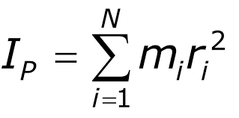
Moments in physics vs Moments in stats
In probability and statistics calculus is used to calculate the moments of probability distribution of random variable about its mean . The central moments includes the first through fourth order of P.D.F (probability density function) which yields expected value (Center) which is an row moment , Variance (Second Moment) , skewness (Third Moment) and Kurtosis (tail-shape of distribution) which is the Forth Moment
Similarly physics has moments which is the velocity, displacement and acceleration.We can easily relate Moments in Stats with Moments in physics
Different Moments Comparison
In general sense Moment or (Moment of Force) is a measure of its tendency to cause a body to rotate about a specific point or axis.
Moment of inertia is sum of product of masses of all the particles of body by square of its distance from central axis.
This can be compared with second moment in statistics.
Raw Moments or First Moment is the distribution of observations or events (masses in physics term) around the mean (central axis in physics term) of an attribute , i.e Expected value of a random variable.
To understand more about expected value let’s consider an example of two six sided dice and chances of getting a particular sum when we roll the two dice.
╔══════════════╦════════════════════════════╗
║ Sum ( event) ║ Chances of occuring (p(i)) ║
╠══════════════╬════════════════════════════╣
║ 2 ║ 1/36 ║
╠══════════════╬════════════════════════════╣
║ 3 ║ 2/36 ║
╠══════════════╬════════════════════════════╣
║ 4 ║ 3/36 ║
╠══════════════╬════════════════════════════╣
║ 5 ║ 4/36 ║
╚══════════════╩════════════════════════════╝
So expected value would be ( 1/36*2)+(2/36*3) … , Which is equal to the mean of frequency of events.
Second Moment (Variance)
The equation is similar to Moment of inertia where p(i) is masses of body and x is distance between the particles of body and central axes ( x - Mean) , This is also called as velocity of acceleration in physics
Similarly Skewness is the ratio of (1) the third moment and (2) the second moment raised to the power of 3/2 (= the ratio of the third moment and standard deviation cubed):
The third moment about the mean is the sum of each value’s deviation from the mean cubed, which (the whole sum) is then divided by the number of values
Table of Moments



