Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
A Proactive Approach to Risk Management
FMEA is a systematic and structured approach to identifying potential failures, analyzing their effects, and taking corrective action to reduce risk. It is a widely used tool in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and nuclear power.
What is FMEA?
FMEA is a bottom-up, inductive process that starts with the identification of individual components or steps in a process. For each item, the team brainstorms all potential failure modes, their causes, and their effects on the system or product. The team then assigns a severity, occurrence, and detection rating to each failure mode. The risk priority number (RPN) is calculated by multiplying these three ratings. This RPN helps the team prioritize the failure modes that require the most attention.
Types of FMEA
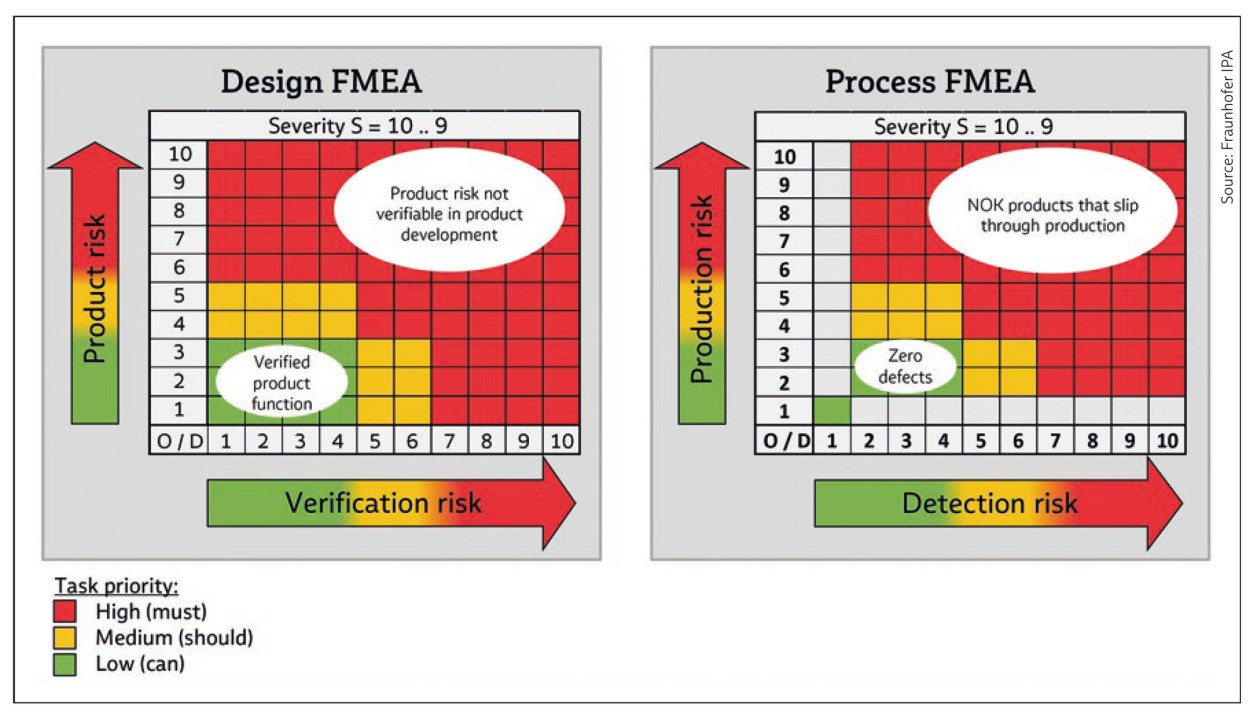
There are three main types of FMEA:
Design FMEA (DFMEA): This type of FMEA focuses on identifying potential failures in the design of a product or system.
Process FMEA (PFMEA): This type of FMEA focuses on identifying potential failures in the manufacturing or assembly process of a product.
System FMEA (SFMEA): This type of FMEA focuses on identifying potential failures in the entire system, including the product, the process, and the human factors.
Benefits of FMEA
FMEA offers several benefits, including:
Improved product and process quality: By identifying and mitigating potential failures, FMEA can help to improve the quality of products and processes.
Reduced risk: FMEA can help to reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, and product recalls.
Increased customer satisfaction: By improving product and process quality, FMEA can help to increase customer satisfaction.
Improved communication and collaboration: FMEA is a team-based activity that can help to improve communication and collaboration among team members.
How to Conduct an FMEA
There are several steps involved in conducting an FMEA:
Define the scope of the FMEA. What product, process, or system will be analyzed?
Assemble a team. The team should include representatives from different disciplines, such as engineering, manufacturing, and quality.
Develop a failure mode list. For each item in the system, identify all possible failure modes.
Analyze the causes and effects of each failure mode. What are the potential causes of each failure mode? What are the potential effects of each failure mode on the system or product?
Assign severity, occurrence, and detection ratings to each failure mode.
Calculate the RPN for each failure mode.
Prioritize the failure modes based on their RPNs.
Develop and implement corrective actions to mitigate the highest-priority failure modes.
Review and update the FMEA as needed.
Conclusion
FMEA is a valuable tool that can help organizations to improve product and process quality, reduce risk, and increase customer satisfaction. By proactively identifying and mitigating potential failures, organizations can save time, money, and lives.
Additional Tips for Conducting an FMEA
Use a standard FMEA form to ensure consistency.
Encourage brainstorming and creativity to identify as many potential failure modes as possible.
Be objective when assigning severity, occurrence, and detection ratings.
Focus on the highest-priority failure modes first.
Document the corrective actions taken and their effectiveness.
Review and update the FMEA regularly.
I hope this article is helpful. Please let me know if you have any questions.
Additional Resources
ASQ: Failure Modes and Effects Analysis: https://asq.org/quality-resources/fmea
AIAG: Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA/DFMEA/PFMEA): https://www.aiag.org/quality/automotive-core-tools/fmea
Wikipedia: Failure mode and effects analysis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Failure_mode_and_effects_analysis