COPEPODI PLANCTONICI / PLANKTONIC COPEPODS ... - SIBM
COPEPODI PLANCTONICI / PLANKTONIC COPEPODS ... - SIBM
COPEPODI PLANCTONICI / PLANKTONIC COPEPODS ... - SIBM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Biol. Mar. Mediterr. (2010), 17 (suppl. 1): 420-431<br />
<strong>COPEPODI</strong> <strong>PLANCTONICI</strong> / <strong>PLANKTONIC</strong> <strong>COPEPODS</strong>:<br />
CALANOIDA, CYCLOPOIDA, HARPACTICOIDA,<br />
MORMONILLOIDA, SIPHONOSTOMATOIDA<br />
Maria Grazia Mazzocchi & Iole Di Capua<br />
Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Villa Comunale - 80121 Napoli, Italia.<br />
grazia.mazzocchi@szn.it, iole.dicapua@szn.it<br />
I copepodi rappresentano la componente<br />
numericamente dominante delle comunità mesozooplanctoniche<br />
marine. Il ruolo dei copepodi è<br />
fondamentale per il funzionamento delle reti trofiche,<br />
essendo essi un importante anello di trasferimento<br />
dai produttori primari (fitoplancton) ai<br />
consumatori secondari, quali pesci e mammiferi<br />
marini. Inoltre, l’alimentazione e le attività metaboliche<br />
dei copepodi contribuiscono al flusso di<br />
materia ed energia lungo la colonna d’acqua.<br />
La classificazione dei copepodi è stata oggetto<br />
di varie revisioni nel corso delle ultime decadi<br />
e numerosi sono stati i cambiamenti rispetto a<br />
quanto riportato nel libro di Rose (1933), tuttora<br />
importante testo di consultazione per chiunque<br />
affronti lo studio tassonomico di questo gruppo.<br />
Una interessante analisi filogenetica è stata pubblicata<br />
da Huys & Boxshall (1991), i quali, sulla<br />
base di accurati studi morfologici, ripercorrono<br />
il cammino evolutivo che ha portato alla straordinaria<br />
diversificazione tassonomica ed ecologica<br />
di questo gruppo. La comparsa dei copepodi<br />
risale presumibilmente al dopo-Precambriano<br />
(Boxshall, 1983; Huys & Boxshall, 1991), ma la<br />
mancanza di fossili impedisce una corretta datazione<br />
cronologica che possa far risalire alla comparsa<br />
dei generi. La colonizzazione dell’ambiente<br />
pelagico da parte dei copepodi calanoidi è probabilmente<br />
databile alla metà del Paleozoico (Bradford-Grieve,<br />
2002).<br />
Il numero totale di circa 11.500 specie di copepodi<br />
è probabilmente sottostimato (Bowman &<br />
Abele, 1982; Humes, 1994). Il numero delle specie<br />
planctoniche marine (circa 2300 conosciute fino<br />
ad oggi) è relativamente modesto rispetto a quello<br />
delle forme parassite e bentoniche.<br />
La sottoclasse Copepoda è rappresentata nel<br />
plancton marino da forme a vita libera appartenenti<br />
a otto dei nove ordini di questo gruppo di<br />
crostacei (Boxshall & Halsey, 2004): Platycopioida,<br />
Calanoida, Mormonilloida, Misophrioida,<br />
Harpacticoida, Cyclopoida, Siphonostomatoida,<br />
Monstrilloida. La scoperta di una nuova famiglia<br />
(Fratiidae) ha profondamente influito sulla<br />
sistematica di questo gruppo, e, di conseguenza,<br />
l’ordine Poecilostomatoida ora non può più essere<br />
considerato come un gruppo filogeneticamente<br />
separato dai Cyclopoida (Boxshall & Halsey,<br />
2004).<br />
Il numero di specie di copepodi planctonici<br />
presenti nei mari italiani che riportiamo nel presente<br />
elenco è molto limitato se confrontato con<br />
Copepods are the most numerous taxonomic<br />
group in marine mesozooplankton communities.<br />
The role of planktonic copepods in the pelagic<br />
ecosystem is essential to the functioning of trophic<br />
webs as they form the link between primary<br />
producers (phytoplankton) and secondary<br />
consumers such as fish and mammals. Moreover,<br />
the feeding and metabolic activities of copepods<br />
contribute to the flow of organic matter and<br />
energy along the water column.<br />
The systematics of Copepoda has been revised<br />
many times in the last few decades, and a number<br />
of changes have been introduced with respect to<br />
Rose’s 1933 book, which is still an important<br />
textbook for planktonic copepod identification.<br />
A very interesting phylogenetic study has been<br />
published by Huys & Boxshall (1991). Based on<br />
very accurate morphological analyses, this book<br />
describes the evolutionary path that has led to the<br />
extraordinary taxonomic and ecological diversity<br />
of copepods. The appearance of copepods dates<br />
back presumably to the post-Precambrian period<br />
(Boxshall, 1983; Huys & Boxshall, 1991), but<br />
the lack of fossils prevents us from dating the<br />
appearance of the genera. The colonization of<br />
the pelagic realm by calanoid copepods probably<br />
dates back to the mid-Paleozoic period (Bradford-<br />
Grieve, 2002).<br />
The total number of about 11,500 species of<br />
Copepoda is probably an underestimate (Bowman<br />
& Abele, 1982; Humes, 1994). The number of<br />
individuals is virtually incalculable. The number<br />
of free-living marine species (approximately 2300<br />
forms known to date) is relatively low compared<br />
to that of parasitic and benthic forms.<br />
The subclass Copepoda is represented in marine<br />
plankton by free-living forms belonging to eight<br />
out of the nine orders of this group of Crustacea<br />
(Boxshall & Halsey, 2004): Platycopioida,<br />
Calanoida, Mormonilloida, Misophrioida,<br />
