Archegoniates
- 1. ARHEGONIATES Prepared By- Dr. Sangeeta Das Assistant Professor Department of Botany Bahona College Jorhat, Assam, India.
- 2. WHAT ARE ARCHEGONIATES? They are plants having archegonia as female reproductive part. Archegonium is a flask shaped female reproductive part. It is found in the archegoniate plants e.g. Bryophyta, Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms.
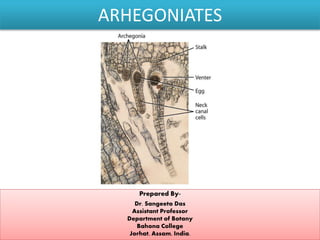
- 3. What is an archegonium? A mature archegonium is a flask shaped structure, without neck canal cells and with an egg (oosphere) in its venter. At the top of the neck of the archegonium there are four cover cells, which become separated from the archegonium, as soon as the gelatinization of the venter and neck canal cells is over.
- 4. Unifying Characteristics of Archegoniates 1. The archegoniates seem to have originated from a monophyletic group of aquatic green algae. 2. Presence of Female sexual organs are called archegonium and the male sexual organs are called antheridium. 3. The presence of Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll a, b and carotene. 4. The presence of multicellular gametophytic and sporophytic generation.
- 5. Unifying Characteristics of Archegoniates 5. Heteromorphic alternation of generation. 6. Provides protection to their embryo 7. Male gametes are flagellated and motile in bryophytes, pteridophytes, (Cycadales, Ginkgoales) while the female gamete (egg) is non-motile. 8. Water is needed for fertilization in Bryophytes and Pteridophytes but not in Gymnosperms.
- 6. Unifying Characteristics of Archegoniates 9. In gymnosperms, pollen grains germinate to form a pollen tube (siphonogamy) which is not dependent on external fluid water to reach the archegonial neck. 10.Differentiated tissues with thickened cell walls (collenchyma) and lignified walls (sclerenchyma) to support the erect habit. 11.Efficient spore dispersal mechanism. 12.The archegoniates evolved several adaptive strategies to survive on land.
- 7. The transition from water to land There are lots of evidences regarding the evolution of land plants from the aquatic environment. The first multicellular organisms that lived in the water are green algae which are considered to be the ancestors of land plants. This transition from water to land habit was made possible due the following adaptations that occurred in those plants.
- 8. 1. Body support Supportive structures developed to withstand the forces of gravity. Such as Rigid cell walls, different types of supportive tissues (e.g., woody tissues, branch cells, etc.). However, the mosses lack these tissues, and are thus limited to land habit. This type of support is found in the ferns, although it is very primitive. In the conifers and flowering plants, the most well- developed adaptations of this nature are observed. Adaptations...
- 9. 2. Transport of materials Another challenge to transform from water to land form. In aquatic forms, transport occurs directly from the surrounding environment. But land plants must absorb water and other materials from the soil. Thus, they need to develop conducting vessels to transport materials from the soil to the plant as well as from the leaves to the different parts of the plant. It also led to the evolution of differentiation of plant parts, such as, evolution of leaf cells having ability to create food via photosynthesis; root cells to transport nutrients from the soil; the cuticle, stomata, phloem, xylem etc. are also developed to regulate the water inside the plant, etc. Adaptations...
- 10. 3. Fertilization A third challenge is to bring sex cells together. In water, sperm are able to swim directly to eggs. However, on land, this is possible only in moist condition as seen in mosses and ferns. Land plants show alternation of generations and the sporophytic generation produces spores inside microscopic gametophytes. The male gametophytes, which form non-swimming sperm, develop within pollen grains. The female gametophytes, which produce eggs, develop on scales (in conifers) or within ovaries (in flowering plants). Pollen is adapted to use wind to transport sperm to eggs, which replaces the need for water in those plants. Adaptations...
