Metacarpus
From WikiLectures
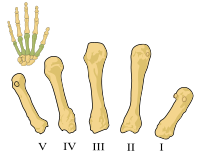
The skeleton of the palm (metacarpus) is made up of five bones (ossa metacarpi). These correspond in shape to long bones, but are classified among short bones (around 10 cm). Metacarpals are located between the carpal bones (carpus) and the finger joints (phalanges), where they are articularly connected to both the carpal bones and the finger joints. All joints are strengthened by ligaments on both sides. Each of the bones then has its characteristic feature, for example, metacarpal axis I is the shortest. We distinguish three parts:
- basis – proximal expanded end with articular socket, articulates with carpus;
- corpus - body (corresponds to the diaphysis);
- caput – distal extension of the bone, the ossa digitorum is attached to it.
All bones are well palpable from the dorsal side. They are numbered from I. to V. in the radioulnar direction.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír. Anatomy 1. 2. edition. Prague : Grada Publishing, a.s., 2008. 516 pp. vol. 1. ISBN 80-7169-970-5.