Harpacticoida, Cyclopoida, Siphonostomatoida,<br />
Monstrilloida. The discovery of a new family<br />
(Fratiidae) has had a major impact on copepod<br />
systematics and, as a consequence, the previously<br />
considered order Poecilostomatoida can no<br />
longer be considered as a group phylogenetically<br />
separated from Cyclopoida (Boxshall & Halsey,<br />
2004).<br />
The number of planktonic copepod species<br />
occurring in the Italian seas referred to in the<br />
present checklist is very limited compared with<br />
the inventory of Marine Planktonic Copepods in
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 421<br />
l’inventario dei Copepodi Planctonici Marini<br />
del Mar Mediterraneo, riportato da C. Razouls,<br />
F. de Bovée e J. Kouwenberg nel sito web<br />
http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en/index.php. La<br />
loro lista comprende tutte le specie elencate a partire<br />
dalla fondamentale monografia di Giesbrecht<br />
(1892 [in realtà “1893”] secondo Holthuis & Vervoort,<br />
2006) fino ad oggi. Tale inventario si basa<br />
sull’analisi di più di cinquemila pubblicazioni, sia<br />
di natura puramente sistematica, sia di carattere<br />
ecologico. È molto probabile che numerose specie<br />
di copepodi riportati nel Mar Mediterraneo, che<br />
non figurano nella nostra lista, siano presenti<br />
anche nei mari italiani.<br />
La nostra lista riporta due specie relitte (Pseudocalanus<br />
elongatus e Temora longicornis) limitate<br />
al Mare Adriatico, e, come recenti ritrovamenti,<br />
Acartia (Acanthacartia) tonsa nell’Adriatico settentrionale,<br />
Paracartia grani in Adriatico e Golfo<br />
di Napoli, e tre specie di Oncaeidae (Triconia<br />
umerus, T. hawii e T. rufa) nel Golfo di Napoli.<br />
Per tutte le altre specie si può ritenere che esse<br />
siano presenti in tutti i nove settori biogeografici<br />
considerati, poichè non esistono, fra tali settori,<br />
barriere evidenti che possano limitare l’espansione<br />
geografica dei copepodi planctonici. Per<br />
questi organismi sono maggiormente significative<br />
le barriere rappresentate dai domini batimetrici,<br />
per cui possono essere distinte specie di acque<br />
superficiali, intermedie, profonde. Inoltre, per<br />
alcune specie le popolazioni si sviluppano solo in<br />
ambienti neritici, mentre per altre la distribuzione<br />
si espande anche in acque di mare aperto al di<br />
là della piattaforma continentale. La loro mancata<br />
segnalazione in alcuni settori è solo dovuta<br />
al fatto che il loro ritrovamento è legato ai corpi<br />
d’acqua esplorati e alle metodiche utilizzate per<br />
il campionamento, che operano una selezione<br />
delle comunità presenti. Ad esempio, pochi sono<br />
gli studi effettuati in acque Italiane su copepodi<br />
planctonici di profondità e pochissimi quelli condotti<br />
sulla frazione dimensionale piccola dello<br />
zooplancton, che viene campionata solo con reti<br />
a maglia più fine (≤70 m) m) rispetto a quella tradizionalmente<br />
utilizzata per il mesozooplancton<br />
(200-250 m). m). Infine, rimane tuttora molto limitato<br />
il numero di pubblicazioni scientifiche sul<br />
mesozooplancton dei mari Italiani che riportino<br />
elenchi dettagliati di specie, ma è auspicabile<br />
un’inversione di tendenza, per la sempre maggior<br />
attenzione rivolta alla biodiversità marina,<br />
soprattutto in relazione agli effetti dei cambiamenti<br />
climatici sugli ecosistemi marini.<br />
La lista è stata compilata sulla base di lavori<br />
scientifici pubblicati e della personale esperienza<br />
nostra e dei colleghi che, in Italia, si occupano<br />
di tassonomia di copepodi marini e che hanno<br />
messo gentilmente a disposizione le loro liste tassonomiche<br />
relative anche a dati non pubblicati.<br />
Ringraziamo per la loro collaborazione: Laura Aguzzi,<br />
Genuario Belmonte, Alessandra Comaschi, Marco Cruscanti,<br />
Alessandra De Olazabal, Iole Di Capua, Serena Fonda-Umani,<br />
Priscilla Licandro, Antonello Mocci, Giacomo Zagami, Tecla<br />
Zunini-Sertorio.<br />
the Mediterranean Sea compiled by C. Razouls,<br />
F.de Bovée and J. Kouwenberg in the web page<br />
http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en/index.php.<br />
Their list includes all the species recorded<br />
starting from Giesbrecht’s fundamental work<br />
(1892 [actually “1893”], after Holthuis & Vervoort,<br />
2006) up to now. That inventory is based on the<br />
analysis of more than five thousand publications,<br />
either of a purely systematic nature, or dealing<br />
with copepod ecology. It is highly probable<br />
that numerous copepod species reported in the<br />
Mediterranean Sea and which do not figure in<br />
our checklist are also present in the Italian seas.<br />
Our checklist mentions two relict species<br />
(Pseudocalanus elongatus and Temora longicornis)<br />
that occur only in the Adriatic Sea, and, as recent<br />
records, Acartia (Acanthacartia) tonsa from the<br />
North Adriatic Sea, Paracartia grani from the<br />
Adriatic and the Gulf of Naples, and three species<br />
of Oncaeidae (Triconia umerus, T. hawii and T.<br />
rufa) from the Gulf of Naples. It can be assumed<br />
that all the other species are present in all nine<br />
bio-geographical sectors under consideration,<br />
