:261–286. doi:10.1144/SP324.18
de Ruijter WPM (2002) Observations of the flow in the Mozambique Channel. Geophys Res Lett 29:3–5. doi:10.1029/2001GL013714
De Buyl M, Flores G (1986) The Southern Mozambique Basin: the most promising hydrocarbon province offshore East Africa. Am Assoc Geol Bull 68:399–425
Dingle RV, Hendey QB (1984) Late Mesozoic and Tertiary sediment supply to the Easter Cape Basin (SE Atlantic) and palaeo-drainage systems in southwestern Africa. Mar Geol 56:13–26
Droz L, Mougenot D (1987) Mozambique upper fan: origin of depositional units. AAPG Bull 71:1355–1365
Emmel B, Kumar R, Ueda K, Jacobs J, Daszinnies MC, Thomas RJ, Matola R (2011) Thermochronological history of an orogen-passive margin system: an example from northern Mozambique. Tectonics. doi:10.1029/2010TC002714
Figueiredo J, Hoorn C, van der Ven P, Soares E (2009) Late Miocene onset of the Amazon River and the Amazon deep-sea fan: Evidence from the Foz do Amazonas Basin. Geology 37:619–622. doi:10.1130/G25567A.1
Flood RD, Manley PL, Kowsmann RO, Appi CJ, Pirmez C (1991) Seismic Facies and Late Quaternary Growth of Amazon Submarine Fan. In: Weimer P, Link MH (eds) Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems. Springer, New York, pp 415–433. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-8276-8_23
Flores G (1973) The Cretaceous and Tertiary sedimentary basins of Mozambique and Zululand. Sediment Basins Afr Coasts 2:81–111
France-Lanord C, Spiess S, Adam K (2015) Neogene and late Paleogene record of Himalayan orogeny and climate: a transect across the Middle Bengal Fan, International Ocean Discovery Program Preliminary Report. International Ocean Discovery Program. doi:10.14379/iodp.pr.354.2015
Gallagher K, Brown R (1999) The Mesozoic denudation history of the Atlantic margins of southern Africa and southeast Brazil and the relationship to offshore sedimentation. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 153:41–53
Gorini C, Haq BU, dos Reis AT, Silva CG, Cruz A, Soares E, Grangeon D (2014) Late Neogene sequence stratigraphic evolution of the Foz do Amazonas Basin, Brazil. Terra Nov 26:179–185. doi:10.1111/ter.12083
Goudie AS (2005) The drainage of Africa since the Cretaceous. Geomorphology 67:437–456. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.11.008
Imran J, Parker G, Katopodes N (1998) A numerical model of channel inception on submarine fans. J Geophys Res 103:1219. doi:10.1029/97JC01721
Imran J, Parker G, Harff P (2002) Experiments on incipient channelization of submarine fans. J Hydraul Res 40:21–32. doi:10.1080/00221680209499870
INP (2014) Natural gas master plan.
Jokat W (2014) The expedition of the Research Vessel ‘Sonne’ to the Mozambique Basin in 2014 (SO230). Reports Polar Mar Res 676:126
Kolla V, Eittreim S, Sullivan L, Kostecki JA, Burckle LH (1980a) Current-controlled, abyssal microtopography and sedimentation in mozambique basin, southwest indian ocean*. Mar Geol 34:171–206
Kolla V, Kostecki JA, Henderson L, Hess L (1980b) Morphology and Quaternary sedimentation of the Mozambique Fan and environs, southwestern Indian Ocean. Sedimentology 27:357–378
Krishna KS, Ismaiel M, Srinivas K, Gopala Rao D, Mishra J, Saha D (2016) Sediment pathways and emergence of Himalayan source material in the Bay of Bengal. Curr Sci 110:363–372
Mahanjane ES (2012) A geotectonic history of the northern Mozambique Basin including the Beira High—A contribution for the understanding of its development. Mar Pet Geol 36:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.05.007
Mahanjane ES, Franke D, Lutz R, Winsemann J, Ehrhardt A, Berglar K, Reichert C (2014) MATURITY AND PETROLEUM SYSTEMS MODELLING IN THE OFFSHORE ZAMBEZI DELTA DEPRESSION AND ANGOCHE BASIN, NORTHERN MOZAMBIQUE. J Pet Geol 37:329–348. doi:10.1111/jpg.12589
Maslin MA, Christensen B (2007) Tectonics, orbital forcing, global climate change, and human evolution in Africa: introduction to the African paleoclimate special volume. J Hum Evol 53:443–464. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2007.06.005
Milliman JD, Summerhayes CP, Barretto HT (1975) Quaternary Sedimentation on the Amazon Continental Margin: A Model. Geol Soc Am Bull 86:610. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<610:QSOTAC>2.0.CO;2
Moore AE, Cotterill FPD, Broderick T, Plowes D (2009) Landscape evolution in Zimbabwe from the Permian to present, with implications for kimberlite prospecting. S Afr J Geol 112:65–88. doi:10.2113/gssajg.112.1.65
Mutti E, Normark WR, 1991. Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems, In: Weimer P, Link MH (eds), Springer, New York, pp. 75–106. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-8276-8_4
Nairn AEM, Lerche I, Iliffe JE (1991) Geology, basin analysis, and hydrocarbon potential of Mozambique and the Mozambique Channel. Earth-Science Rev. 30:81–123. doi:10.1016/0012-8252(91)90014-7
Nelson CH, Escutia C, Damuth JE, Twichell DC, 2011. Interplay of mass-transport and turbidite-system deposits in different active tectonic and passive continental margin settings: external and local controlling factors. SEPM Spec Publ 39–66
Partridge TC, Maud RR (1987) Geomorphic evolution of souther Africa since the Mesozoic. S Afr J Geol 90:179–208
Reichert C (2007) Cruise Report: MoBaMaSis-BGR07.
