Abstract
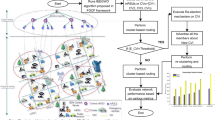
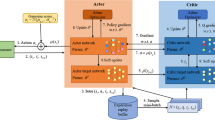
As the deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices becomes more widespread, the demand for data analysis services is also increasing in both range and volume. Despite the increasing demand for services due to the rise of IoT devices, efficiently processing latency-sensitive data analysis tasks (DATs) remains a significant challenge, especially in areas where communication infrastructure is limited or unavailable. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can enhance communication coverage and quality by leveraging their flexible deployment characteristics, particularly in areas where network coverage is limited for IoT devices. UAVs can provide edge computing services while simultaneously offering network coverage, making them a valuable asset for improving communication in such areas. In this paper, we propose an Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) system that utilizes multiple UAVs equipped with edge servers to offer latency-sensitive analytical services to IoT devices on the ground. However, traditional task scheduling algorithms are challenging to adapt to dynamic and complex edge network environments, particularly for scheduling tasks with dependencies. To address this challenge, we employ deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to develop Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) task scheduling algorithms and UAV deployment optimization algorithms. Our algorithm enables us to obtain optimal scheduling and deployment adjustment strategies in dynamic and changing environments. Simulation experiments demonstrate that in a MEC system comprising of multiple UAVs, our algorithm can swiftly converge to the optimal value, resulting in a significant reduction in DAT response time and cluster energy consumption compared to baseline algorithms.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter, R., & Sofi, S. A. (2022). Precision agriculture using iot data analytics and machine learning. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 34(8), 5602–5618.
Jouhari, M., Amhoud, E.M., Saeed, N., & Alouini, M.-S. (2022). A survey on scalable lorawan for massive iot: recent advances, potentials, and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.11082.
Guo, F., Yu, F. R., Zhang, H., Li, X., Ji, H., & Leung, V. C. (2021). Enabling massive iot toward 6g: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(15), 11891–11915.
Cai, Z., & He, Z. (2019). Trading private range counting over big iot data. In IEEE 39th international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS). IEEE, 2019:144–153.
Valavanis, K. P., & Vachtsevanos, G. J. (2015). Handbook of unmanned aerial vehicles. Springer.
Yin, L., Zhang, N., & Tang, C. (2021). On-demand UAV base station deployment for wireless service of crowded tourism areas. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 1–13.
Huang, H., & Savkin, A. V. (2022). Deployment of heterogeneous UAV base stations for optimal quality of coverage. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(17), 16429–16437.
Mandloi, D., Sharma, R., & Arya, R. (2022). Energy efficient deployment of multiple uav mounted base stations: a machine learning-based approach. International Journal of Ultra Wideband Communications and Systems, 5(3), 126–135.
Grasso, C., Raftopoulos, R., & Schembra, G. (2022). Slicing a fanet for heterogeneous delay-constrained applications. Computer Communications, 195, 362–375.
Somula, R. S., & Sasikala, R. (2018). A survey on mobile cloud computing: Mobile computing+ cloud computing (mcc= mc+ cc). Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience, 19(4), 309–337.
Abbas, N., Zhang, Y., Taherkordi, A., & Skeie, T. (2017). Mobile edge computing: A survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(1), 450–465.
Dinh, T. Q., Tang, J., La, Q. D., & Quek, T. Q. (2017). Offloading in mobile edge computing: Task allocation and computational frequency scaling. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 65(8), 3571–3584.
Othman, M., Madani, S. A., Khan, S. U., et al. (2013). A survey of mobile cloud computing application models. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(1), 393–413.
Feng, C., Han, P., Zhang, X., Yang, B., Liu, Y., & Guo, L. (2022). Computation offloading in mobile edge computing networks: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 202, 103366.
Shakarami, A., Ghobaei-Arani, M., & Shahidinejad, A. (2020). A survey on the computation offloading approaches in mobile edge computing: A machine learning-based perspective. Computer Networks, 182, 107496.
Lv, X., Du, H., & Ye, Q. (2022). Tbtoa: A dag-based task offloading scheme for mobile edge computing, In ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications. IEEE, pp. 4607–4612.
Convolbo, M. W., & Chou, J. (2016). Cost-aware dag scheduling algorithms for minimizing execution cost on cloud resources. The Journal of Supercomputing, 72, 985–1012.
