The Prologue
*Welcome to the course Web Content Management System (WCMS).
This is a Nano course that can help a beginner to understand what is web content management and the significance of the same in enterprises.*
You will dive into the following topics as you move forward in the course.
- What is Web Content Management System?
- Key Features of WCMS
- WCM Process and Architecture
- Learn about some of the widely used WCMS
So let us begin!
What is Content Management System?
A
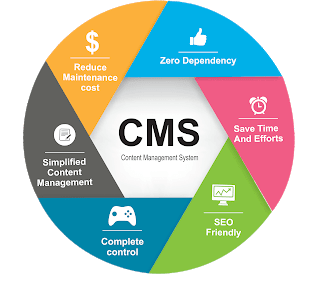
Content management system (CMS) allows users to create, manage, edit, and publish digital content.CMS comes with out-of-the-box features such as versioning, indexing, workflows, and provides a collaborative environment, making content management
simple and efficient.Types of CMS
There are different types of CMS, each serving a different purpose.
· Web Content Management System (WCMS)
· Digital Asset Management System (DAM)
· Enterprise Content Management System (ECMS)
· Document Management System (DMS) or Electronic Document Management System (EDM)
· Learning Content Management System (LMS)
· Component Content Management System (CCMS)
In this course, we will focus mainly on WCMS.
Web Content Management System (WCMS)
One can build a business without a marketing automation platform, but every business needs a website.
Web content Management System as the name suggests, is a content management system used to create, edit, version, and publish the content on websites.WCMs makes it easy to create/maintain websites with limited programming knowledge.
Role of Websites in Marketing
Website is the face of the Brand.
Most of the other marketing channels such as email, social media, print, and ads directly or indirectly refer to the website – ***
making websites a critical marketing channel***.In addition, by leveraging tags and web analytics, websites provide key insights into customer behaviour. These insights can further help fine-tune, and drive marketing communications and campaigns effectively.
WCMS Overview
Why WCMS?
Most of the WCMs provide tools and feature that help ensure
· Ease of Maintenance and content authoring
· Brand consistency across channels (E.g., Web, Mobile) by separating content from presentation
· Control customers online experiences through personalization
· Ensure high content quality through workflows
· Integration with other enterprise marketing platforms
Key Players in WCMS
There are hundreds of WCMs in the market, and each of them come with a different set of plugins and integration features to help you deliver the intended experiences. Here are a few widely used WCMs.
· Open Source WCMs – WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, and Umbraco
· Commercial WCMs – Adobe Experience Manager, Sitecore Web Experience Manager, and Open Text
Moving On
In the next few modules, you will learn:
· Features of WCMS
· Integration Features
· WCM Process
· WCMS Architecture
· Considerations for choosing WCMS
Key Features of WCMS
The main job of WCMS is to allow users to design websites, create content, approve and publish the content.
Below are a few features that help in this process.
· Content Authoring Tools
· Templates
· Workflows and Access Control
· Taxonomy and Classification
· Personalization
· Versioning
· Customization
· Multilingual support
· Integration
Content Authoring Tools
Content Authoring is the process in which one or more users can create web pages and publish them.
The most important aspects in authoring are the authoring environment and tools.
Templates
Templates are an effective option to create pages with similar themes and design.
Example: Product Pages/Articles.
Most of the WCMS come with a basic set of templates to create web pages. In addition, they offer the ability to create custom templates as needed.
· Templates are typically created by the developers and are stored in the file system.
· They are plugged in with the right content objects to render the desired output or webpage.
Workflows and Access Control
Content authoring, review and publishing is typically done by different users in the organization.
User roles control the level of access and permissions each of these users have.
· An author creates/updates content using the content authoring tools, and the content is stored in a database.
· Workflows ensure the content is reviewed and approved by authorized personnel before it is published to the world.
These interactions are controlled via audit trails, workflow, and security, and stored as well as tracked in a database.
Taxonomy and Classification
The content created by authors and editors are generally stored in a content repository that can be an RDBMS or a hierarchal database.
Taxonomy and classification is the method of making the content searchable by tagging them using metadata.
Metadata along with a sitemap ensures websites are search engine optimized.
Personalization
Some of the WCMS contain a Personalization engine that helps in delivering the right content at the right time to the right segment of users.
Segmentation can be based on customer age, gender, geographical location, behavior, journey, etc.
For example, based on customers purchase pattern, you can send customers personalized promotional offers.
Delivering Personalized experiences will help increase conversions, improve brand loyalty and offer a competitive advantage.
Versioning
· Versioning is useful when the content needs frequent updates.
· Versioning follows the “ version stack” to identify which version needs to be published.
· In the version stack, old versions are kept at the bottom of the stacks, and new versions are kept at the top of the stack.
Versioning in the WCMS follows
Serial stacking based upon the date on which the digital asset is created.Multilingual Sites
Enterprises or brands that launch global websites, catering to multiple languages would need WCMS with localization capability. That would include the ability to:
· integrate with translation services
· initiate workflow for translating new/updated content
· specify what needs to be translated and what should be retained in the local language
· manage versions of content.
Integration
WCM can be integrated with various Enterprise and third-party platforms. APIs enable integration capability, bringing in flexibility in design and development.
Some of the examples of potential integrations:
· Pulling data from other enterprise systems. E.g., Contact information for CRM.
· Exporting data from WCMS to other systems. E.g., Sending Newsletter subscription to CRM.