Ridderinkhof H, De Ruijter WPM (2003) Moored current observations in the Mozambique Channel. Deep Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 50, 1933–1955. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(03)00041-9
Roberts GG, White N (2010) Estimating uplift rate histories from river profiles using African examples. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 115:1–24. doi:10.1029/2009JB006692
Rouby D, Bonnet S, Guillocheau F, Gallagher K, Robin C, Biancotto F, Dauteuil O, Braun J (2009) Sediment supply to the Orange sedimentary system over the last 150 My: an evaluation from sedimentation/denudation balance. Mar Pet Geol 26:782–794. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.08.004
Said A, Moder C, Clark S, Ghorbal B (2015) Cretaceous–Cenozoic sedimentary budgets of the Southern Mozambique Basin: Implications for uplift history of the South African Plateau. J Afr Earth Sci 109:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.05.007
Salazar MU, Baker D, Malcolm F, Kornpihl D, Tekena W (2013) Frontier exploration offshore the Zambezi Delta, Mozambique. First Break 31:135–144
Salman G, Abdula I (1995) Development of the Mozambique and Ruvuma sedimentary basins, offshore Mozambique. Sediment Geol 738:7–41
Schouten MW, De Ruijter WPM, Van Leeuwen PJ, Ridderinkhof H, (2003) Eddies and variability in the Mozambique Channel. Deep Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 50:1987–2003. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(03)00042-0
Schulz H, Lückge A, Emeis KC, Mackensen A (2011) Variability of Holocene to Late Pleistocene Zambezi riverine sedimentation at the upper continental slope off Mozambique, 15°–21°S. Mar Geol 286:21–34. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2011.05.003
Stow DAV, Howell DG, Nelson CH (1985) Sedimentary, tectonic, and sea-level controls, In: Bouma AH, Normark WR, Barnes NE (eds), Springer, New York, pp. 15–22. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-5114-9_4
Tinker J, de Wit M, Brown R (2008) Linking source and sink: Evaluating the balance between onshore erosion and offshore sediment accumulation since Gondwana break-up, South Africa. Tectonophysics 455:94–103. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.040
Van der Lubbe JHJL, Tjallingii R, Prins MA, Brummer, G.J.A., Jung, S.J.A., Kroon D, Schneider RR (2014) Sedimentation patterns off the Zambezi River over the last 20,000 years. Mar Geol 355:189–201. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2014.05.012
Walford H, White N, Sydow J (2005) Solid sediment load history of the Zambezi Delta. Earth Planet Sci Lett 238:49–63. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.07.014
Weatherall P, Marks KM, Jakobsson M, Schmitt T, Tani S, Arndt JE, Rovere M, Chayes D, Ferrini V, Wigley R (2015) A new digital bathymetric model of the world’s oceans. Earth Sp Sci 2:331–345. doi:10.1002/2015EA000107
Weimer P, Link MH, 1991. Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems, In: Weimer P, Link MH (eds), Springer, New York, pp. 3–7. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-8276-8_1
Wessel P, Smith, W.H.F., Scharroo R, Luis J, Wobbe F (2013) Generic mapping tools: Improved version released. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 94:409–410. doi:10.1002/2013EO450001
Wildman M, Brown R, Beucher R, Persano C, Stuart F, Gallagher K, Schwanethal J, Carter A (2016) The chronology and tectonic style of landscape evolution along the elevated Atlantic continental margin of South Africa resolved by joint apatite fission track and (U-Th-Sm)/He thermochronology. Tectonics 35:511–545. doi:10.1002/2015TC004042
Wiles E, Green A, Watkeys M, Jokat W, Krocker R (2014) A new pathway for Deep water exchange between the Natal Valley and Mozambique Basin? Geo-Marine Lett 34:525–540. doi:10.1007/s00367-014-0383-1
Wiles E, Green A, Watkeys M, Jokat W (2017) Zambezi continental margin: Compartmentalized sediment transfer routes to the abyssal Mozambique Channel. Mar Geophys Res. doi:10.1007/s11001-016-9301-4
Acknowledgements
We thank the French polar institute (IPEV) for the logistic and financial support and the captain and crew of Marion Dufresne II (IPEV) for their excellent work during the expedition. We are grateful to the contributions of Graeme Eagles, two anonymous reviewers and E. S. Mahanjane in improving the content and for the English corrections. All maps were created using GMT 5.0 (Wessel et al. 2013). GEBCO 2014: (Weatherall et al. 2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castelino, J.A., Reichert, C. & Jokat, W. Response of Cenozoic turbidite system to tectonic activity and sea-level change off the Zambezi Delta. Mar Geophys Res 38, 209–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-017-9305-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-017-9305-8