Human Leg |Definition, Anatomy, and functions|
https://www.blogger.com/blog/posts/5616672100227710177
Leg, limb, or appendage of associate degree animal, accustomed support the body, give locomotion, and, in changed kind, assist in capturing and uptake prey (as in sure shellfish, spiders, and insects). In four-limbed vertebrates, all four appendages square measure ordinarily known as legs, however in bipedal animals, together with humans, solely the posterior or lower 2 square measure therefore known as.
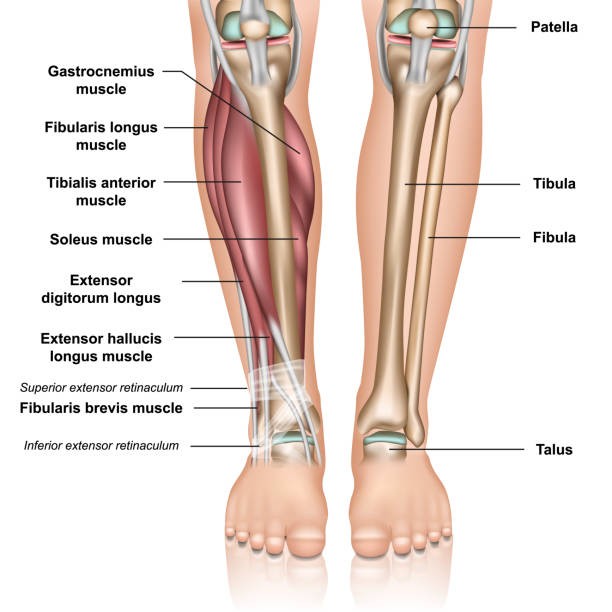
The bones of the human leg, like those of different mammals, comprise a basal section, the leg bone (thighbone); associate degree intermediate section, the shin (shinbone) and also the smaller fibula; and a distal section, the pes (foot), consisting of tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges (toes). For the actions of the key muscles of the class leg, see adductor muscle; striated muscle; skeletal muscle; striated muscle muscles; extensor muscle; skeletal muscle; skeletal muscle.
In birds and barmy, the forelimb has evolved into the wing. varied different variations of the leg embrace modifications for swimming, digging, leaping, and running, as seen within the dolphin, the mole, the marsupial, and also the horse, severally. The appendages of the many invertebrates are called legs.
The legs square measure the 2 lower limbs of the body. they supply support and a variety of movements.
Each leg contains 5 regions. They’re called the:
upper leg
knee
lower leg
ankle
foot
Upper leg anatomy and performance
The higher leg is usually known as the thigh. It’s the realm that runs from the hep to the knee in every leg.
Upper leg bones
Femur. conjointly known as the thigh bone, this can be the longest bone within the body. It’s conjointly one in every of the strongest. It will account for a few quarters of someone’s height.
Upper leg muscles
Hamstrings
The hamstrings square measure 3 muscles situated on the rear of the thigh. they permit the knees to bend.
The 3 hamstrings square measure the:
semimembranosus
semitendinosus
biceps femur
Learn how to forestall and treat hamstring pain.
Quadriceps
The quad square measure four muscles situated on the front of the thigh. they permit the knees to straighten from a bent position.
The four quad squares measure the:
vastus lateralis
vastus medialis
vastus intermedius
rectus femur
Adductors
The adductors square measure 5 muscles situated within the thigh. they permit the thighs to come back along.
The 5 adductors square measure the:
adductor magnus
adductor longus
adductor brevis
obturator externus
gracilis
Knee anatomy and performance
The knee joins the higher leg and also the lower leg. It’s conjointly the biggest joint within the body. additionally, to bear the burden of the higher body, the knee permits walking, running, and jumping. It conjointly permits rotation and pivoting.
Knee bones
Patella. conjointly known as the kneecap, the patella is some extent of attachment for various tendons and ligaments. It conjointly helps shield them from harm.
Knee ligaments
Ligaments square measure bands of animal tissue that surround a joint. they assist support joints and keep them from moving an excessive amount.
The knee contains four major ligaments:
Anterior symmetrical ligament. This prevents the shin within the lower leg from moving too way forward.
Posterior symmetrical ligament. This prevents the knee from moving too way backward.
Medial collateral ligament. This gives soundness to the inward knee.
Lateral collateral ligament. This helps stabilize the outer knee.
Knee tendons
Tendons are bands of animal tissue. They’re found on the ends of muscles, wherever they assist attach muscle to bone. the biggest connective tissue within the knee is the sesamoid bone connective tissue. It attaches the shin to the patella. The {quadriceps|quadriceps femoris|musculus quad femoris|quad|extensor muscle|extensor} connective tissue attaches the quadriceps muscle to the patella.
Other necessary structures
The knee contains a spread of structures that facilitate its support weight and permit a variety of movements. a number of the foremost necessary structures include:
Bursa. Bursae (plural) square measure little sacs crammed with fluid within the knee. There square measure fourteen of them on every knee. they assist scale back friction and inflammation within the knee.
