Abstract
Purpose
This study was to investigate the regulation of sulfur status in continuous-cropping soybean soil by Funneliformis mosseae and Thiobacillus thioparus and promote the absorption of sulfur in soybean. To explore the interactions among F. mosseae, T. thioparus and soybean plants, this study laid a theoretical foundation for the application of F. mosseae and T. thioparus as biological agents in agricultural production.
Methods
Pot culture, a two-compartment system and shake-flask culture were used in the experiment. Using F. mosseae and T. thioparus as experimental inoculants, the effects of F. mosseae on sulfur oxide of T. thioparus and their interaction on the growth of soybean plants were studied from the aspects of soil sulfur content, sulfur functional genes and the growth of soybean and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria.
Results
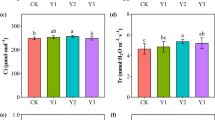
The F. mosseae and T. thioparus inoculation significantly increased the abundance of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and available sulfur content in the soil, stimulated the expression of sulfate transporter genes in soybean roots, and promoted the absorption of sulfur nutrients in soybean. F. mosseae stimulated the expression of the T. thioparus sulfur-oxidation gene and enhanced the sulfur-oxidation capacity, while T. thioparus enhanced F. mosseae colonization of soybean roots. Thus, F. mosseae and T. thioparus promoted soil sulfur cycling and sulfate transport in soybean roots, which proved that F. mosseae could effectively improve the sulfur-oxidation capacity of T. thioparus.
Conclusion
Double inoculation with F. mosseae and T. thioparus significantly promoted soybean plant growth and increased soil sulfur utilization.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alarcón-Poblete E, Inostroza-Blanchetea C, Alberdi M, Rengel Z, Reyes-Díaz M (2018) Molecular regulation of aluminum resistance and sulfur nutrition during root growth. Planta 247:27–39
Andrino A, Guggenberger G, Kernchen S, Mikutta R, Sauheitl L, Boy J (2021) Production of organic acids by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their contribution in the mobilization of phosphorus bound to iron oxides. Front Plant Sci 12:661842
Ansori A, Gholami A (2015) Improved nutrient uptake and growth of maize in response to inoculation with Thiobacillus and mycorrhiza on an alkaline soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 46:2111–2126
Bahadur A, Batool A, Nasir F, Jiang S, Mingsen Q, Zhang Q, Feng H (2019) Mechanistic insights into arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-mediated drought stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 20:4199
Bharadwaj DP, Alström S, Lundquist PO (2012) Interactions among Glomus irregulare, arbuscular mycorrhizal spore-associated bacteria, and plant pathogens under in vitro conditions. Mycorrhiza 22:437–447
Birch G (1963) Spectrophotometric determination of glucose content in glucose derivatives. Proc Assoc Clin Biochem 2:216–217
Böhringer J, Fischer D, Mosler G, Hengge-Aronis R (1995) UDP-glucose is a potential intracellular signal molecule in the control ofexpression of sigma S and sigma S-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:413–422
Chaudhary S, Dhanker R, Singh K, Brar B, Goyal S (2022) Characterization of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria isolated from mustard (Brassica juncea L.) rhizosphere having the capability of improving sulfur and nitrogen uptake. J Appl Microbiol 133:2814–2825
Chavarría M, Rodríguez DG, Krell T, Santiago C, Brezovsky J, Damborsky J (2014) Fructose 1-phosphate is the one and only physiological effector of the Cra (FruR) regulator of Pseu-domonas putida. FEBS Open Bio 4:377–386
Cui J, Bai L, Liu X, Jie W, Cai BY (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the rhizosphere of a continuous cropping soybean system at the seedling stage. Braz J Microbiol 49:240–247
Deng L, Huang J, Zhang W (2009) Determination of sulfate in drinking water by ultrasonic-acidic barium chromate spectrophotometry. China Trop Med 9:363–364
Deutscher J (2008) The mechanisms of carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:87–93
Diagne N, Ngom M, Djighaly PI, Fall D, Hocher V, Svistoonoff S (2020) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth and performance: importance in biotic and abiotic stressed regulation. Diversity 12:370
