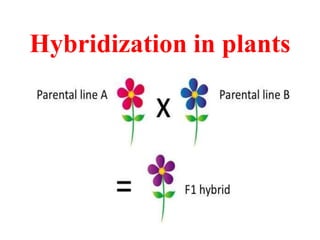
Hybridization
- 2. Hybrid/Hybridization • Hybrid: Individual produced as a result of cross between two genetically different parents is known as hybrid. • Hybridization: The production of a hybrid by crossing two individuals of unlike genetical constitution is known as hybridization. Or the mating or crossing of two plants or lines of dissimilar genotype is known as hybridization. • Hybridization is an important method of combining characters of different plants. • Hybridization does not change genetic contents of organisms but it produces new combination of genes.
- 3. Hybrid plants • Hybrid Lilies • Sweet Corn • Meyer Lemon Trees • Hybrid Maize • Better Boy Tomatoes • Rabbage • coconut
- 4. History • The first natural hybridization was recorded by Cotton Mather (1716) in corn. The first artificial inter- specific plant hybrid was produced by Thomas Fairchild in 1717. It is commonly known as ‘Fairchild Mule’. • Hybridization was first of all practically utilized in crop improvement by German botanist Joseph Koerauter in 1760. • Mendel onward, the hybridization had become the key method of crop improvement. • Today, it is the most common method of crop improvement, and the vast majority of crop varieties have resulted from hybridization.
- 5. Objectives 1. To artificially create a variable population for the selection of types with desired combination of characters. 2. To combine the desired characters into a single individual, and 3. To exploit and utilize the hybrid varieties.
- 7. Types of Hybridization: (i) Inter-varietal hybridization: • The crosses are made between the plants of the same species. • It is also called intra-species hybridization • Commonly used method • Example: Crossing of two varieties of wheat, rice, carrot, etc. • It is further classified into two A) Intra-specific B) Inter-specific
- 11. (ii) Distant hybridization/Intra-varietal hybridization: • The crosses are made between the plants of the same varieties.
- 15. Procedure OR methods of Hybridization: It involves the following steps: (i) Selection of parents. (ii) Selfing of parents or artificial self- pollination. (iii) Emasculation. (iv) Bagging (v) Tagging (vi) Crossing (vii) Harvesting and storing the F1 seeds (viii) Raising the F1 generation.
- 16. Selection of parents. • The selection of parents depends upon the aims and objectives of breeding. • Parental plants must be selected from the local areas and are supposed to be the best suited to the existing conditions. • There are various methods by which plant selection is carried out, namely selection for uniform plants, known as pure line selection(selection of single best plant progeny among traditional varieties); selection from field-grown plants, known as bulk selection or mass selection; and selection from a well-documented list of parentage, commonly known as the pedigree system.
- 17. Selfing of parents or artificial self- pollination. • It is essential for inducing homozygosity (state of possessing two identical forms of a particular gene) for eliminating the undesirable characters and obtaining inbreeds. • There are two types of self-pollination: in autogamy, pollen is transferred to the stigma of the same flower; • In Geitonogamy, pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on the same flowering plant.
- 21. Emasculation • It is the third step in hybridization. Inbreeds are grown under normal conditions and are emasculated. • Emasculation is the removal of stamens from female parent before they burst and shed their pollens. • It can be defined as the removal of stamens or anthers or the killing of the pollen grains of a flower without affecting in any way the female reproductive organs. • Emasculation is not required in unisexual plants but it is essential in bisexual or self-pollinated plants.
- 23. unisexual plants • Date palms flower • Sagittaria flower • Corn flower • Papaya flower • Cucumber flower • Rye • Carrot • Sweetpotato
- 25. Bisexual or self-pollinated plants. • Habiscus plant • Mustard plant
- 26. Various methods used for emasculation are: •Assignments
- 27. Bagging • The emasculated flower or inflorescence is immediately bagged to avoid pollination by any foreign pollen. • The bags may be made of paper, polyethene paper, butter paper, glassine or fine cloth. • Butter paper or vegetable parchment bags are most commonly used.
- 28. Tagging: • The emasculated flowers are tagged just after bagging. Generally circular tags of about 3 cm or rectangular tags of about 3 x 2 cm are used. The tags are attached to the base of flower or inflorescence with the help of thread. • The information on tag must be as brief as possible but complete bearing the following information: (i) Number referring to the field record (ii) Date of emasculation (iii) Date of crossing (iv) Name of the female parent is written first followed by a cross sign (x) and then the male parent, E.g., C x D denotes that C is the female parent and D is the male parent.
- 30. Crossing: • It can be defined as the artificial cross-pollination between the genetically unlike plants. In this method mature, fertile and viable pollens from the male parent are placed on the receptive stigma of emasculated flowers to bring about fertilization. • Pollen grains are collected in petridishs (e.g., Wheat, cotton etc.) or in paper bags {e.g., maize) and applied to the receptive stigmas with the help of a camel hair brush, piece of paper, tooth pick or forceps. In some crops (e.g., Jowar, Bajra) the inflorescences of both the parents are enclosed in the same bag.
- 32. Significance of Hybridization • New plants with variations in genetic characters are produced • It incorporates many desirable characters of other plants(like high yield, resistant to pests, etc) into a single variety of plant • It produces hybrids which are better adapted to changes in the environment • Hybridization is also development by asexual hybridization or protoplast fusion in tissue culture media.
- 33. LET COVID-19 NOT STOP YOUR LEARNING. CONTINUE WITH OUR SYLLABUS