· Integration with Social Media Channels.
· Integration with Enterprise Search Servers. E.g., Apache Solr to improve content search.
· Integration with other third-party portals. E.g., A campaign created in a WCM can be shown in a secured portal to a bank customer.
· Integration with database and security platforms like LDAP.
WCMS Features Conclusion
What we have covered in this module are some of the important features of WCMS.
However, there are a lot more rich features that can be enabled through plugins, custom components and integration with enterprise/third party APIs.
This is just a trailer, and you will learn in detail with hands-on implementation in other WCM tool specific courses.
WCMS Architecture
WCMS works based on Publish Subscribe Design Pattern. Now let’s briefly look at the architecture of a typical WCMS.
Users layer consists of the authors, editors, and publishers who are internal users. Also, this layer includes agents and policyholders who are external users.
Security layer takes care of the user security for both public and secured portals.
WCM components layer consists of three types of components:
· Base components
· Rendering components
· Custom components
Web Content Management Process
·
· Web Content Management primarily involves:
Content Management
· Editors or authors will create and manage the content on the website. Content Edits trigger a notification to the content reviewer.
Content Approval
· Content publishers push the content to the live site after a thorough review and approval.
Content Delivery
· Content delivery involves picking approved data from the repository and displaying to the user.
Coupled and Decoupled Publishing
· In coupled publishing, editors manage content and visitors consume content on the same server and location.
· In decoupled publishing, the content is created and managed in one place, and it is published in another place.
· The content is delivered to another server through different transmission methods.
1. FTP or SFTP
2. File Copy (on the same network)
3. WebDAV
4. rsync
5. SCP
6. Web Service
Adobe Experience Manager
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) is known to be an integral part of the Adobe Marketing Cloud.
By default, it comes with digital asset management capability, analytics, and targeting features. Also, it enables content reuse through content analytics and algorithmic asset tagging.
Complete integration with other Adobe products makes it easy to address Marketing needs.
Drupal
Drupal is one of the most popular Open source CMS , backed by large open-source community.
Any new API, within hours you can find a Drupal module. Thousands of features are readily available as Drupal modules that can be used as Lego blocks for your digital platform.
It is well suited for not just websites, but also, e-commerce, community portals, social networks, enterprise applications, etc.
Sitecore
Sitecore is another commercial CMS that is well known for its personalization capabilities.
Sitecore is .NET-based and is useful for companies that need to develop websites from scratch. Development requires considerable programming and hence a need for strong IT team.
Also, it comes with numerous extensions for integration with Sharepoint, web analytics, and SEO, making it ideal for large enterprises.
IBM Web Content Manager
IBM Content Manager offers good collaboration capability, personalization and multi lingual functionality.
Digital Data Connector allows integration of external content sources using the IBM WCsentation components.
It comes with industry standard security model and enables content access for other enterprise consumption as well.
More WCMS
Here are few other commonly used WCMS.
· Oracle Content Management System
· SDL Tridion
· OpenText
· Magnolia
· Coremedia
· Episerver
Business needs like personalization, customization, transactions, user-generated content, integration with other products, etc. will drive the WCMS which will be most suitable.
Business Need
Businesses are now moving from static websites to highly complex and dynamic websites with rich features.
Websites are a way for brands to connect with their customer and with increasing competition, it is becoming essential for a business to stay ahead by leveraging technology.
Businesses are now looking for:
· Delivering Consistent Cross-Channel Experience
· Understand customers and provide a personalized customer experience
· Faster time to market
WCMS that are
scalable, extensible and are easy to use position themselves above others.Choosing WCMS
· The unique challenge for every organization is to pick a right web content management system platform.
· There are hundreds of web content management systems that provide good editing and workflow capabilities.
Other Factors to Consider
Features to consider while choosing a WCMS
· Ability to personalize
· Customize
· Localize
· Search
· Site analytics
· Ease of integration
· Security
· e-Commerce
· Multi-Channel Delivery
· User Experience Management
Security Concerns in WCMS
Following are the security concerns that can happen in the web content management system.
· Confidential data destruction
· Data Modification
· Misuse of the web server for illegal activities
· Denial of service
Precaution while Using WCMS
· WCMS backups should regularly be made.
· Use only safe hosting providers.
· Avoid showing sensitive information on the website.
· Use only safe plugins.
· Better to hide email addresses.
The Right WCMS
Choices are vast, and one needs to choose the platform based on business need, licensing cost, fitment in the current enterprise ecosystem, and in-house technical ability.
WCMS – Epilogue
You have come to the end of the course. So far in this course, you have read the following topics:
· What is Web Content Management System?
· Key Features of WCMS
· WCM Process and Architecture
· Most Popular WCMS
Where to go from here?
This course sets the context for you to go forward and start learning any specific WCMS such as AEM and Drupal.
Most Important question and answers
Meta tags help in SEO.
True
DAM is
_____________.Digital Asset Management
Who is responsible for designing templates in WCMS?
Web Developer
Which of the following business needs the drive for WCMS?
All the options mentioned
Which one of these is not a WCMS?
Microsoft Sharepoint
Template in WCM context is
____________________.page and its components
What is personalization?
Delivering right content to right people
Which one of the following is not an Open Source WCMS?
SDL Tridion
WCMS uses the following design pattern:
publish-subscribe
The ability to predict customer behavior, needs and tailors offers and communications very precisely is known as
___________. ________________predective Personalization