Abstract
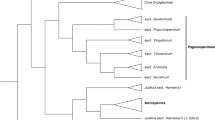
Stenogrammitis, a new genus of grammitid ferns, is segregated from Lellingeria based on morphological and molecular evidence. It differs from Lellingeria by linear leaves usually less than 5 mm wide, clathrate iridescent rhizome scales that are glabrous except for a single apical cilium, veins unbranched and only one per segment, fertile veins usually with the dark sclerenchyma visible beneath the sporangia, and x = 33. In contrast, Lellingeria has broader laminae, veins pinnate within the segments, and fertile veins not visible beneath the sporangia. Melpomene, which is sister to Stenogrammitis and Lellingeria, differs from those two genera by reddish setae on the leaves and rhizome scales papillate at the apex. Some species of Stenogrammitis are also distinctive by hemidimorphic laminae that have the fertile portion less dissected than the sterile. Stenogrammitis is pantropical and currently comprises 24 species, 12 of which occur in the Neotropics, six in Africa, four in Madagascar, and two on Pacific Islands. New combinations are made for Stenogrammitis aethiopica, S. anamorphosa, S. ascensionensis, S. boivinii, S. delitescens, S. jamesonii, S. hartii, S. hellwigii, S. hildebrandtii, S. limula, S. luetzelburgii, S. myosuroides, S. nutata, S. oosora, S. paucipinnata, S. prionodes, S. pumila, S. ruglessii, S. rupestris, S. saffordii, S. strangeana, S. tomensis, S. subcoriacea, and S. wittigiana. Lectotypifications are made for Grammitis muscosa, Polypodium itatiayense, P. oosorum var. micropecten, P. serrulatum forma major, P. serrulatum forma minor, S. luetzelburgii, S. myosuroides, and S. wittigiana. Illustrations are presented for the diagnostic characters of the genus, as well as a map with the geographical distribution.
Resumo
Stenogrammitis, um gênero novo de samambaias grammitidóides, é aqui segregado de Lellingeria com base em dados moleculares em morfológicos. Difere de Lellingeria pelas frondes lineares, geralmente com menos de 5 mm de largura, escamas do rizoma iridescentes, inteiramente glabras, ou com apenas um cílio apical, nervuras não ramificadas e apenas uma por segmento, nervuras férteis geralmente com o ápice esclerenquimatoso, negro, visível entre os esporângios, e x = 33. De maneira oposta, Lellingeria apresenta frondes mais amplas, segmentos com nervuras pinadas, e nervuras férteis não visíveis por entre os esporângios. Melpomene, que é o grupo irmão de Stenogrammtis e Lellingeria, difere destes dois gêneros por apresentar frondes setosas, e escamas do rizoma papiladas no ápice.Algumas espécies de Stenogrammitis são distintas por apresentar a lâmina hemidimorfa, com a porção fértil da lâmina menos dividida que a estéril. Stenogrammitis apresenta distribuição pantropical e compreende 24 espécies, 12 das quais ocorrem no Neotrópico, seis na África, quatro em Madagascar, e duas nas Ilhas do Pacífico. Novas combinações são feitas para Stenogrammitis aethiopica, S. anamorphosa, S. ascensionensis, S. boivinii, S. delitescens, S. jamesonii, S. hartii, S. hellwigii, S. hildebrandtii, S. limula, S. luetzelburgii, S. myosuroides, S. nutata, S. oosora, S. paucipinnata, S. prionodes, S. pumila, S. ruglessii, S. rupestris, S. saffordii, S. strangeana, S. tomensis, S. subcoriacea, and S. wittigiana. Lectotipificações são feitas para Grammitis muscosa, Polypodium itatiayense, P. oosorum var. micropecten, P. serrulatum forma major, P. serrulatum forma minor, S. luetzelburgii, S. myosuroides, e S. wittigiana. São apresentadas ilustrações para os caracteres diagnósticos do gênero, bem como um mapa com a distribuição geográfica.




Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bishop, L. E. 1988. Ceradenia, a new genus of Grammitidaceae. American Fern Journal 78: 1–5.
———. 1989. Zygophlebia, a new genus of Grammitidaceae. American Fern Journal 79: 103–118.
Brade, A. C. 1966. Os gêneros Xiphopteris e Grammitis no Brasil (Grammitidaceae). Sellowia 18: 73–85.
Copeland, E. B. 1947. Genera filicum. Chronica Botanica Co. Waltham, Massachusetts: 247 p.
———. 1952. The American species of Xiphopteris. American Fern Journal 42: 93–110.
Desvaux, N. A. 1827. Prodromé de la famille des fougères. 1827. Mémoires de la Societé Linneéne de Paris 6: 171–337
Geiger, J. M. O., T. A. Ranker, J. M. Ramp Neale & S. T. Klimas. 2007. Molecular biogeography and origins of the Hawaiian fern flora. Brittonia 59: 142–158.
Labiak, P. H. & J. Prado. 2005. As espécies de Lellingeria A. R. Sm. & R. C. Moran (Grammitidaceae—Pteridophyta) do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Botânica 28: 1–22.
———, M. Sundue & G. Rouhan. 2010a. Phylogeny and taxonomy of Leucotrichum (Polypodiaceae), a new genus of the grammitid ferns from the Neotropics. Taxo 59(3): 911–921.