Meniscus. The knee contains 2 menisci (plural), called the medial cartilage and lateral cartilage. They’re discs of animal tissue that act as shock absorbers. additionally, they assist in equally distributing weight, providing balance and stability.
Lower leg anatomy
The lower leg extends from the knee to the mortise joint. This space is usually spoken because of the calf.
Lower leg bones
Tibia. conjointly referred to as the shin bone, the shin is that the longer of the 2 bones within the lower leg. It acts on the grounds that the principal weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Fibula. The calf bone is found next to the shin. It principally is an associate degree attachment purpose for the muscles of the lower leg.
Lower leg muscles
Gastrocnemius. this can be one of the muscles within the calves. It permits for a kind of movement referred to as area flexion within the mortise joint. this permits the toes to purpose downward.
Soleus. this massive muscle is found behind the striated muscle. It conjointly helps with area flexion.
Plantaris. this can be a little muscle within the back of the lower leg. just like the striated muscle and striated muscle, it’s concerned with area flexion.
Tibialis muscles. These muscles are tracked down on the front and rear of the lower leg. The muscles within the front give flexure. This involves informing the toes upward. The muscles within the back facilitate area flexion and support the arch of the foot.
Peroneus muscles. These muscles are chosen as the front feature of the lower leg. they help with flexure.
Other necessary structures
Fibular nerves. Fibular nerves stimulate the muscles of the front a part of the lower leg.
Tibial nerves. These nerves are branches of the nerve. this can be one of the most nerves within the leg. leg bone nerves stimulate muscles within the back of the lower leg.
Achilles sinew. The Achilles tendon attaches the muscles of the calves to the bones of the mortise joint and foot.
Ankle anatomy
The mortise joint could be a joint that connects the lower leg to the foot. It's main operation is to permit for area flexion and flexure of the foot.
Ankle bones
The mortise joint is created off the shin and calf bone of the leg in addition because of the talus of the foot.
Ankle ligaments
The mortise joint contains 2 teams of ligaments:
the medial ligaments, generally referred to as the deltoid ligaments, within the inner mortise joint
the lateral ligaments, within the outer mortise joint
Both teams of ligaments facilitate stabilizing the mortise joint and stop it from turning too so much inward or outward.
Foot anatomy
The feet are created of several bones, muscles, and ligaments. In fact, nearly one-quarter of the bones within the body is found within the feet.
Foot bones
Tarsals
The tarsal bones are found close to the mortise joint, within the middle of the foot, wherever they type associate degree arch. The seven tarsal bones are the:
talus
calcaneus
navicular
cuboid
medial cuneiform
intermediate cuneiform
lateral cuneiform
Metatarsals
The metatarsal bones are found between the tarsal and phalange bones.
The 5 metatarsals are the:
first metatarsal
second metatarsal
third metatarsal
fourth metatarsal
fifth metatarsal
Phalanges
These are the bones that frame the toes. There are fourteen of them on every foot. aside from the massive toe, every toe has 3 phalanges, referred to as the:
proximal phalanges
middle phalanges
distal phalanges
The big toes solely have proximal and distal phalanges.
Sesamoids
Sesamoids are bones that are implanted in ligaments. They're tracked down in various joints all through the body.
There are 2 little sesamoids within the ball of the foot. they assist absorb weight and assist in giving a ratio to the sinew.
Foot muscles
Each foot contains quite twenty muscles that offer support and permit a variety of movements.
Some of the muscles of the foot embrace the:
Extensors. These facilitate raising the toes upward.
Flexors. These facilitate the toes to curl inward.
Tibialis posterior. This supports the curve of the foot.
Tibialis anterior. this permits the foot to maneuver upward.
Tibialis leg bone. This controls the movement of the outer mortise joint.
Foot ligaments
The ligaments of the foot facilitate hold along with the bones that support the arch. the most ligaments of the foot embrace the:
Plantar connective tissue. this can be the longest ligament within the foot. It runs from the heel to the toes, shaping the curve.
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament. This ligament is found within the sole of the foot, wherever it connects the bone and also the navicular bones.
Plantar calcaneocuboid ligament. This ligament helps the area connective tissue support the foot’s arch. It conjointly connects the bone and tarsal bones.
Conclusion
The flexor agreement is to twist an appendage at a joint. Then, the extensor agreements to broaden or fix the appendage at a similar joint. For instance, to walk, you need the other hand to twist and fix the leg, so the quadriceps (front) and the hamstrings (back) cooperate to move your leg.
Muscle irregular characteristics, inadequately molded hamstrings, and an absence of versatility will prompt various issues like low back torment and ACL wounds. Squats, thrusts, and deadlifts will assist with fostering your hamstrings, constructing muscle around powerless joints, and assist with advancing strength and portability.
Legs are useful to do numerous exercises like football, strolling, moving, swimming, skating, and so on. Legs are a significant piece of the human body that empowers them to remain in the right stance. Perhaps the main capacity of the leg is that it assists us with locomoting starting with one spot and then onto the next without any problem.