Are you confused by conventional project management approaches?
Are you looking for project management methods or frameworks to elevate your projects? Do you want to know how to drive exceptional results?
With so many options available, feeling overwhelmed and unsure is easy. Not to mention the time, money, and effort a mistake could cost you.
This article dives deep into the eight best project management methods. This comprehensive guide provides information on which to use, when, and why.
Get ready to:
- Explore eight methods and frameworks that can revolutionize your approach.
- Discover the core concepts and practical applications of each.
- Learn how to choose the right methodology.
- Experience how Motion can seamlessly enhance your workflow across different methodologies.
Let’s jump right in.
What are project management methodologies?
Project management methodologies are ways to plan, execute systematically, and control projects. They offer a set of guidelines, principles, and practices to help people and teams navigate the complexities of their work. These methods serve as roadmaps for managing tasks, resources, and timelines.
Imagine trying to build a house without a blueprint. It’d be chaotic and prone to errors. Similarly, in project management, methodologies bring order and efficiency.
Within the realm of project management, eight popular methods and frameworks stand out:
- Agile
- Waterfall
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Lean
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- PRINCE2
- Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
The choice of a project management methodology depends on various factors (which we'll go over soon).
What are project management frameworks?
In addition to methodologies, project management frameworks are born out of Agile. These frameworks help to plan, execute, and control projects more precisely.
Let’s briefly explore some frameworks commonly used within the Agile methodology and where they came from:
- Scrum: is an Agile framework that originated in the early 1990s.
- Kanban: is a project management framework that emerged in the late 1940s in Toyota’s manufacturing plants in Japan.
- Lean: is a management philosophy and project management approach that originated at Toyota in the 1940s and 1950s.
The 8 best project management methods & frameworks
Over the years, various methods and frameworks have emerged. Each offers its unique approach to help project managers achieve successful outcomes. Anyone looking to use them can adopt these methods if they invest in learning.
 |
Let’s take a look at these eight popular project management methodologies in detail.
1. Agile methodology
Agile methodology is a flexible and iterative approach to project management. It focuses on adaptability, teamwork, and customer satisfaction.
The Agile approach is ideal when a project requires frequent feedback and continuous improvement. It's also effective when dealing with projects that have uncertain environments. It's well-suited for software development, product launches, and where customer engagement is crucial. It works where the deliverable can be useful as pieces are delivered.
According to this survey, Agile teams also enable more effective remote working environments.
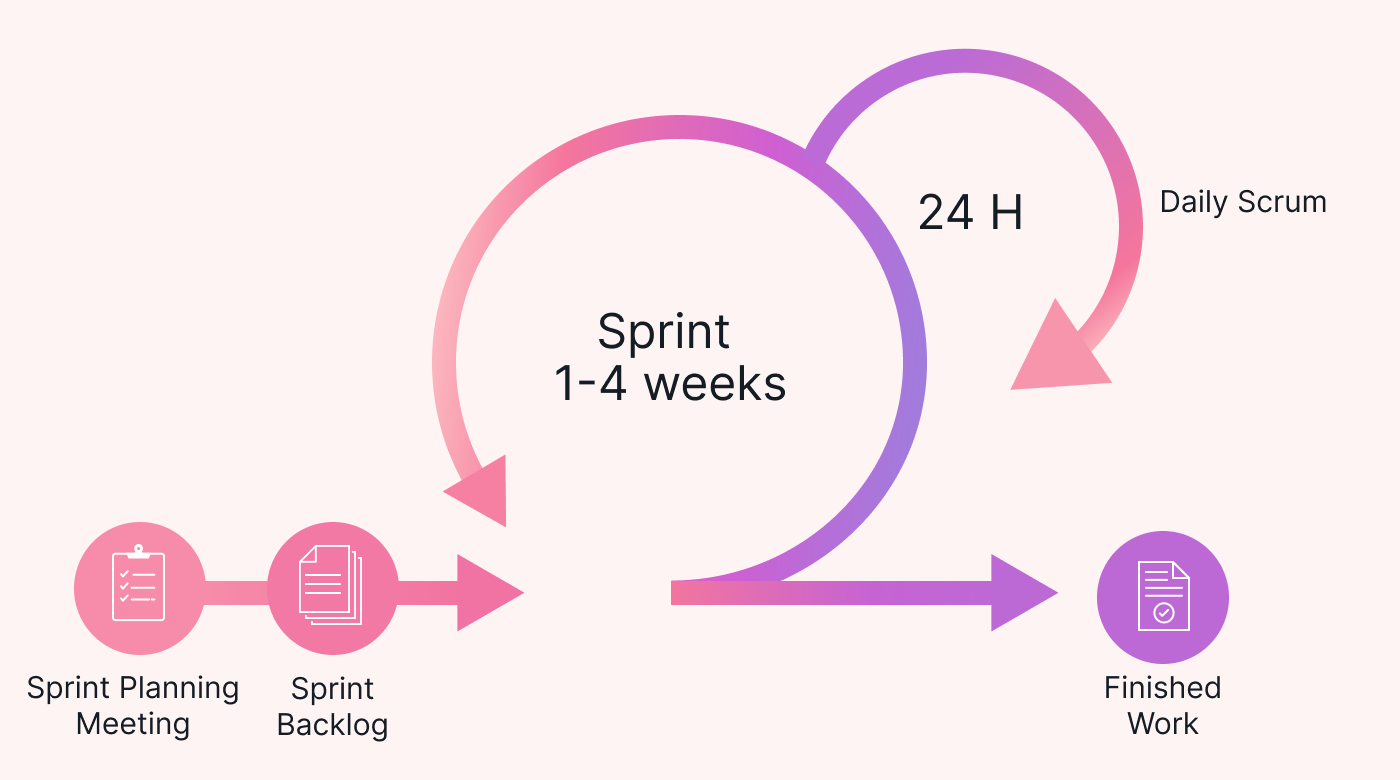
To implement Agile methodology (in a nutshell):
- Start by creating a prioritized list of features or tasks called the product backlog.