Ding Y, Zhou X, Zuo L, Wang H, Yu D (2016) Identification and functional characterization of the sulfate transporter gene GmSULTR1; 2b in soybean. BMC Genomics 17:1–19
Doutre DA, Hay GW, Hood A, Vanloon GW (1978) Spectrophotometric methods to determine carbohydrates in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 10:457–462
Emmett BD, Lévesque-Tremblay V, Harrison MJ (2021) Conserved and reproducible bacterial communities associate with extraradical hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. ISME J 15:2276–2288
Eweda W, Hassan E, Heggo A, Mohamed A (2015) Impact of endomycorrhizae and acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with sulfur and phosphorus nutrition on onion (Allium cepa L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) plants under field conditions. British Microbiology Research Journal 9:1–15
Franzen DW (2018) Limitations of the sulfate-sulfur soil test as a predictor of sulfur response. Ext. Publ. SF1880. North Dakota St. Ext., Fargo
Fuentes-Lara LO, Medrano-Macías J, Pérez-Labrada F, Rivas-Martínez EN, García-Enciso EL, González-Morales S, Benavides-Mendoza A (2019) From elemental sulfur to hydrogen sulfide in agricultural soils and plants. Molecules 24:2282
Ghaderi J, Malakouti MJ (2018) Effect of elemental sulfur and Thiobacillus bacteria on some chemical properties of soil and nutrients uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) crop. Appl Soil Res 6:131–142
Giovannetti M, Giovannetti M, Tolosano M, Volpe V (2014) Identification and functional characterization of a sulfate transporter induced by both sulfur starvation and mycorrhiza formation in Lotus japonicus. New Phytol 204:609–619
Giovannini L, Palla M, Agnolucci M, Avio L, Sbrana C, Turrini A, Giovannetti M (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated microbiota as plant biostimulants: research strategies for the selection of the best performing inocula. Agronomy 10:106
Görke B, Stülke J (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:613–624
Gray DJS (1950) Critical factors in the resorcinol reaction for the determination of fructose. Analyst 75:314–317
Hasenqi MG, He FG (2002) Resorcinol-spectrophotometric method for the determination of fructose in mustard Leaf's amylose. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 3:446–448
Hellal FA, Abdelhamid MT (2013) Nutrient management practices for enhancing soybean (Glycine max L.) production. Acta Biológica Colombiana 18:239–250
Heydari S, Pirzad A (2020) Mycorrhizal fungi and Thiobacillus co-inoculation improve the physiological indices of Lallemantia iberica under salinity stress. Curr Microbiol 77:2523–2534
Heydari S, Pirzad A (2021) Efficiency of Funneliformis mosseae and Thiobacillus sp. on the secondary metabolites (essential oil, seed oil and mucilage) of Lallemantia iberica under salinity stress. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 96:249–259
Jeckelmann JM, Erni B (2020) Transporters of glucose and other carbohydrates in bacteria. Pflügers Archiv-Eur J Physiol 472:1129–1153
Kormanik PP, Bryan WC, Schultz RC (1980) Procedures and equipment for staining large numbers of plant root samples for endomycorrhizal assay. Can J Microbiol 26:536–538
Kowalenko CG (1993) Total and fractions of sulfur. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis 231–246
Lager I (2010) Changes in external pH rapidly alter plant gene expression and modulate auxin and elicitor responses. Plant Cell Environ 33:1513–1528
Lee SY, Kim EG, Park JR, Ryu YH, Moon W, Park GH, Ubaidillah M, Ryu SN, Kim KM (2021) Effect on chemical and physical properties of soil each peat moss, elemental sulfur, and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Plants 10:1901
Liu X, Jin J, Wang G, Herbert SJ (2008) Soybean yield physiology and development of high-yielding practices in Northeast China. Field Crop Res 105:157–171
Luginbuehl LH, Menard GN, Kurup SV, Erp H, Radhakrishnan GV (2017) Fatty acids in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are synthesized by the host plant. Science 356:1175–1178
Majewska ML, Rola K, Zubek S (2017) The growth and phosphorus acquisition of invasive plants Rudbeckia laciniata and Solidago gigantea are enhanced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 27:83–94
Meng L, Feldman L (2010) A rapid TRIzol-based two-step method for DNA-free RNA extraction from Arabidopsis siliques and dry seeds, vol 5. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, pp 183–186
Mohamed AA, Eweda WE, Heggo AM, Hassan EA (2014) Effect of dual inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Sulphur-oxidising bacteria on onion (Allium cepa L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) grown in sandy soil under greenhouse conditions. Ann Agric Sci 59:109–118
Ogura M, Kanesaki Y (2018) Newly identified nucleoid-associated-like protein YlxR regulates metabolic gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Msphere 3:e00501–e00518
Ortaş I, Rafique M, Ahmed İA (2017) Application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi into agriculture. Arbuscular mycorrhizas and stress tolerance of plants 305–327
Osman JR, Cardon H, Montagnac G, Picard A, Daniel I (2021) Pressure effects on sulfur-oxidizing activity of Thiobacillus thioparus. Environ Microbiol Rep 13:169–175
Pourbabaee AA, Koohbori DS, Seyed Hosseini HM, Alikhani HA, Emami S (2020) Potential application of selected sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and different sources of sulfur in plant growth promotion under different moisture conditions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51:735–745
Sacchi GA, Nocit FF (2019) Plant sulfate transporters in the low phytic acid network: some educated guesses. Plants 8:616
Sayahi A, Souri B (2019) Evaluation of simultaneous application of powder sulfur and Thiobacillus thioparus to improve calcareous soils of western Iran. Iran J Soil Water Res 50:753–762
Sharma S, Compant S, Ballhausen MB, Ruppel S, Franken P (2020) The interaction between Rhizoglomus irregulare and hyphae attached phosphate solubilizing bacteria increases plant biomass of Solanum lycopersicum. Microbiol Res 240:126556
Tan KH (1986) Degradation of soil minerals by organic acids. Interact Soil Miner Nat Organics Microbes 17:1–27
Tran BT, Watts-Williams SJ, Cavagnaro TR (2019) Impact of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on the growth and nutrition of fifteen crop and pasture plant species. Funct Plant Biol 46:732–742
Yang F, Zhang S, Song J, Du Q, Li G (2019) Synthetic humic acids solubilize otherwise insoluble phosphates to improve soil fertility. Angew Chem 131:18989–18992
Yang W, Cheng P, Adams CA, Zhang S, Sun Y, Yu H, Wang F (2022) Effects of microplastics on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in a soil spiked with ZnO nanoparticles. Soil Biol Biochem 155:108179
Zhang L, Feng G, Declerck S (2018) Signal beyond nutrient, fructose, exuded by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus triggers phytate mineralization by a phosphate solubilizing bacterium. ISME J 12:2339–2351
Zhang XQ, Bai L, Sun HB, Yang C, Cai BY (2020) Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis revealed the effect of Funneliformis mosseae in soybean roots differential expression genes and proteins. J Proteome Res 19:3631–3643
Zheng BX, Zhu YG, Sardans J, Penuelas J, Su J (2018) QMEC: a tool for high-throughput quantitative assessment of microbial functional potential in C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycling. Sci China-Life Sci 61:1451–1462
Zheng H, Wang M, Chen S, Li S, Lei X (2019) Sulfur application modifies cadmium availability and transfer in the soil-rice system under unstable pe+pH conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109641
Zheng S, Bian T, Wang S, Zhang X, Li X, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2021) Decoupling of P from C, N, and K elements in cucumber leaves caused by nutrient imbalance under a greenhouse continuous cropping system. Horticulturae 27:528
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31972502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced this work.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jiayin Pang.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ronglin Liu and Donghao Chang shared the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Chang, D., Sun, Z. et al. Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Thiobacillus thioparus on sulfur utilization in soybean sterilized soil under continuous cropping. Plant Soil 490, 357–370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06081-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06081-9