Abstract
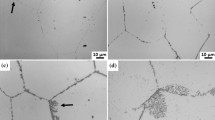
It is important to understand the correlation between grain morphology and intervariant boundaries of the α phase after heat treatment below β transus of the electron beam melted (EBMed) Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis have shown about 99% α phase and 1% β phase in the heat-treated samples when the temperature rises to 950 °C. Four distinct types of α grain morphology have been found: allotromorphous α, relatively coarse α plate, large precipitation α and granular α. A single peak of the intervariant boundary with the misorientation of 60°/\(\left[ {11\bar{2}0} \right]\) associated with Burgers orientation relationship (OR) was found in the allotromorphous α colony. Multiple intervariant boundaries mixed with a fraction of general high-angle grain boundary (GHABs, not Burgers OR) were present in the relatively coarse α plate colony. Almost only low-angle grain boundaries (LABs) with the misorientation of < 5° were found in the large precipitation α grains. β phase tends to distribute around the boundaries of relatively coarse α plates. It suggests that different formation mechanisms are involved in the distinct types of α grain morphology.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy L. Variation in Mechanical Behavior Due to Different Build Directions of Ti–6Al–4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing Technology. Alabam: The University of Alabama; 2013. 10.
Hao YL, Li SJ, Yang R. Biomedical titanium alloys and their additive manufacturing. Rare Met. 2016;35(9):661.
Pan L, Wang CM, Xiao SF, Chen YG. Hydrogenation behaviors and characteristics of bulk Ti–6Al–4V alloy at different isothermal temperatures. Rare Met. 2019;38(12):1131.
Ghods S, Schultz E, Wisdom C, Shur R, Pahuja R, Montelione A, Arola D, Ramulu M. Electron beam additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V: evolution of powder morphology and part microstructure with powder reuse. Materialia. 2020;9:100631.
Facchini L, Magalini E, Robotti P, Molinari A, Höges S, Wissenbach K. Ductility of a Ti–6Al–4V alloy produced by selective laser melting of prealloyed powders. Rapid Prototyp J. 2010;16(6):450.
Zheng HD, Liu LL, Deng CL, Shi ZF, Ning CY. Mechanical properties of AM Ti6Al4V porous scaffolds with various cell structures. Rare Met. 2019;38(6):561.
Sun T, Liu Y, Li SJ, Li JP. Effect of HIP treatment on fatigue notch sensitivity of Ti–6Al–4V alloy fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Metall Sin (Engl. Lett.) 2019; 32:869.
Liu Y, Zhang J, Li SJ, Hou WT, Wang H, Xu QS, Hao YL, Yang R. Effect of HIP treatment on fatigue crack growth behavior of Ti–6Al–4V alloy fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett) 2017; 30(12):1163.
Harrysson OLA, Cansizoglu O, Marcellin-Little DJ, Cormier DR, Ii HAW. Direct metal fabrication of titanium implants with tailored materials and mechanical properties using electron beam melting technology. Mater Sci Eng C (Mater Biol Appl). 2008;28(3):366.
Gong XB, Anderson T, Chou K. Review on Powder-Based Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing Technology. ASME/ISCIE 2012 International Symposium on Flexible Automation EDP Sciences. Missouri; 2012. 9.
He WW, Jia WP, Liu HY, Tang HP, Kang XT, Huang Y. Research on preheating of titanium alloy powder in electron beam melting technology. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2011;40(122):2072.
Kruth JP, Froyen L, Van Vaerenbergh J, Mercelis P, Rombouts P, Lauwers B. Selective laser melting of iron powder. Biomed Eng. 1967;1(1):40.
Mumtaz KA, Erasenthiran P, Hopkinson N. High density selective laser melting of Waspaloy®. J Mater Process Technol. 2008;195(1–3):77.
Klingbeil NW, Beuth JL, Chin RK, Amon CH. Residual stress-induced warping in direct metal solid freeform fabrication. Int J Mech Sci. 2002;44(1):57.
Shiomi M, Osakada K, Nakamura K, Yamashita T, Abe F. Residual stress within metallic model made by selective laser melting process. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol. 2004;53(1):195.
Murr LE, Esquivel EV, Quinones SA, Gaytan SM, Lopez MI, Martinez EY. Microstructures and mechanical properties of electron beam-rapid manufactured Ti–6Al–4V biomedical prototypes compared to wrought Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Charact. 2009;60(2):96.
Al-Bermani SS, Blackmore ML, Zhang W, Todd I. The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti–6Al–4V. Metall Mater Trans A. 2010;41(13):3422.
Zhai Y, Galarraga H, Lados DA. Microstructure evolution, tensile properties, and fatigue damage mechanisms in Ti–6Al–4V alloys fabricated by two additive manufacturing techniques. Proc Eng. 2015;114:658.
Vrancken B, Thijs L, Kruth JP, Humbeeck JV. Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd. 2012;541:177.
Rack HJ, Qazi JI. Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C-Biol Sci. 2006;C26(8):1269.
Vilaro T, Colin C, Bartout JD. As-fabricated and heat-treated microstructures of the Ti–6Al–4V alloy processed by selective laser melting. Metall Mater Trans A. 2011;42(10):3190.
Wang M, Li HQ, Lou DJ, Qin CX, Jiang J, Fang XY, Guo YB. Microstructure anisotropy and its implication in mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloy processed by electron beam melting. Mater Sci Eng A. 2019; 743(16):123.
Simonelli M, Tse YY, Tuck C. On the texture formation of selective laser melted Ti–6Al–4V. Metall Mater Trans A. 2014;45(6):2863.
Antonysamy AA. Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Property Evolution During Additive Manufacturing of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy for Aerospace Applications. Manchester: University of Manchester; 2012. 30.
Yadroitsev I, Krakhmalev P, Yadroitsava I. Selective laser melting of Ti–6Al–4V alloy for biomedical applications: temperature monitoring and microstructural evolution. J Alloys Compd. 2014;583:404.
Wang SC, Aindow M, Starink MJ. Effect of self-accommodation on α/α boundary populations in pure titanium. Acta Mater. 2003;51(9):2485.
Farabi E, Hodgson PD, Rohrer GS, Beladi H. Five-parameter intervariant boundary characterization of martensite in commercially pure titanium. Acta Mater. 2018;154:147.
Lutjering G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α + β) titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 1998;243(1–2):32.
Filip R, Kubiak K, Ziaja W, Sieniawski J. The effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties of two-phase titanium alloys. J Mater Process Technol. 2003;133(1–2):84.
Xia QF, Liang YL, Yang CL, Zhang S, Ou GM. Tensile deformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2019;43(9):765.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Key R&D Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology (No. 2018YFB1105900), the Shandong Province Key R&D Project (No. 2018GGX103017) and the Zibo City and SDUT Integration Project (No. 2018ZBXC154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Li, HQ., Guo, H. et al. Evolution of microstructure and intervariant boundaries of α phase in electron beam melted and heat-treated Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Rare Met. 40, 2118–2126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01612-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01612-0