since there are no barriers between the sectors<br />
that would limit the expansion of planktonic<br />
copepods. For marine copepods, only depth<br />
horizons represent significant barriers and species<br />
can be divided up into deep-, intermediate-, and<br />
surface-water species. Only in a few cases are<br />
copepods restricted to coastal waters, while for<br />
the vast majority of species that flourish in the<br />
neritic domain distribution also extends to open<br />
waters beyond the continental slope. If species<br />
are not reported in some geographic sectors, this<br />
is only because of the water masses explored and<br />
the sampling methods used (type of tow, net and<br />
mesh size), whereby plankton communities are<br />
selected on the basis of species size and behaviour.<br />
In particular, very few surveys have focused on<br />
deep water zooplankton in Italian seas, and there<br />
is still only a limited number of studies on the<br />
small- sized zooplankton that is collected using<br />
finer mesh (≤70 µm ) nets than those traditionally<br />
deployed for sampling mesozooplankton (200-<br />
250 µm). Moreover, there is a general lack of<br />
scientific publications on mesozooplankton that<br />
provide accurate and detailed lists of species,<br />
but hopefully this tendency will soon be reversed<br />
with renewed attention being paid to marine<br />
biodiversity, especially in relation to the effects<br />
of global climate change on marine ecosystems.<br />
The checklist presented here is based on<br />
information available from scientific publications<br />
and on our own personal work and experience as<br />
well as that of Italian colleagues working on the<br />
taxonomy and ecology of marine copepods who<br />
have made available their taxonomic lists and<br />
also unpublished data.<br />
For their kind collaboration we are very grateful to: Laura<br />
Aguzzi, Genuario Belmonte, Alessandra Comaschi, Marco<br />
Cruscanti, Alessandra De Olazabal, Iole Di Capua, Serena<br />
Fonda-Umani, Priscilla Licandro, Antonello Mocci, Giacomo<br />
Zagami, Tecla Zunini-Sertorio.
422<br />
M.G. Mazzocchi & I. Di Capua<br />
Bibliografia/References<br />
ANDRONOV V.N., 1970. Some problems of taxonomy of the family Paracalanide (Copepoda). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 49 (7):<br />
980-985 (Russian).<br />
BARTHÉLÉMY R.M. 1999. Functional morphology and taxonomic relevance of the female genital structures in Acartiidae<br />
(Copepoda: Calanoida). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK, 79 (5): 857-870.<br />
BERNARD M., 1958. Révision des Calocalanus (Copépodes Calanoida) avec description d’un genre nouveau et deux espèces<br />
nouvelles. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 83: 185-199.<br />
BOXSHALL G.A., 1983. Three new genera of misophrioid copepods from the near-bottom plankton community in the North<br />
Atlantic Ocean. Bullettin of the British Museum (Natural History), 44 (2): 103-124.<br />
BOWMAN T.E & ABELE L.G., 1982. Classification of the recent Crustacea. In: The Biology of Crustacea. Vol. 1. Systematic,<br />
the fossil record, and biogeography. Academic Press: 1-27.<br />
BOXSHALL G.A. & HALSEY S.H., 2004. An Introduction to Copepod Diversity. Part I and II. The Ray Society: 966 pp.<br />
BRADFORD-GRIEVE J.M., 1994. Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda: Megacalanidae, Calanidae, Paracalanidae, Mecynoceridae, Eucalanidae,<br />
Spinocalanidae, Clausocalanidae. New Zealand Oceanographic Institute Memoir, 102: 1-160.<br />
BRADFORD-GRIEVE J.M., 1999. The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: pelagic Calanoid Copepoda: Bathypontiidae, Arietellidae,<br />
Augaptilidae, Heterorhabdidae, Lucicutiidae, Metridinidae, Phyllopodidae, Centropagidae, Pseudodiaptomidae, Temoridae,<br />
Candaciidae, Pontellidae, Sulcanidae, Acartiidae, Tortanidae. NIWA Biodiversity Memoir, 111: 5-268.<br />
BRADFORD-GRIEVE J.M., 2002. Colonization of the pelagic realm by calanoid copepods. Hydrobiologia, 485: 223-244.<br />
BRADFORD-GRIEVE J.M., 2008. Mecynocera clausi I.C. Thompson, 1888 (Copepoda: Calanoida) is a paracalanid. Zootaxa,<br />
1852: 59-64.<br />
GELETIN Y.V., 1976. The ontogenic abdomen formation in copepods of genera Eucalanus and Rhincalanus (Copepoda, Eucalanidae)<br />
and new system of these copepods. Issled. Fauny Morei, 18 (26): 75-93 (Russian).<br />
HERON G.A. & FROST B.W., 2000. Copepods of the family Oncaeidae (Crustacea: Poecilostomatoida) in the northeast Pacific<br />
Ocean and inland coastal waters of Washington State. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 113 (4): 1015-1063.<br />
HIROMI J., 1987. Present knowledge and problems of taxonomy of the family Paracalanidae. Bulletin of the College of Agriculture<br />
and Veterinary Medicine, Nihon University, 44: 147-159.<br />
HOLTHUIS L.B. & VERVOORT W., 2006. The date of publication of Wilheim Giesbrecht’s “Pelagische Copepoden”. In: Fauna<br />
des Golfes von Neapel. Vol. 19. Crustaceana, 79 (3): 371-374.<br />
HUYS R. & BÖTTGER-SCHNACK R., 1996/97. On the diphyletic origin of the Oncaeidae Giesbrecht, 1892 (Copepoda:<br />
Poecilostomatoida) with a phylogenetic analysis of the Lubbockiidae fam. nov. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 235: 243-261.<br />