———, M. Sundue & G. Rouhan. 2010b. Molecular phylogeny, character evolution, and biogeography of the grammitid fern genus Lellingeria (Polypodiaceae). American Journal of Botany 97(4): 1354–1364.
Lehnert, M., M. Kessler, A. N. Schimdt-Lebuhn, S. A. Klimas, S. D. Fehlberg & T. A. Ranker. 2009. Phylogeny of the fern genus Melpomene (Polypodiaceae) inferred from morphology and chloroplast DNA analysis. Systematic Botany 34: 17–27.
Lellinger, D. B. 1977. Nomenclatural and taxonomic notes on the pteridophytes of Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia, I. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 89: 703–732.
McNeill, J., F. R. Barrie, H. M. Burdet, V. Demoulin, D. L. Hawksworth, K. Marhold, D. H. Nicolson, J. Prado, P. C. Silva, J. E. Skog, J. H. Wiersema & N. J. Turland. 2006. International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (Vienna Code). A. R. G. Gantner Verlag KG, Ruggell. Regnum Vegetabile 146.
Maxon, W. R. 1905. On the name of three Jamaican species of Polypodium. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 32: 72–75.
———. 1914. Notes upon Polypodium duale and its allies. Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 17: 398–406.
Moran, R. C. & A. R. Smith. 2001. Phytogeographic relationships between neotropical and African-Madagascan pteridophytes. Brittonia 53: 304–351.
Parris, B. S. 1997. Themelium, a new genus of Grammitidaceae (Filicales). Kew Bulletin 52: 737–741.
———. 1998. Chryso grammitis, a new genus of Grammitidaceae (Filicales). Kew Bulletin 53: 909–918.
———. 2002. New species and new combinations in African Grammitidaceae (Filicales). Kew Bulletin 57: 423–434.
———. 2007. Five new genera and three new species of Grammitidaceae (Filicales) and the re–establishment of Oreogrammitis. Gardens’ Bulletin of Singapore 58: 233–274.
Proctor, G. R. 1985. Ferns of Jamaica. British Museum (Natural History), London.
Ranker, T. A., A. R. Smith, B. S. Parris, J. M. O. Geiger, C. H. Haufler, S. C. K. Straub & H. Schneider. 2004. Phylogeny and evolution of grammitid ferns (Grammitidaceae): a case of rampant morphological homoplasy. Taxon 53: 415–428.
Schneider, H., A. R. Smith, R. Cranfill, V. Hildebrand, C. H. Haufler & T. A. Ranker. 2004. Unraveling the phylogeny of polygrammoid ferns (Polypodiaceae and Grammitidaceae): exploring aspects of the diversification of epiphytic plants. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 31: 1041–1063.
Schuettpelz, E. & K. M. Pryer. 2007. Fern phylogeny inferred from 400 leptosporangiate species and three plastid genes. Taxon 56: 1037–1050.
Smith, A. R. 1993. Terpsichore, a new genus of Grammitidaceae (Pteridophyta). Novon 3: 478–489.
———, R. C. Moran & L. E. Bishop. 1991. Lellingeria, a new genus of Grammitidaceae. American Fern Journal 81: 76–88.
———, & R. C. Moran. 1992. Melpomene, a new genus of Grammitidaceae (Pteridophyta). Novon 2: 426–432.
Smith, J. 1875. Historia Filicum. MacMillan & Co., London, UK. 409 pp.
Stokey, A. G. & L. R. Atkinson. 1958. The gametophyte of the Grammitidaceae. Phytomorphology 8: 391–403.
Sundue, M.A, M. Islam & T. A. Ranker. 2010. Systematics of grammitid ferns (Polypodiaceae): using morphology and plastid sequence data to resolve the circumscription of Melpomene and portions of the polyphyletic genera Lellingeria and Terpsichore. Systematic Botany.
Tryon, R. M. & A. F. Tryon. 1982. Ferns and allied plants, with special reference to tropical America. Springer Verlag, New York.
Wagner, F. S. 1980. New basic chromosome numbers for genera of Neotropical ferns. American Journal of Botany 67: 733–738.
Walker, T. G. 1966. A cytotaxonomic survey of the pteridophytes of Jamaica. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 66: 169–237.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by a grant to the senior author from the CNPq—Brazil (PDE CNPq Proc. no. 201782/2008–1), and by a grant from the United States National Science Foundation to Dr. Robbin Moran (DEB-0717056). Fieldwork was partially funded by the “Fundação O Boticário de Proteção à Natureza” (Proc. 0756/2007–2). I thank The New York Botanical Garden for providing herbarium and laboratory facilities, as well as the Curators of the following herbaria for loans: AAU, B, BM, BR, F, FR, GH, HB, HBR, K, MAPR, MBM, MICH, MO, NY, P, PACA, R, RB, S, SP, SPF, U, UC, UPCB, US, and WU. I also thank Fernando Matos for his help with the chromosome counting, and Robbin C. Moran, Alan R. Smith, Michael Sundue and Jefferson Prado for helpful comments on the manuscript. Diana Carneiro prepared the line drawings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labiak, P.H. Stenogrammitis, a new genus of grammitid ferns segregated from Lellingeria (Polypodiaceae). Brittonia 63, 139–149 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12228-010-9148-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12228-010-9148-y