Abstract
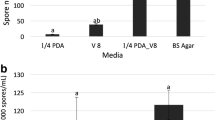
This study was conducted to investigate sporulation of Leptosphaerulina trifolii (Rost.) Petrak and to improve infection of white clover plants during experimental screening of germplasm for resistance to this ascomycete. Sporulation at 23 ± 2°C was greatest after 9 ± 1 days growth on V-8 juice agar under fluorescent and near-ultraviolet lights. Infection was greatly promoted by keeping leaf surfaces wet during the initial period of ascospore deposition. Increasing the period of ascospore deposition beyond 12 h did not significantly increase plant infection. The number of pepper spot lesions which appeared on leaves was significantly correlated with the number of ascospores released by sporulating cultures suspended over plants during the spore deposition period. More leaf spots were produced when the temperature was 25°C during ascospore deposition and 20°C during incubation than when a regime of 20/15°C was used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker MJ, Williams WM (Eds) (1987) ‘White clover.’ (CAB International: Wallingford)
Barbetti MJ (1991) Effects of temperature and humidity on disease caused by Phoma medicaginis and Leptosphaerulina trifolii in lucerne (Medicago sativa). Plant Pathology 40, 296–301.
Latch GCM, Skipp RA (1987) Diseases. In ‘White clover’. (Eds M J Baker and W M Williams) pp. 421–460. (CAB International, Wallingford)
Leath KT, Hill, RR Jr (1974) Leptosphaerulina briosiana on alfalfa: relation of lesion size to leaf age and light intensity. Phytopathology 64, 243–245.
Martinez ES, Hanson EW (1963) Factors affecting growth, sporulation, pathogenicity, and dissemination of Leptosphaerulina briosiana. Phytopathology 53, 938–945.
Michaud R, Richard C, Surprenant J (1984) Selection for resistance to Leptosphaerulina leaf spot in alfalfa. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift 110, 69–77.
Miller PM (1955) V-8 juice agar as a general purpose medium for fungi and bacteria. Phytopathology 45, 461–462.
Olanya OM, Campbell CL (1990) Isolate characteristics and epidemic components of Leptosphaerulina leaf spots on alfalfa and white clover. Phytopathology 80, 1278–1282.
Pandey MC, Wilcoxson RD (1970) The effect of light and physiologic races on Leptosphaerulina leaf spot of alfalfa and selection for resistance. Phytopathology 60, 1456–1462.
Rao CJS, Rao AN (1983) Fruiting of Leptosphaerulina crassiasca (Sechet) Jackson and Bell on different media under visible light. Geobios 10, 73–76.
Skipp RA, Lambert MG (1984) Damage to white clover foliage in grazed pastures caused by fungi and other organisms. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 27, 313–320.
Sundheim L, Wilcoxson RD (1965) Leptosphaerulina briosiana on alfalfa: infection and disease development, host-parasite relationships, ascospore germination and dissemination. Phytopathology 55, 546–553
Thomas CE, Halpin JE (1967) The effect of five agar media and three light conditions on the growth and sporulation of Leptosphaerulina australis. Fitopatologia 2, 34–38
Webster J (1970) ‘Introduction to fungi.’ (Cambridge University Press: London)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L.Y., Skipp, R.A. Optimisation of inoculum production and incubation conditions for screening white clover for resistance to Leptosphaerulina trifolii. Australasian Plant Pathology 30, 53–57 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP00067
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP00067