Elastic arteries like your aorta and pulmonary artery are arteries that carry a large amount of blood away from your heart. Their high elastic content lets them handle the force of blood coming from your heart nearby. This is important because your heart switches between pumping and resting instead of sending blood in a steady flow.
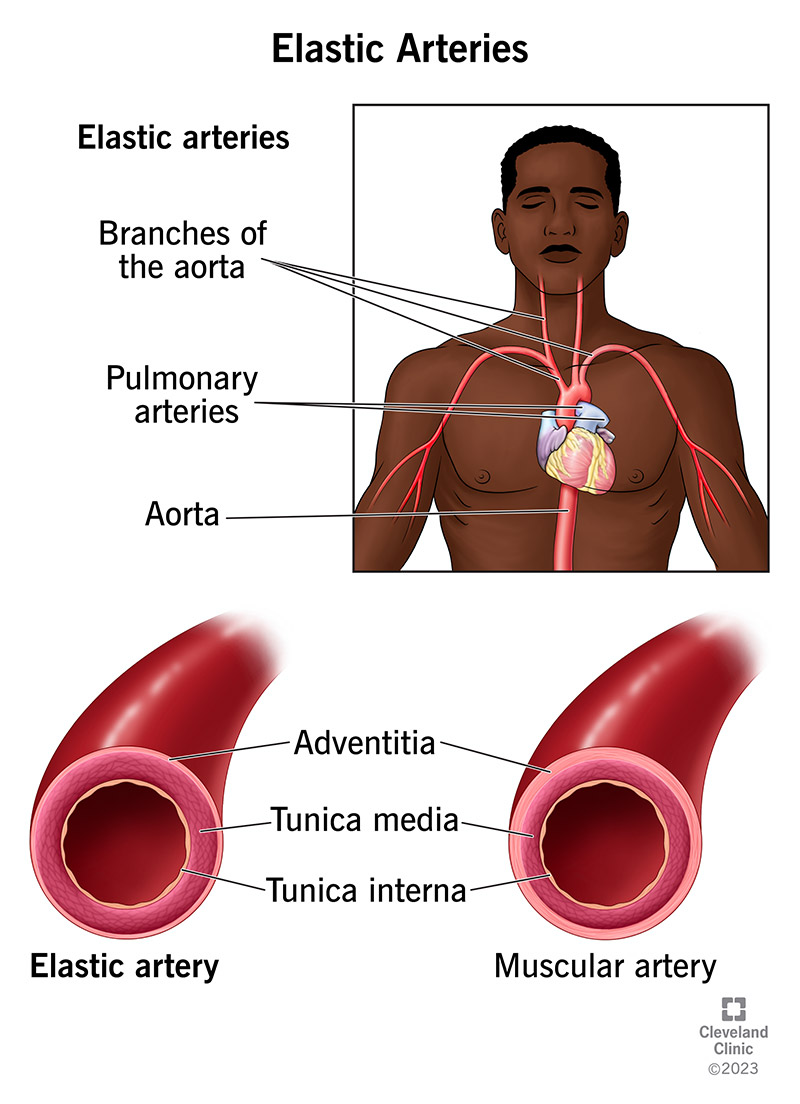
Elastic arteries are a type of artery that’s flexible enough to keep blood flowing steadily. They can do this even though your heart pumps blood in bursts, alternating between pumping and resting.
Elastic artery examples include your pulmonary arteries, aorta and the aorta’s branches. These arteries branch from your aorta:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Elastic arteries are vital to getting oxygen and nutrients to your body’s cells. They have to be able to handle the high pressure and volume of blood that your heart pumps. They’re like the big pipes that bring water to your neighborhood and send it to smaller pipes that go to your house. The smaller pipes are your other arteries that handle a smaller volume of blood.
Your pulmonary arteries are the only elastic arteries (or any type of artery) that carry oxygen-poor blood. Your pulmonary arteries’ job is to get that blood to your lungs, where it can pick up oxygen.
Elastic arteries are very close to your heart. Your aorta, your largest artery, sits right above your heart and runs behind and below it. Your aorta connects to your heart through an aortic valve on the left side of your heart. This valve lets oxygen-rich blood into your aorta so it can send it to your body.
Other elastic arteries branch off your aorta in your upper chest:
Your pulmonary arteries are right above your heart, as well. A pulmonary valve on the right side of your heart connects your pulmonary arteries to your heart so it can send oxygen-poor blood to your pulmonary arteries. Your pulmonary arteries take blood to your lungs, where your blood gets oxygen.
Advertisement
Like most blood vessels, elastic arteries have three layers:
Elastic arteries are large, cylinder-shaped tubes that are hollow in the middle to allow blood to flow through them. Your aorta has a different shape than the others. It looks like a large candy cane with legs.
The biggest elastic artery, your aorta, has an internal diameter of 2.5 centimeters (nearly 1 inch). Your aorta’s wall is 2 millimeters (.07 inches) thick.
Elastic arteries have small fibers of muscle and collagen.
Advertisement
Common conditions that affect elastic arteries include:
Symptoms of elastic artery conditions include:
Healthcare providers can use various tests to check the health of your elastic arteries, such as:
Treatments for elastic artery conditions include:
Habits that are good for your heart and blood vessels are good for your elastic arteries. These good habits include:
Elastic arteries have more elastic tissue in their middle layer, while muscular arteries have more muscular tissue there.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your elastic arteries play an important role in your body. They make sure you get oxygen-rich blood to all of your body’s cells. That’s why taking care of them is an investment in your health. Keep them healthy and they’ll keep delivering the blood your body needs.
Last reviewed on 03/01/2023.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy