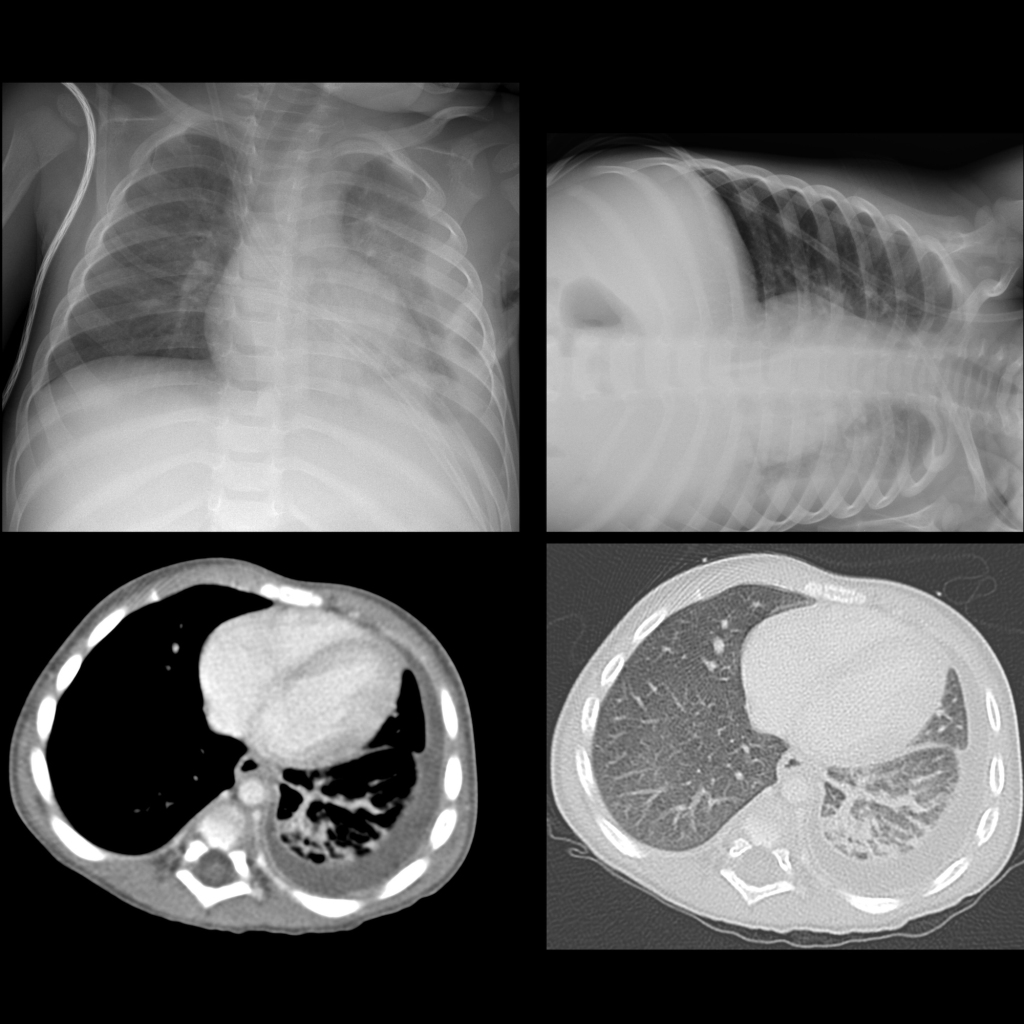
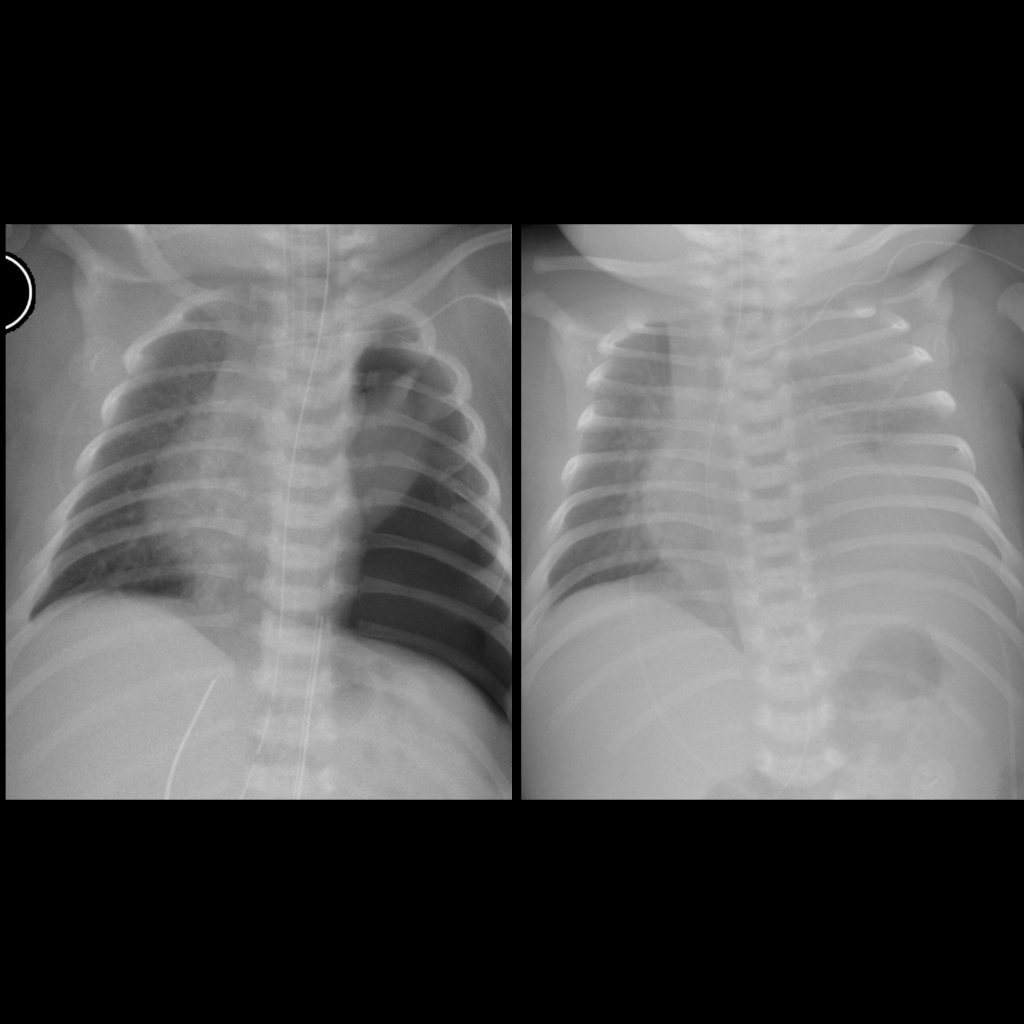
- Etiology: non-infected fluid in pleural space, common causes are infection (Streptococcus pneumonia, Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, Mycoplasma, Tuberculosis), cardiac failure
- CXR: meniscus sign on AP view, free flowing on decubitus view
- US: clear pleural fluid
Radiology Cases of Pleural Effusion