- 11. 4. Development and dispersal of the embryo A fourth challenge. In aquatic environments, a fertilized egg can develop into an embryo without facing the problem of dehydration. In addition, the embryo can receive water and nutrients directly from the surrounding environment. Whereas, in land plants, an embryo and exists in an environment where water and nutrients exist in the ground and thus can dry out rapidly. This problem is mitigated as the seeds enclose an embryo in a moist environment, and the tissues within seeds provide food for a developing embryo. Finally, seeds represent a way of dispersing the young of plants away from water as well as away from the parent plant. The seed plants include the conifers and flowering plants. Adaptations...
- 12. Alternation of generation Alternation of generation in Bryophytes.
- 13. 1. The life cycle of bryophytes shows regular alternation of gametophytic and sporophytic generations. 2. The haploid phase (n) is the gametophyte or sexual generation. 3. It bears the sexual reproductive organs, which forms gametes, i.e. antherozoids and eggs gametic union a zygote is formed which develops into a sporophyte (2n) deploid phase. 4. Sporophyte forms spores, which always germinate to form gametophytes 5. During the formation of spores, the spore mother cells divide meiotically and haploid spores are formed. Alternation of Generation in Bryophytes..
- 14. 6. The production of the spores is the beginning of the gametophytic or haploid phase 7. The spores germinate and form gametophytic or haploid phase 8. The spores germinate and produce gametophytes, which bear sex organs 9. Ultimately, the gametic union takes place and zygote is resulted. It is diploid (2n). 10.This is the beginning of the sporophytic or diploid phase. Alternation of Generation in Bryophytes..
- 15. 11.Here the two generations are morphologically different, the type of alternation of generations is called heteromophic 12.The gametophytic generation is conspicuous and longer-lived phase of life-cycle in comparison to that of sporophyte generation 13.In bryophytes, the gametophyte is quite independent whereas the sporophyte is dependent somehow or other on the gametophyte for its nutrition 14.The gametophyte produces sporophyte and sporophyte to the gametophyte and thus there is regular alternation of generations Alternation of Generation in Bryophytes..
- 16. Alternation of Generation in Pteridophytes..
- 17. 1. In Pteridophytes, the haploid phase (n) is gametophytic generation or sexual phase. 2. It bears reproductive organs -antheridia and archegonia. 3. The Antheridia and archegonia produces flagellate antherozoids and egg respectively. 4. Gametophyte may be monoecious as in homosporous sp. / dioecious in heterosporous sp. 5. The Gametophyte is independent in Pteris and dependent in Selaginella. Alternation of Generation in Pteridophytes..
- 18. 6. Diploid phase (2n) or sporophytic stage forms from zygote after fertilization 7. Meiosis in SMC (spore mother cell) forms non- motile haploid spore, which germinate to form gametophyte again. 8. This cycle continues with alternation between gametophye and sporophyte. 9. All spore formed may be of one type i.e. homosporous species (Lycopodium, Dryopteris). 10.Spores formed may be of two types i. e. heterosporous species (Selaginella, Marsilea). Alternation of Generation in Pteridophytes..
- 19. 10.Microspores/male spores developed in male sporangia germinate to form male gametophyte. 11.Megaspores/female spore developed in megasporangia germinate to form female gametophyte. 12.Sporophyte is dominant phase in life cycle. 13.It is independent of the gametophyte (prothallus) and grows to a much greater size. 14.Sporophytes are differentiated into stems, leaves and roots and shows well developed conducting tissues. Alternation of Generation in Pteridophytes..
- 20. Alternation of Generation in Gymnosperms..
- 21. 1. The dominant phase in the life cycle is the diploid (sporophyte) stage. 2. The gametophytes are very small and cannot exist independent of the parent plant. 3. The reproductive structures of the sporophyte (cones), produce two different kinds of haploid spores: microspores (male) and megaspores (female). 4. This phenomenon of sexually differentiated spores is called heterospory. Alternation of Generation in Gymnosperms..
- 22. 5. These spores give rise to similarly sexually differentiated gametophytes, which in turn produce gametes. 6. Fertilization occurs when a male and female gamete join to form a zygote resulting an embryo sac. 7. Resulting embryo, encased in a seed coating, become sporophyte. Alternation of Generation in Gymnosperms..
- 23. THANK YOU