- Then, plan short iterations known as sprints, typically lasting one to four weeks.
- The development team works together on the chosen backlog items during each sprint. And they deliver a working increment of the project by the end of the sprint.
- Host regular meetings, such as daily stand-ups and sprint reviews, so everything stays on track.
Imagine you are developing a mobile application. With Agile, you'd break down the project into sprints. You'd then focus on delivering a working increment of the application at the end of each sprint. Throughout the project, you engage with the client to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments. By doing this, you make sure the final product meets their evolving needs.
2. Waterfall methodology
Waterfall methodology follows a linear progression, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. This structured approach provides clear milestones and allows for meticulous project planning and documentation.
The waterfall method is suitable for projects with stable and predictable requirements. It works well when the outcome has to stay consistent throughout the whole project lifecycle. It's also useful for projects where a clear scope is critical to success, and it works where the deliverable can only be used as a whole.
Here's a simplified breakdown of how waterfall methodology works:
- Requirements: are gathered and documented at the beginning of the project.
- Design: is based on the gathered requirements.
- Implementation: is where the design translates into an actual product or solution.
- Testing: happens once the implementation (development) is complete.
- Deployment: is when the final product is deployed or released to the end-users or stakeholders.
For example, imagine you are building a bridge using the waterfall methodology. You'd start by gathering and documenting the requirements. Then move on to designing the bridge. Followed by construction, testing, and finally, the bridge's completion and deployment. The bridge can only be used when it’s all there.
3. Scrum
Scrum is an Agile framework emphasizing collaboration, adaptability, and iterative development. It provides Agile’s flexible approach and structure and helps the team be self-sufficient. Almost 80% of Scrum practitioners say they recommend this approach.
Scrum is suitable for projects where requirements evolve or change often. They work well in fast-paced business environments, both small and large.
The key components of Scrum include:
- Sprint backlog: a prioritized list of requirements and features for the upcoming sprint.
- Scrum team: a self-organizing cross-functional team.
- Sprint planning: for the work to do in the upcoming sprint.
- Daily Scrum: sprint meetings where team members sync their work and identify any obstacles.
- Sprint review: held at the end of each sprint.
- Sprint retrospective: where the team reviews its process and identifies areas for improvement in the next sprint.
For example, imagine you are developing a website using Scrum. Each sprint would focus on delivering a specific set of functionalities. This way, there's space for continuous feedback and improvement. The team would also be able to handle any change requests with ease. This way, they can continue to evolve the product and deliver better results.
4. Kanban
Kanban is an Agile framework that visualizes work, limits work in progress, and optimizes flow. Created for manufacturing, Kanban is now found in many industries.
At its core, Kanban uses a visual board, often divided into columns representing different stages of work. A card or sticky note represents each work item, moving across the board as it progresses.
For example, imagine you are managing a marketing campaign using Kanban. Your Kanban board may have columns like “Ideas,” “To Do,” “In Progress,” “Review,” and “Completed.” As tasks move across the board, team members can easily visualize the status of work and ensure a smooth flow.
Key principles of Kanban include:
- Visualize: using a visual representation of the workflow.
- Limit WIP: on the number of work items allowed in each column.
- Flow optimization: to improve the flow of work.
5. Lean
Lean project management is a framework focused on maximizing value while minimizing waste. Lean principles are used to clean processes and deliver value after rising in the manufacturing industry.
Lean applies to a wide range of projects, from manufacturing and construction to software and services.
The core principles of lean project management include:
- Value: from the customer's perspective and removing non-value-adding activities.
- Waste reduction: such as overproduction, waiting, unnecessary motion, defects, and excess inventory.
- Continuous improvement: to drive efficiency and enhance the quality of deliverables.
In lean, there's a need for clear communication and teamwork. You also need to empower employees to make decisions and contribute to process improvement.
For instance, imagine you are managing a software development project using lean principles. You'll focus on removing unnecessary steps in the development process. You'll reduce reworks and optimize the flow of features to deliver value to end-users more efficiently.
6. Critical path method (CPM)
CPM is a project management technique mostly used within waterfall. It focuses on identifying the longest sequence of dependent activities, known as the critical path. Doing this helps to find activities that are critical to its timely completion.
CPM involves the following key steps:
- Activity sequencing: identifying all project activities and determining their dependencies.
- Estimating durations: estimating the time required to complete each activity.
- Critical path analysis: to find the longest activity sequence that impacts the project's duration.
CPM is particularly useful for projects with well-defined and sequential processes. It helps you see the critical activities that require monitoring and attention.
7. PRINCE2 method
The PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) method is a very popular method in Europe. It provides a structured framework for effective project execution. PRINCE2 is now applied across various industries.
PRINCE2 is suitable for projects of various sizes and complexities. It follows a scalable framework that you can tailor to specific project requirements. It promotes a proactive approach to project management. Likewise, it focuses on risk management, change control, and continuous improvement.
Key aspects of the PRINCE2 method include:
- Defined roles and responsibilities: of project stakeholders & team members.
- Phased approach: each phase has specific objectives, deliverables, and review points.
- Focus on business justification: for project initiation and beyond.
8. Critical chain project management (CCPM)
CCPM is a popular method that focuses on resource optimization and efficient task scheduling. It aims to ensure project completion within the specified time frame by identifying and managing the critical chain of tasks.
CCPM is particularly beneficial for projects with limited resources and complex dependencies. It helps mitigate common challenges such as resource conflicts, multitasking, and unrealistic scheduling.
Key aspects of the CCPM method include:
- Resource optimization: by considering their availability and constraints. It aims to prevent resource overloads and delays.
- Buffer management: to accommodate uncertainties and protect the critical chain. These buffers help absorb variations and prevent them from affecting the project's critical path.
- Project tracking and control: of potential risks and constraints.
For example, let’s consider a software development project using CCPM. The project team would focus on identifying the critical chain of tasks. They’d then allocate resources effectively and manage buffers to ensure timely delivery.
Other leading project management approaches
Besides the project management methods and frameworks we've explored so far, there are two others: PMBoK and Six sigma. These are not typical methodologies but stricter approaches implemented by organizations.
PMBoK
PMBoK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) is a globally recognized standard published by the Project Management Institute (PMI). It serves as a comprehensive guide to project management processes, best practices, and guidelines.
PMBoK outlines key knowledge areas, process groups, inputs, and outputs for project management. It offers a systematic and structured approach to managing projects. It covers areas such as scope, time, cost, quality, risk, communications, and stakeholder management.
PMI, an authoritative institution in the field of project management, offers various certifications. These are to validate professionals' expertise and knowledge. PMBoK is particularly popular in the United States, like PRINCE2 is well-regarded in Europe.
Six Sigma
While not strictly a project management methodology, Six Sigma is an effective approach used primarily in operations processes. However, you can use it to enhance project management processes as well. This is especially true when the project's purpose is to improve some operational aspects of the business.
Six Sigma aims to reduce process variations and defects to achieve high levels of quality and efficiency.
Six Sigma projects typically follow the define, measure, analyze, improve, and control (DMAIC) framework. Certified practitioners known as Six Sigma Black Belts or Green Belts usually implement them.
Criteria to keep in mind when choosing a method
Certain criteria can guide you when choosing a method or framework.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Project complexity. Assess the complexity and nature of your project. Is it a simple, straightforward endeavor or a complex initiative with many interdependencies?
- Team composition. Evaluate the skills and experience of your team members. Some methods may require specific expertise or work better with cross-functional teams.
- Project requirements. Determine your project's specific needs and objectives. Consider factors such as time constraints, budget limitations, and stakeholder expectations.
- Organizational culture. Consider your organization's culture and readiness for change. Some methods align better with certain cultural environments.
- Flexibility vs. structure. Consider the level of flexibility and structure that best suits your project. Agile methods offer more adaptability (deliver a little at a time), while traditional methods provide a more rigid framework (have to deliver the whole thing at once).
Tools of the trade
Project management tools play a valuable role in supporting effective project execution.
 |
These tools help facilitate communication, track progress, manage resources, and enhance project visibility. Popular platforms, like Motion, offer features such as automated task management and Kanban boards.
Use Motion for any method
No matter which project management method or framework you choose, Motion can adapt to support your approach.
 |
Motion's versatile platform integrates seamlessly with other project management software through Zapier. Integrations let you connect with other popular tools and streamline your workflows.
Motion acts as a hub for project communication, task tracking, file sharing, and milestone management. You can efficiently execute your projects with Motion's intuitive interface and powerful features.
Get the all-in-one PM solution
Use Motion to streamline your project management approach and unlock unparalleled efficiency. From Agile to Waterfall and Scrum to Kanban, Motion helps you to adapt and thrive in any project environment.
Motion offers that and so much more, like:
- Customizable workflows
- Adaptable processes so you can effortlessly switch between methodologies
- AI calendar manager
- Motion fosters teamwork
- AI task automation capabilities
- Productivity features that save you time and make you more efficient
Start your 7-day free trial now.