Answer
390.9k+ views
Hint: This starts after copulation when the ovary matures. A membrane is secreted around the clitellum by membrane secreting glands. Inside this one sperm gets fertilized with ova to form a zygote. The young worm is developed inside this structure and comes out after 2-3 weeks.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The clitellum is part of the reproductive system. The clitellum is a thick, saddle-like ring found in the epidermis (skin) of the worm, which is usually a light-colored pigment. For the formation of cocoon for its eggs, the clitellum secretes a viscous fluid. The main function performed by clitellum is cocoon formation. In earthworms, the clitellum is only found when the worm is sexually mature.
Earthworms are hermaphrodite animals, i.e., each individual carries both male and female sex organs. As invertebrates, they lack a true skeleton, but they maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelomic chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.
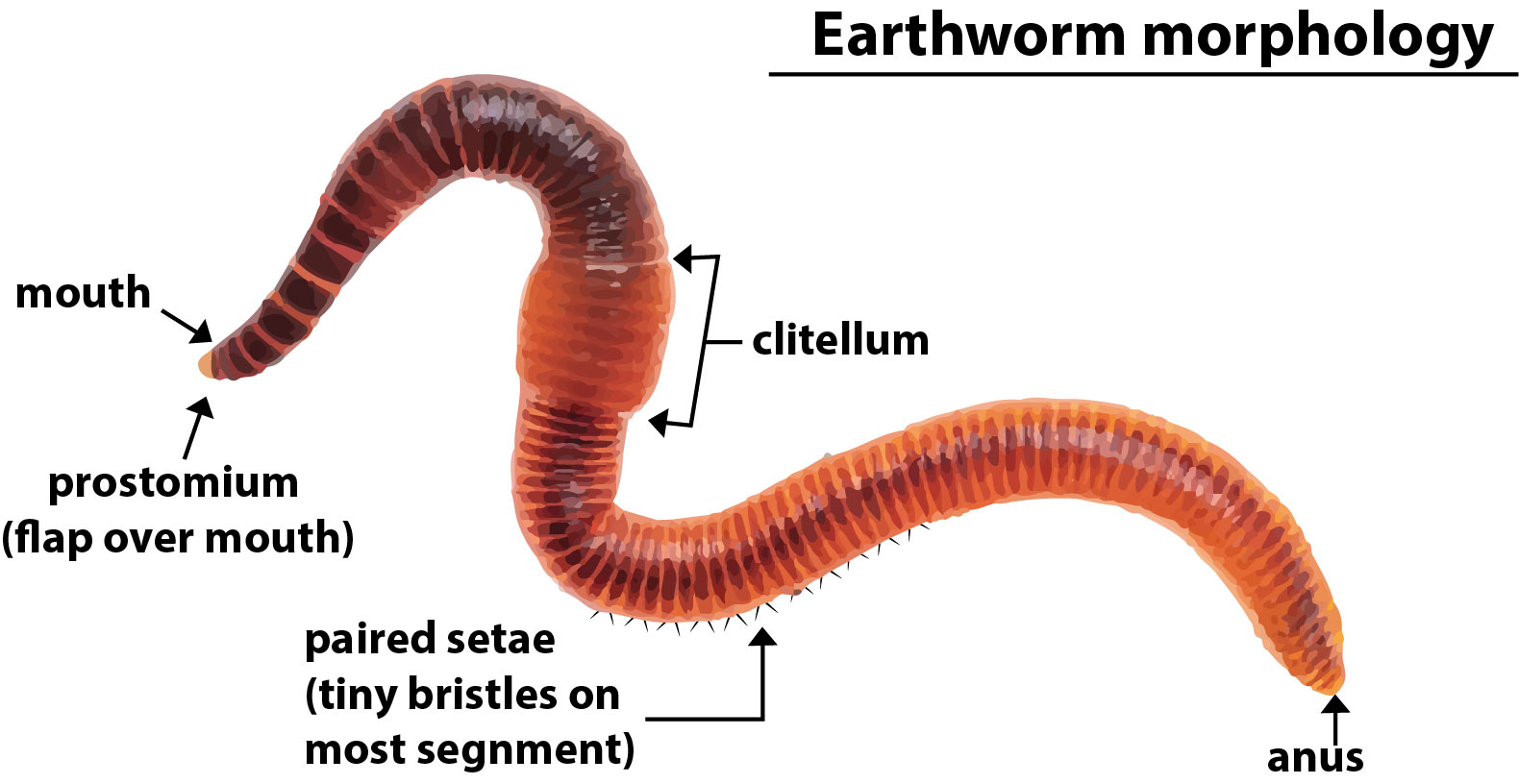
The sexual organs in an earthworm are located through segments 9 to 15. Pheretima has one or two pairs of testes that are contained within sacs. They have two or four pairs of seminal vesicles that produce, store, and release sperms via the male pores. Ovaries and oviducts are seen in segment 13 that release eggs via the female pores on segment 14, while the sperm is expelled from segment 15. One or more pairs of spermathecae are seen in segments 9 and 10 which are internal sacs that receive and store sperm from the other worm during copulation.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Cocoon Formation.’
Note: Copulation and reproduction are two separate processes in earthworms. Though they are hermaphrodites, each earthworm obtains sperms from a different worm. So, each earthworm is the father to offspring of a different worm and mother to its own. This ensures genetic variation.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The clitellum is part of the reproductive system. The clitellum is a thick, saddle-like ring found in the epidermis (skin) of the worm, which is usually a light-colored pigment. For the formation of cocoon for its eggs, the clitellum secretes a viscous fluid. The main function performed by clitellum is cocoon formation. In earthworms, the clitellum is only found when the worm is sexually mature.
Earthworms are hermaphrodite animals, i.e., each individual carries both male and female sex organs. As invertebrates, they lack a true skeleton, but they maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelomic chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.

The sexual organs in an earthworm are located through segments 9 to 15. Pheretima has one or two pairs of testes that are contained within sacs. They have two or four pairs of seminal vesicles that produce, store, and release sperms via the male pores. Ovaries and oviducts are seen in segment 13 that release eggs via the female pores on segment 14, while the sperm is expelled from segment 15. One or more pairs of spermathecae are seen in segments 9 and 10 which are internal sacs that receive and store sperm from the other worm during copulation.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Cocoon Formation.’
Note: Copulation and reproduction are two separate processes in earthworms. Though they are hermaphrodites, each earthworm obtains sperms from a different worm. So, each earthworm is the father to offspring of a different worm and mother to its own. This ensures genetic variation.
Recently Updated Pages
How do you arrange NH4 + BF3 H2O C2H2 in increasing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Is H mCT and q mCT the same thing If so which is more class 11 chemistry CBSE

What are the possible quantum number for the last outermost class 11 chemistry CBSE

Is C2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic class 11 chemistry CBSE

What happens when entropy reaches maximum class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Calculate the volume occupied by 88 gram of CO2 at class 11 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic class 11 biology CBSE

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Change the following sentences into negative and interrogative class 10 english CBSE

How many millions make a billion class 6 maths CBSE

Fill the blanks with proper collective nouns 1 A of class 10 english CBSE

Give 10 examples for herbs , shrubs , climbers , creepers

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE