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Zhao, Q., Du, S., Zhou, A., Ma, X., & Yang, F. (2020). Dependency-aware task scheduling in vehicular edge computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(6), 4961–4971.
Zhang, Z., Hua, Q.-S., Zhang, X., Jin, H., & Liao, X. (2022). Dag scheduling with communication delays based on graph convolutional neural network. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9013361
Yuan, X., Xie, Z., & Tan, X. (2022). Computation offloading in uav-enabled edge computing: A stackelberg game approach. Sensors, 22(10), 3854.
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z.-Y., Min, L., Tang, C., Zhang, H.-Y., Wang, Y.-H., & Cai, P. (2021). Task offloading and trajectory control for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access, 9, 53708–53719.
He, Y., Zhai, D., Huang, F., Wang, D., Tang, X., & Zhang, R. (2021). Joint task offloading, resource allocation, and security assurance for mobile edge computing-enabled uav-assisted vanets. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1547.
Xie, Y., Wu, F., Zhang, K., & Leng, S. (2021). A dag-based secure cooperative task offloading scheme in vehicular networks. In 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT). IEEE, pp. 870–875.
Liang, J., Li, K., Liu, C., & Li, K. (2021). Joint offloading and scheduling decisions for dag applications in mobile edge computing. Neurocomputing, 424, 160–171.
Fu, X., Tang, B., Guo, F., & Kang, L. (2021). Priority and dependency-based dag tasks offloading in fog/edge collaborative environment. In 2021 IEEE 24th International conference on computer supported cooperative work in design (CSCWD). IEEE, pp. 440–445.
Liu, J., Wu, Z., Liu, J., & Tu, X. (2022). Distributed location-aware task offloading in multi-uavs enabled edge computing. IEEE Access, 10, 72416–72428.
Hadi, M., & Ghazizadeh, R. (2022). Joint resource allocation, user clustering and 3-d location optimization in multi-uav-enabled mobile edge computing. Computer Networks, 218, 109420.
Mao, S., He, S., & Wu, J. (2020). Joint uav position optimization and resource scheduling in space-air-ground integrated networks with mixed cloud-edge computing. IEEE Systems Journal, 15(3), 3992–4002.
Hu, J., Jiang, M., Zhang, Q., Li, Q., & Qin, J. (2019). Joint optimization of uav position, time slot allocation, and computation task partition in multiuser aerial mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(7), 7231–7235.
Xiong, J., Guo, H., & Liu, J. (2019). Task offloading in uav-aided edge computing: Bit allocation and trajectory optimization. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(3), 538–541.
Coldrey, M., Berg, J.-E., Manholm, L., Larsson, C., & Hansryd, J. (2013). Non-line-of-sight small cell backhauling using microwave technology. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(9), 78–84.
Mao, Y., You, C., Zhang, J., Huang, K., & Letaief, K. B. (2017). Mobile edge computing: Survey and research outlook. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.01090.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A., Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., & Riedmiller, M. (2013). Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5602.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Veness, J., Bellemare, M. G., Graves, A., Riedmiller, M., Fidjeland, A. K., Ostrovski, G., et al. (2015). Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 518(7540), 529–533.
Hu, Q., Cai, Y., Yu, G., Qin, Z., Zhao, M., & Li, G. Y. (2018). Joint offloading and trajectory design for uav-enabled mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 1879–1892.
Liu, Z., Tan, X., Wen, M., Wang, S., & Liang, C. (2021). An energy-efficient selection mechanism of relay and edge computing in uav-assisted cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 5(3), 1306–1318.
Yuan, L., He, Q., Tan, S., Li, B., Yu, J., Chen, F., Jin, H., & Yang, Y. (2021). Coopedge: A decentralized blockchain-based platform for cooperative edge computing. Proceedings of the Web Conference, 2021, 2245–2257.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Projects(2022YFB4500800); Applied Basic Research Program Project of Liaoning Province(2023JH2/101300192); The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(N2116014); The National Natural Science Foundation of China (2032013, 62072094); New Generation Information Technology Innovation Project of Ministry of Education(2021ITA10011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Pan, Y., Xia, Y. et al. Optimizing dag scheduling and deployment for Iot data analysis services in the multi-UAV mobile edge computing system. Wireless Netw (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03451-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03451-0