In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are growing more sophisticated, organizations face an ever-increasing risk of security breaches.
As organizations harden their security measures, they induct more tools into their security stack to protect their networks and sensitive data. Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is one such crucial tool.
This blog post will discuss intrusion detection and prevention systems, their benefits, and how they compare to similar solutions. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the intrusion detection system and its potential to safeguard your network from intrusions.
We’ll begin with an introduction to intrusion detection and prevention systems.
Table Of Content
- What is an Intrusion Detection System?
- Intrusion Detection Systems vs. Intrusion Prevention Systems
- How Does IDS Work?
- Types of IDS Detection Methods
- IDS vs. Firewalls: The Major Differences
- Intrusion Detection System Benefits
- Intrusion Detection System Challenges
- The Best Intrusion Detection and Prevention System on the Market
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is an Intrusion Detection System?
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a security technology that monitors networks and systems for malicious behavior.
IDS generates alerts and blocks suspicious activity. During this, IDS provides early warnings and detects unauthorized access and downloads. As a result, an intrusion detection system dramatically enhances an organization’s ability to respond to threats.
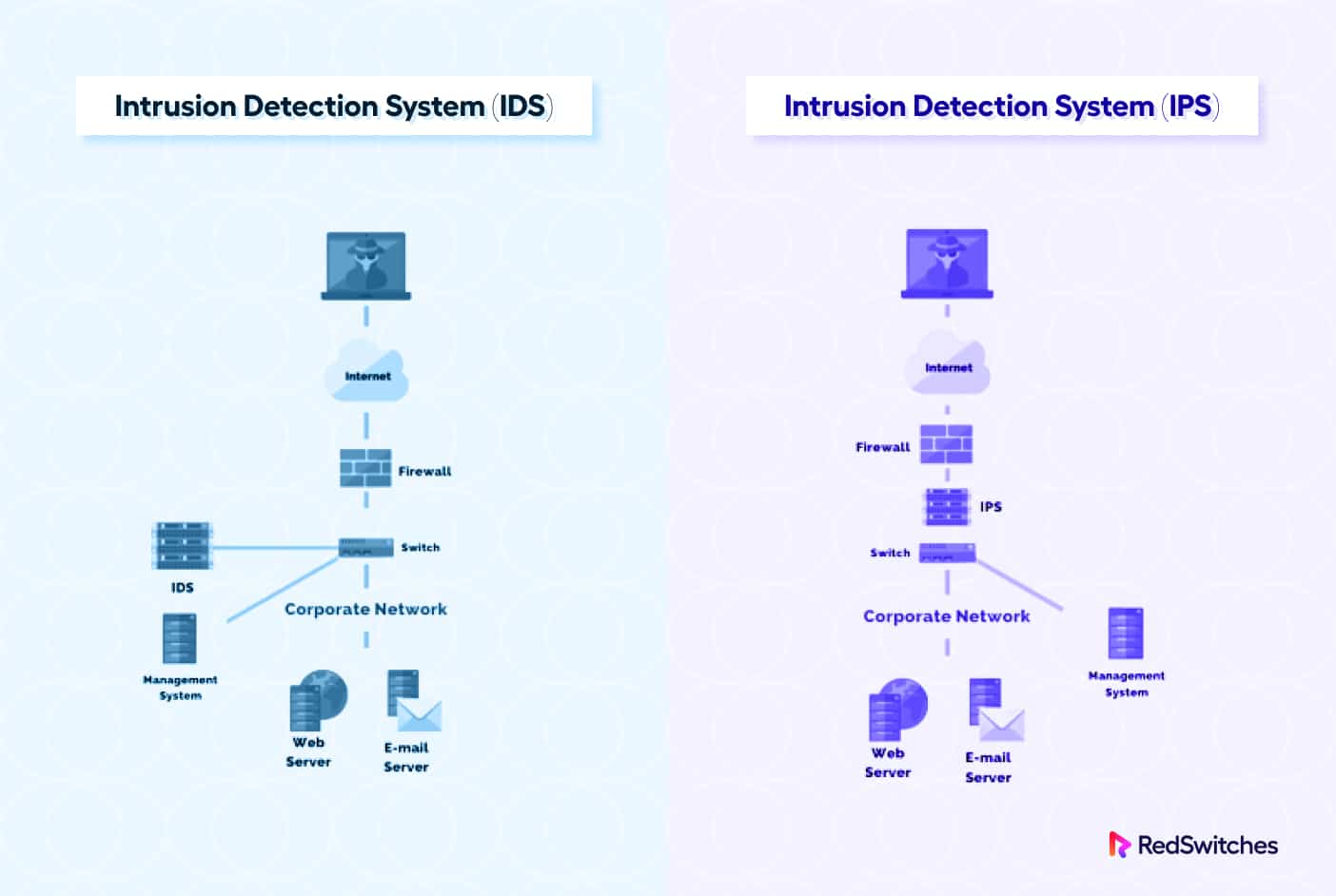
Intrusion Detection Systems vs. Intrusion Prevention Systems
After that brief introduction, let’s discuss two essential categories of intrusion detection and prevention systems.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
The following are the defining characteristics of IDS:
- IDS monitors network traffic and system activities to identify potential security breaches and malicious behavior.
- It compares logs and recorded data against known attack patterns to detect abnormal behavior pointing toward a possible attack.
- IDS generates alerts and notifications to inform security personnel about potential intrusions.
- The primary focus of IDS is to detect and provide insights for manual investigation and response.
- It helps organizations identify unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and other cyber threats.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
IPS offers the following features and benefits:
- IPS actively prevents intrusions by blocking or filtering malicious traffic in near real-time.
- It inspects network packets and applies deep packet inspection and protocol analysis techniques.
- IPS takes proactive measures to stop suspicious or harmful traffic before it can reach the target network or system.
- IPS enhances network security by actively mitigating the impact of security incidents.
- It provides an additional layer of defense to prevent attacks that attempt to eavesdrop or brute-force their way into compromising the network or systems.
You should consider IDS and IPS as two components of the infrastructure protection system. While IDS acts as a watchdog, IPS inspects and filters traffic that might hit the infrastructure during a DDoS or similar attack.
Many modern IDS include IPS as a core or add-on feature to ensure they can offer complete 360-degree protection to the infrastructure.
After this comparison, let’s do a deep dive into intrusion detection systems’ operations, benefits, and challenges.
How Does IDS Work?
As mentioned above, an IDS monitors network traffic and system activities to detect and flag potential security issues and malicious behavior. This process involves the following activities.
Monitoring
The IDS continuously monitors network traffic and system events for abnormal behavior. It also collects data from various sources, such as network packets, log files, and system calls for deeper analysis.
Data Analysis
The data IDS collects is analyzed using different techniques. One standard method is signature-based detection, where the IDS compares the incoming data against a database of known attack signatures or patterns. If a match is found, the system flags it as a potential intrusion.
Another approach is anomaly-based detection. The IDS establishes a baseline of normal behavior by learning the typical patterns and activities in the network and systems. It then raises alerts when it detects deviations from the established baseline because deviations usually indicate potential malicious activity.
Alert Generation and Response
The IDS generates alerts or notifications when it determines suspicious or abnormal activities. These alerts typically include information about the attack or behavior observed, the affected system or network, and any additional details that can help in investigation and response.
The generated alerts are sent to designated security personnel and system administrators, who can investigate the incident further and take appropriate action. This may involve isolating affected systems, blocking suspicious network traffic, and initiating incident response procedures.
To sum up, IDS continuously monitors network traffic and system activities to detect new threats or changes in set behavior. It helps organizations stay vigilant and respond promptly to emerging security incidents.
Types of IDS Detection Methods
An intrusion detection system employs various methods to identify potential security incidents and malicious behavior. Here are the common IDS detection techniques that help the system identify potential incidents:
Signature-based Detection
This method compares network traffic or system events against known attack signatures and patterns databases. It looks for exact matches to verify that the system got hit by a known threat or malware.
Anomaly-based Detection
Anomaly detection identifies deviations from normal behavior or activity patterns within the network or system. The system builds baseline(s) of typical behavior and raises alerts when activities significantly differ from the norm.
A good example is a user accessing a resource they are not authorized to use. The IDS detects this deviation from the baseline and generates an alert for a potential system breach.
Heuristic-based Detection
Heuristic detection uses predefined rules or algorithms to identify suspicious or potentially malicious behavior. It looks for patterns or characteristics associated with standard attack methods/patterns and flags them as potential threats. This method is often used to distinguish malware from other user-generated packages.
Statistical-based Detection
Statistical analysis is used to identify anomalies or unusual patterns in network traffic or system behavior. It involves analyzing traffic volume, event frequency, or statistical deviations to detect potential intrusions. This method is often used in historical analysis to find and identify aberrant patterns in IDS data.
Protocol-based Detection
This method monitors and analyzes network protocols to detect abnormalities or non-compliance with protocol standards. It looks for protocol-specific attacks or violations indicating unauthorized access or malicious activity.
Hybrid Detection
IDS solutions typically combine multiple detection methods (for instance, signature-based, anomaly-based, and heuristic-based approaches). This hybrid approach provides a more comprehensive and accurate detection capability, minimizes false positives, and enhances detection accuracy.
IDS vs. Firewalls: The Major Differences
Some organizations consider IDS and firewalls similar systems because both appear to filter network traffic. In some cases, organizations even attempt to replace one with the other to save costs.
However, from the security point of view, IDS and firewalls are crucial network security components that serve very different purposes. That’s because they have distinct functionalities that make them complementary.
Here’s a rundown of the different features and options to compare IDS and firewalls.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- IDS monitors network traffic and system activities.
- It offers data analysis capabilities so that the ITSEC teams can conduct deep analysis to discover known attack patterns or abnormal behaviors.
- IDS generates alerts and notifications so that the teams can initiate mitigation processes.
- IDS focuses on detection and provides insights for incident handling.
- The system is designed to help identify unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and other cyber threats.
Firewalls
- Firewalls primarily act as a barrier between internal and external networks.
- They control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules or policies.
- Firewalls enforce access control by allowing or blocking specific network connections or ports.
- They can filter and block traffic based on IP addresses, protocols, or application-level information.
- Firewalls provide a first line of defense by preventing unauthorized access and protecting the network from external threats.
So as you saw, firewalls only take care of the traffic side of network security. As such, they cover a relatively narrow range of network security. In contrast, IDS covers much more ground by monitoring traffic and internal system activities.
In practical terms, IDS and firewalls complement each other and, in most cases, are integrated through API. Data sharing further hardens the organization’s security and establishes a coordinated security process that protects it from all internal and external threats.
Intrusion Detection System Benefits
Now that you know how IDS operates, it’s time to see its benefits to the organization.
Early Threat Detection
IDS helps detect potential security breaches or malicious activities early. This often gives the team ample time to respond to the incident and minimize the impact on the operations.
Facilitate Incident Mitigation
IDS alerts contain all the information the team needs to quickly investigate the incident and select appropriate processes to respond to the situation.
Insight Into Network Activities
IDS provides valuable insights into network behavior that you can use to manage incidents as they happen or for historical and heuristic analysis. You can identify vulnerabilities, optimize network performance, and improve security configurations.
Regulator/Legislation Compliance Support
IDS assists organizations in meeting industry-specific compliance requirements regarding reporting and incident monitoring. Organizations can use detailed logs and notification history to produce reports for regulatory and compliance purposes.
Enhanced Incident Handling
IDS often provides detailed incident handling capabilities, including raising the flag, alerting the concerned team members, offering on-the-spot analysis, and helping security teams respond effectively, contain incidents, and prevent further damage.
Malware Detection
IDS can identify known malware signatures and detect suspicious activities that could indicate the presence of malware, viruses, and other types of malicious code. In some cases, IDS can automatically clean out malware or flag the items for the security teams.
Support for Forensic Analysis
IDS captures detailed information about network traffic and system activities. These logs can significantly help in post-incident forensics by presenting evidence in the required form(s),
Intrusion Detection System Challenges
Despite the benefits mentioned above, using IDS is not without its challenges. Here are a few things you should watch out for when implementing an IDS for your organization:
False Positives and Negatives
IDS may generate false alerts or miss genuine threats. To counter this, you must fine-tune detection processes to minimize inaccuracies at all touchpoints.
Overwhelming Volume of Alerts
IDS can generate high signals, making prioritizing and addressing critical incidents challenging. A quick fix is to segment alerts so that only the designated team members receive them instead of the entire team.
Complex Configuration and Maintenance
Implementing and managing IDS can be difficult because you require expertise to set all IDS components correctly. Similarly, applying updates and patches requires knowledge of the IDS system.
Limited Visibility into Encrypted Traffic
IDS may have limited visibility into encrypted traffic coming into the network. This can affect threat detection because IDS might need additional steps to decrypt and analyze this traffic.
Evolving Attack Landscape
Attackers are continuously developing new strategies and complicated attack methods. Keeping IDS updated to match and counter emerging threats requires dedicated attention.
Scalability Challenges
IDS performance may degrade when protecting high-speed or high-volume networks. This requires IDS to be scalable to handle the increasing traffic volume without compromising protection.
Additional Efforts For Integration With Other Security Tools
Integrating IDS with other security tools and systems (such as firewalls) may require additional effort and resources that often get overlooked in an organization’s budget.
Potential Impact on Operational Performance
IDS processes might add performance overhead to business processes. As a result, you might see latency and performance degradation. You must carefully tune and optimize operations to eliminate or minimize this overhead.
The Best Intrusion Detection and Prevention System on the Market
Determining the “best” intrusion detection and prevention system depends on various factors, including an organization’s specific needs and requirements. However, to help shorten your search, here are some highly regarded IDPS solutions known for their effectiveness.
Snort: Snort is an open-source IDPS that combines signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods. It offers extensive community support, regular updates, and a comprehensive rule-based attack identification system.
Suricata: Suricata is another open-source IDPS that emphasizes high-performance network monitoring. It supports multi-threading, provides real-time traffic analysis, and efficiently handles high-speed networks.
Cisco Firepower: Cisco Firepower is a comprehensive security platform that combines network firewall capabilities with advanced IDPS features. It offers a range of threat intelligence, real-time monitoring, and incident response capabilities.
Palo Alto Networks: Palo Alto Networks offers a suite of security solutions, including their Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) with integrated IDPS functionality. Their IDS/IPS capabilities provide advanced threat detection and prevention capabilities.
McAfee Network Security Platform: McAfee Network Security Platform offers a robust IDPS solution that combines signature-based and behavioral-based detection techniques. It provides real-time threat intelligence, centralized management, and automatic updates.
IBM QRadar: IBM QRadar is a security information and event management (SIEM) solution incorporating IDPS capabilities. It offers advanced threat detection and centralized log management for comprehensive security monitoring.
Check Point IPS: Check Point IPS is an IDPS solution that combines signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods. It provides a range of predefined security profiles, threat intelligence integration, and centralized management.
Conclusion
An intrusion detection system is essential for network security, providing early threat detection and incident response capabilities. They differ from an intrusion prevention system by focusing on detection rather than immediate prevention.
IDS offers benefits such as early threat detection, compliance support, enhanced incident handling, and network visibility. However, implementing IDS presents challenges that require significant time and resources. By considering factors like detection methods and vendor support, organizations can select the best
IDS solution for their needs and strengthen their network security.
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
A.IDS focuses on detecting and alerting about potential intrusions or malicious activities within a network, while IPS takes action to prevent or block such threats.
Q. How does an IDS work?
A. An intrusion detection system analyzes real-time network traffic, system logs, or events, comparing them against known attack patterns or behavior anomalies to identify potential security breaches.
Q. What are the different types of IDS detection methods?
A. Different IDS detection methods include signature-based, anomaly-based, heuristic-based, statistical-based, protocol-based, and hybrid detection.
Q. How does an IDS compare to a firewall?
A. Firewalls enforce access control and act as a barrier between networks, while IDS focuses on detecting potential intrusions and malicious activities within the network.
Q. What are the benefits of implementing an IDS?
A. Implementing an IDS provides benefits such as early threat detection, incident response capabilities, insight into network activity, compliance support, enhanced incident handling, malware detection, and support for forensic analysis.
Q. What challenges are associated with IDS implementation?
A. Challenges of IDS implementation include dealing with false positives and negatives, complex configuration and maintenance requirements, limited visibility into encrypted traffic, and scalability challenges.