HUYS R. & BOXSHALL G.A., 1991. Copepod evolution. The Ray Society, London: 468 pp.<br />
HUMES A.G. 1994. How many copepods? In: Ferrari F.D., B.P. Bradley (eds), Ecology and Morphology of Copepods. Hydrobiologia,<br />
292/293: 1-7.<br />
IVANENKO V.N. & DEFAYE D., 2006. Planktonic deep-water copepods of the family Mormonillidae Giesbrecht, 1893 from<br />
the East Pacific Rise (13° N), the north eastern Atlantic and near the North Pole (Copepoda, Mormonillida). Crustaceana, 79<br />
(6): 707-726.<br />
MARKHASEVA E.L., 1996. Calanoid copepods of the family Aetideidae of the World Ocean. Proceedings of the Zoological<br />
Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg: 331 pp.<br />
MATTHEWS J.B.L., 1972. The genus Euaugaptilus (Crustacea, Copepoda). New descriptions and a review of the genus in relation<br />
to Augaptilus, Haloptilus and Pseudaugaptilus. Bull. Brit. Mus. Nat. Hist., Zool., 24 (1): 1-71.<br />
PARK T., 1995. Taxonomy and Distribution of the Marine Calanoid Copepod Family Euchaetidae. University of California Press:<br />
203 pp.<br />
ROSE M., 1933. Copépodes pélagiques. Faune de France, 26: 1-374.<br />
WALTER C.T. & BOXSHALL G.A. World Copepoda database. World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org/<br />
copepoda/. Retrieved December 31, 2009.<br />
(I. Di Capua)
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 423<br />
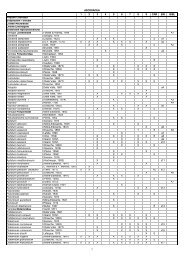
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Classe Maxillopoda<br />
Sottoclasse Copepoda<br />
Infraclasse Neocopepoda<br />
Ordine Calanoida<br />
Famiglia Acartiidae<br />
Acartia 10194 Dana, 1846 A1<br />
Acartia (Acartia) danae 10195 Giesbrecht, 1889 x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acartia) negligens 10196 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acanthacartia) 10197 Steuer, 1915 x x x<br />
Acartia (Acanthacartia)<br />
bifilosa<br />
(Giesbrecht, 1881)<br />
10198<br />
x x x<br />
Acartia (Acanthacartia)<br />
italica<br />
Steuer, 1910<br />
10199<br />
x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acanthacartia)<br />
tonsa<br />
Dana, 1849<br />
10200<br />
x AL<br />
Acartia (Acartiura) 10201 Steuer, 1915<br />
Acartia (Acartiura) clausi 10202 Giesbrecht, 1889 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acartiura)<br />
discaudata<br />
(Giesbrecht, 1881)<br />
10203<br />
x x x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acartiura) enzoi 10204 Crisafi, 1974 x<br />
Acartia (Acartiura)<br />
longiremis<br />
(Lilljeborg, 1853)<br />
10205<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acartiura) margalefi 10206 Alcaraz, 1976 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Acartiura) teclae 10207 Bradford, 1976 x x<br />
Acartia (Hypoacartia) 10208 Steuer, 1915 x x x x x<br />
Acartia (Hypoacartia)<br />
adriatica<br />
Steuer, 1910<br />
10209<br />
x x x x x<br />
Paracartia 10210 Scott T., 1894 A2<br />
Paracartia grani 10211 Sars G.O., 1904 x x x x x x x x AL<br />
Paracartia latisetosa 10212 (Kriczaguin, 1873) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Pteriacartia 10213 Belmonte, 1998<br />
Pteriacartia josephinae 10214 (Crisafi, 1974) x x x x x x x x a1<br />
Famiglia Aetideidae<br />
A3<br />
Aetideopsis 10215 Sars G.O., 1903<br />
Aetideopsis armatus 10216 (Boeck, 1872) x x x x x x x a2<br />
Aetideopsis rostrata 10217 Sars G.O., 1903 x x x x x x x<br />
Aetideus 10218 Brady, 1883<br />
Aetideus armatus 10219 (Boeck, 1872) x x x x x x x x<br />
Aetideus giesbrechti 10220 (Cleve, 1904) x x x x x x x x<br />
Chiridius 10221 Giesbrecht, 1893<br />
Chiridius poppei 10222 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Euchirella 10223 Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
Euchirella bitumida 10224 With, 1915 x x x<br />
Euchirella messinensis 10225 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x a3<br />
Euchirella rostrata 10226 (Claus, 1866) x x x x x x x x a4<br />
Gaetanus 10227 Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
Gaetanus kruppi 10228 Giesbrecht, 1903 x x x x x x x x a5<br />
Gaetanus tenuispinus 10229 (Sars G.O., 1900) x x x x a6<br />
Pseudochirella 10230 Sars G.O., 1920<br />
Pseudochirella obtusa 10231 (Sars G.O., 1905) x x x a7<br />
Famiglia Arietellidae<br />
Arietellus 10232 Giesbrecht, 1893<br />
Arietellus setosus 10233 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Augaptilidae<br />
Augaptilus 10234 Giesbrecht, 1889<br />
Augaptilus longicaudatus 10235 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x a8
424<br />
M.G. Mazzocchi & I. Di Capua<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Augaptilus spinifrons 10236 Sars G.O., 1907 x x x x x x x<br />
Euaugaptilus 10237 Sars G.O., 1920 a9 A4<br />
Euaugaptilus filigerus 10238 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x a10<br />
Euaugaptilus hecticus 10239 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x<br />
Euaugaptilus truncatus 10240 (Sars G.O., 1905) x x x<br />
Haloptilus<br />
Giesbrecht in Giesbrecht &<br />
10241<br />
Schmeil, 1898<br />
a11<br />
Haloptilus acutifrons 10242 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus angusticeps 10243 Sars G.O., 1907 x x x<br />
Haloptilus fertilis 10244 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus longicornis 10245 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus mucronatus 10246 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus ornatus 10247 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus oxycephalus 10248 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus plumosus 10249 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus spiniceps 10250 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus tenuis 10251 Farran, 1908 x x x x x x x<br />
Haloptilus validus 10252 Sars G.O., 1920 x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Bathypontiidae<br />
Temorites 10253 Sars G.O., 1900<br />
Temorites brevis 10254 Sars G.O., 1900 x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Calanidae<br />
Calanus 10255 Leach, 1816<br />
Calanus helgolandicus 10256 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Mesocalanus 10257 Bradford & Jillet, 1974<br />
Mesocalanus tenuicornis 10258 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Nannocalanus 10259 Sars G.O., 1925<br />
Nannocalanus minor 10260 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Neocalanus 10261 Sars G.O., 1925<br />
Neocalanus gracilis 10262 (Dana, 1852) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Neocalanus robustior 10263 (Giesbrecht, 1888) x<br />
Famiglia Candaciidae<br />
Candacia 10264 Dana, 1846<br />
Candacia aethiopica 10265 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia armata 10266 Boeck, 1872 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia bipinnata 10267 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia elongata 10268 (Boeck, 1872) x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia giesbrechti 10269 Grice & Lawson, 1977 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia longimana 10270 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia tenuimana 10271 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia varicans 10272 (Giesbrecht, 1892) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia bispinosa 10273 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Candacia simplex 10274 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Centropagidae<br />
Centropages 10275 Kröyer, 1849<br />
Centropages bradyi 10276 Wheeler, 1901 x<br />
Centropages chierchiae 10277 Giesbrecht, 1889 x x<br />
Centropages hamatus 10278 (Lilljeborg, 1853) x x x<br />
Centropages kröyeri 10279 Giesbrecht, 1892 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Centropages ponticus 10280 Karavaev, 1895 x x x x x x x x<br />
Centropages typicus 10281 Kröyer, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Centropages violaceus 10282 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Isias 10283 Boeck, 1865<br />
Isias clavipes 10284 Boeck, 1865 x x x x x x x x
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 425<br />
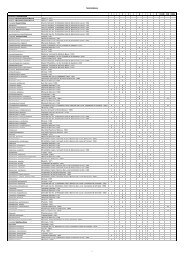
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Famiglia Clausocalanidae x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus 10285 Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
Clausocalanus arcuicornis 10286 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus furcatus 10287 (Brady, 1883) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus jobei 10288 Frost & Fleminger, 1968 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus lividus 10289 Frost & Fleminger, 1968 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus mastigophorus 10290 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus parapergens 10291 Frost & Fleminger, 1968 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus paululus 10292 Farran, 1926 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Clausocalanus pergens 10293 Farran, 1926 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Ctenocalanus 10294 Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
Ctenocalanus vanus 10295 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Microcalanus 10296 Sars G.O., 1903<br />
Microcalanus pygmaeus 10297 (Sars G.O., 1900) x x x x x x x x<br />
Pseudocalanus 10298 Boeck, 1872<br />
Pseudocalanus elongatus 10299 (Boeck, 1865) x x x<br />
Famiglia Diaixidae<br />
Diaixis 10300 Sars G.O., 1902<br />
Diaixis pygmaea 10301 (Scott T., 1894) x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Discoidae<br />
Disco 10302 Grice & Hulsemann, 1965<br />
Disco minutus 10303 Grice & Hulsemann, 1965 x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Eucalanidae<br />
A5<br />
Eucalanus 10304 Dana, 1852<br />
Eucalanus elongatus 10305 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Pareucalanus 10306 Geletin, 1976<br />
Pareucalanus attenuatus 10307 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x a12<br />
Rhincalanus 10308 Dana, 1853<br />
Rhincalanus cornutus 10309 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x<br />
Rhincalanus nasutus 10310 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x x x<br />
Subeucalanus 10311 Geletin, 1976<br />
Subeucalanus crassus 10312 (Giesbrecht, 1888) x x x x x x x x x a13<br />
Subeucalanus monachus 10313 (Giesbrecht, 1888) x x x x x x x x x a14<br />
Famiglia Euchaetidae<br />
A6<br />
Euchaeta 10314 Philippi, 1843<br />
Euchaeta acuta 10315 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x x a15<br />
Euchaeta marina 10316 (Prestandrea, 1833) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Euchaeta spinosa 10317 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x a16<br />
Paraeuchaeta 10318 Scott A., 1909<br />
Paraeuchaeta bisinuata 10319 (Sars G.O., 1907) x x x<br />
Paraeuchaeta hansenii 10320 (With, 1915) x x x<br />
Paraeuchaeta hebes 10321 (Giesbrecht, 1888) x x x x x x x x<br />
Paraeuchaeta sarsi 10322 (Farran, 1908) x x x<br />
Famiglia Heterorhabdidae<br />
Heterorhabdus<br />
Giesbrecht in Giesbrecht &<br />
10323<br />
Schmeil, 1898<br />
Heterorhabdus abyssalis 10324 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x<br />
Heterorhabdus clausi 10325 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x<br />
Heterorhabdus papilliger 10326 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Heterorhabdus spinifrons 10327 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Lucicutiidae<br />
Lucicutia<br />
Giesbrecht in Giesbrecht &<br />
10328<br />
Schmeil, 1898<br />
Lucicutia clausi 10329 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x a17
426<br />
M.G. Mazzocchi & I. Di Capua<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Lucicutia curta 10330 Farran, 1904 x x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia flavicornis 10331 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia gaussae 10332 Grice, 1963 x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia gemina 10333 Farran, 1926 x x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia grandis 10334 (Giesbrecht, 1895) x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia longiserrata 10335 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia lucida 10336 Farran, 1909 x<br />
Lucicutia ovalis 10337 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia pera 10338 Scott A., 1909 x x x x x x x<br />
Lucicutia simulans 10339 Sars G.O., 1920 x<br />
Famiglia Mecynoceridae<br />
Mecynocera 10340 Thompson I.C., 1888 A7<br />
Mecynocera clausi 10341 Thompson I.C., 1888 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Mecynocera tenuis 10342 (Farran, 1926) x x x x x x x x a18 A8<br />
Famiglia Megacalanidae<br />
Megacalanus 10343 Wolfenden, 1904<br />
Megacalanus longicornis 10344 (Sars G.O., 1905) x x x<br />
Famiglia Metridinidae<br />
Metridia 10345 Boeck, 1865<br />
Metridia princeps 10346 Giesbrecht, 1889 x x x<br />
Pleuromamma<br />
10347<br />
Giesbrecht in Giesbrecht &<br />
Schmeil, 1898<br />
Pleuromamma abdominalis 10348 (Lubbock, 1856) x x x x x x x x<br />
Pleuromamma borealis 10349 (Dahl F., 1893) x x x x<br />
Pleuromamma gracilis 10350 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x<br />
Pleuromamma piseki 10351 Farran, 1929 x x x x x x x x<br />
Pleuromamma robusta 10352 (Dahl F., 1893) x x x x x x x x<br />
Pleuromamma xiphias 10353 (Giesbrecht, 1889) x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Paracalanidae<br />
Calocalanus 10354 Giesbrecht, 1888 A9<br />
Calocalanus adriaticus 10355 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus contractus 10356 Farran, 1926 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus elegans 10357 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus longisetosus 10358 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus neptunus 10359 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus ovalis 10360 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus pavo 10361 (Dana, 1852) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus pavoninus 10362 Farran, 1936 x x x<br />
Calocalanus plumatus 10363 Shmeleva, 1965 x x x x x<br />
Calocalanus plumulosus 10364 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x a19<br />
Calocalanus styliremis 10365 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Paracalanus 10366 Boeck, 1864<br />
Paracalanus aculeatus 10367 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x<br />
Paracalanus denudatus 10368 Sewell, 1929 x x x x x x x x<br />
Paracalanus nanus 10369 Sars G.O., 1925 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Paracalanus parvus 10370 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Parapontellidae<br />
Parapontella 10371 Brady, 1878<br />
Parapontella brevicornis 10372 (Lubbock, 1857) x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Phaennidae<br />
Onchocalanus 10373 Sars G.O., 1905<br />
Onchocalanus trigoniceps 10374 Sars G.O., 1905 x x x x x x x<br />
Phaenna 10375 Claus, 1863<br />
Phaenna spinifera 10376 Claus, 1863 x x x x x x x
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 427<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Xanthocalanus 10377 Giesbrecht, 1893<br />
Xanthocalanus agilis 10378 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x<br />
Xanthocalanus minor 10379 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x<br />
Famiglia Pontellidae<br />
Anomalocera 10380 Templeton, 1837<br />
Anomalocera patersoni 10381 Templeton, 1837 x x x x x x x x<br />
Labidocera 10382 Lubbock, 1853<br />
Labidocera brunescens 10383 (Czerniavsky, 1868) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Labidocera wollastoni 10384 (Lubbock, 1857) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Pontella 10385 Dana, 1846<br />
Pontella atlantica 10386 (Milne Edwards, 1840) x x x<br />
Pontella lobiancoi 10387 (Canu, 1888) x x x x x x x<br />
Pontella mediterranea 10388 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Pontellina 10389 Dana, 1853<br />
Pontellina plumata 10390 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x<br />
Pontellopsis 10391 Brady, 1883<br />
Pontellopsis regalis 10392 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x<br />
Pontellopsis villosa 10393 Brady, 1883 x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Scolecitrichidae<br />
A10<br />
Archescolecithrix<br />
Vyshkvartzeva in Vyskvartzeva,<br />
10394<br />
1989<br />
Archescolecithrix auropecten 10395 (Giesbrecht, 1892) x x x x x x x a20<br />
Amallothrix 10396 Sars G.O., 1925<br />
Amallothrix tenuiserrata 10397 (Giesbrecht, 1892) x x x x x x x<br />
Falsilandrumius 10398 Vyshkvartzeva, 2001<br />
Falsilandrumius lobatus 10399 (Sars G.O., 1920) x x x a21<br />
Scaphocalanus 10400 Sars G.O., 1900<br />
Scaphocalanus curtus 10401 (Farran, 1926) x x x x x x x<br />
Scaphocalanus invalidus 10402 Hure & Scotto di Carlo, 1968 x x x x x x x<br />
Scaphocalanus similis 10403 Hure & Scotto di Carlo, 1968 x x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithricella 10404 Sars G.O., 1902<br />
Scolecithricella abyssalis 10405 (Giesbrecht, 1888) x x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithricella dentata 10406 (Giesbrecht, 1892) x x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithricella ovata 10407 (Farran, 1905) x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithricella vittata 10408 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithrix 10409 Brady, 1883<br />
Scolecithrix bradyi 10410 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x x x x<br />
Scolecithrix danae 10411 (Lubbock, 1856) x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Spinocalanidae<br />
Mimocalanus 10412 Farran, 1908<br />
Mimocalanus cultrifer 10413 Farran, 1908 x x x x x x<br />
Mimocalanus heronae 10414 Damkaer, 1975 x x x x x x x<br />
Monacilla 10415 Sars G.O., 1905<br />
Monacilla typica 10416 Sars G.O., 1905 x x x x x x x x<br />
Spinocalanus 10417 Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
Spinocalanus abyssalis 10418 Giesbrecht, 1888 x x x x x x x<br />
Spinocalanus longicornis 10419 Sars G.O., 1900 x x x x x x x<br />
Spinocalanus magnus 10420 Wolfenden, 1904 x x x x x x x<br />
Spinocalanus oligospinosus 10421 Park, 1970 x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Stephidae<br />
A11<br />
Stephos 10422 Scott T., 1892<br />
Stephos cryptospinosus<br />
Zagami, Campolmi &<br />
10423<br />
Costanzo, 2000<br />
x<br />
Stephos gyrans 10424 (Giesbrecht, 1893) x
428<br />
M.G. Mazzocchi & I. Di Capua<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Stephos marsalensis<br />
Zagami, Campolmi &<br />
10425<br />
Costanzo, 2000<br />
x<br />
Famiglia Temoridae<br />
Temora 10426 Baird, 1850<br />
Temora longicornis 10427 (Müller, 1792) x x x x<br />
Temora stylifera 10428 (Dana, 1849) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Temoropia 10429 Scott T., 1894<br />
Temoropia mayumbaensis 10430 Scott T., 1894 x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Tharybidae<br />
Undinella 10431 Sars G.O., 1900<br />
Undinella stirni 10432 Grice, 1971 x x x<br />
Ordine Cyclopoida<br />
Famiglia Corycaeidae<br />
A12<br />
Corycaeus 10433 Dana, 1845<br />
Corycaeus (Ditrichocorycaeus)<br />
Lubbock, 1857<br />
anglicus 10434<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Ditrichocorycaeus)<br />
Steuer, 1910<br />
brehmi 10435<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Corycaeus) clausi 10436 Dahl F., 1894 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Agetus) flaccus 10437 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Urocorycaeus)<br />
furcifer<br />
Claus, 1863<br />
10438<br />
x x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Onychocorycaeus)<br />
Dahl F., 1894<br />
giesbrechti 10439<br />
x x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Onychocorycaeus)<br />
Dana, 1849<br />
latus 10440<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Agetus) limbatus 10441 Brady, 1883 x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Onychocorycaeus)<br />
Claus, 1863<br />
ovalis 10442<br />
x x x x x x x x x<br />
Corycaeus (Agetus) typicus 10443 Kröyer, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Farranula 10444 Wilson C.B., 1932 a22<br />
Farranula carinata 10445 (Giesbrecht, 1891) x a23<br />
Farranula rostrata 10446 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x a24<br />
Famiglia Lubbockiidae<br />
A13<br />
Lubbockia 10447 Claus, 1863<br />
Lubbockia aculeata 10448 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Lubbockia squillimana 10449 Claus, 1863 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Oithonidae<br />
Oithona 10450 Baird, 1843<br />
Oithona atlantica 10451 Farran, 1908 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona brevicornis 10452 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona decipiens 10453 Farran, 1913 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona hebes 10454 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona linearis 10455 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona longispina<br />
Nishida, Tanaka & Omori,<br />
10456<br />
1977<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona nana 10457 Giesbrecht, 1892 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona plumifera 10458 Baird, 1843 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona setigera 10459 Dana, 1852 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona similis 10460 Claus, 1866 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona tenuis 10461 Rosendorn, 1917 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oithona vivida 10462 Farran, 1913 x x x x x x x x<br />
Paroithona 10463 Farran, 1908 a25<br />
Paroithona parvula 10464 Farran, 1908 x x x x<br />
Famiglia Oncaeidae<br />
A14<br />
Conaea 10465 Giesbrecht, 1891
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 429<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Conaea rapax 10466 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Monothula 10467 Böttger-Schnack, 2001<br />
Monothula subtilis 10468 (Giesbrecht, 1893 ["1892"]) x x x x x x x x a26 A15<br />
Oncaea 10469 Philippi, 1843<br />
Oncaea curta 10470 Sars G.O., 1916 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea media 10471 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea mediterranea 10472 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea notopus 10473 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea ornata 10474 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea scottodicarloi<br />
Heron & Bradford-Grieve,<br />
10475<br />
1995<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
Oncaea venusta 10476 Philippi, 1843 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Triconia 10477 Böttger-Schnack, 1999 A16<br />
Triconia conifera 10478 (Giesbrecht, 1891) x x x x x x x x x a27<br />
Triconia dentipes 10479 (Giesbrecht, 1891) x x x x x x x x a28<br />
Triconia hawii<br />
(Böttger-Schnack & Boxshall,<br />
10480<br />
1990)<br />
x<br />
AL<br />
Triconia minuta 10481 (Giesbrecht, 1893 ["1892"]) x x x x x x x x x a29<br />
Triconia rufa 10482 (Boxshall & Böttger, 1987) x AL<br />
Triconia similis 10483 (Sars G.O., 1918) x x x x x x x x a30<br />
Triconia umerus<br />
10484<br />
(Böttger-Schnack & Boxshall,<br />
1990)<br />
Famiglia Ozmanidae<br />
Pachos 10485 Stebbing, 1910 A17<br />
Pachos punctatum 10486 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Sapphirinidae<br />
Copilia 10487 Dana, 1849<br />
Copilia denticulata 10488 Claus, 1863 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Copilia mediterranea 10489 (Claus, 1863) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Copilia quadrata 10490 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x<br />
Copilia vitrea 10491 (Haeckel, 1864) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina 10492 Thompson, 1830<br />
Sapphirina angusta 10493 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina auronitens 10494 Claus, 1863 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina bicuspidata 10495 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina darwinii 10496 Haeckel, 1864 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina gemma 10497 Dana, 1852 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina intestinata 10498 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina iris 10499 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina lactens 10500 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina maculosa 10501 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina metallina 10502 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina nigromaculata 10503 Claus, 1863 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina opalina 10504 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina ovatolanceolata 10505 Dana, 1849 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina pyrosomatis 10506 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina sali 10507 Farran, 1929 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina scarlata 10508 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina sinuicauda 10509 Brady, 1883 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Sapphirina vorax 10510 Giesbrecht, 1891 x x x x x x x x x<br />
Vettoria 10511 Wilson C.B., 1924<br />
Vettoria granulosa 10512 (Giesbrecht, 1891) x x x x x x x x<br />
Vettoria longifurca 10513 (Rose & Vaissière, 1952) x x x x x x x x<br />
Vettoria parva 10514 (Farran, 1936) x x x x x x x x<br />
x<br />
AL
430<br />
M.G. Mazzocchi & I. Di Capua<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CAR SIN NOTE<br />
Ordine Harpacticoida<br />
Famiglia Clytemnestridae<br />
Clytemnestra 10515 Dana, 1848<br />
Clytemnestra rostrata 10516 (Brady, 1883) x x x x x x x x<br />
Clytemnestra scutellata 10517 Dana, 1849 x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Ectinosomatidae<br />
Microsetella 10518 Brady & Robertson, 1873<br />
Microsetella norvegica 10519 (Boeck, 1865) x x x x x x x x<br />
Microsetella rosea 10520 (Dana, 1848) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Miraciidae<br />
Macrosetella 10521 Scott A., 1909<br />
Macrosetella gracilis 10522 (Dana, 1847) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Macrosetella oculata 10523 (Sars G.O., 1916) x<br />
Famiglia Euterpinidae<br />
A18<br />
Euterpina 10524 Norman, 1903<br />
Euterpina acutifrons 10525 (Dana, 1847) x x x x x x x x x<br />
Ordine Mormonilloida<br />
Famiglia Mormonillidae<br />
Neomormonilla 10526 Ivanenko & Defaye, 2006 A19<br />
Neomormonilla minor 10527 (Giesbrecht, 1891) x x x x x x x a31<br />
Ordine Siphonostomatoida<br />
Famiglia Pontoeciellidae<br />
Pontoeciella 10528 Giesbrecht, 1895<br />
Pontoeciella abyssicola 10529 (Scott T., 1894) x x x x x x x<br />
Famiglia Rataniidae<br />
Ratania 10530 Giesbrecht, 1893<br />
Ratania flava 10531 Giesbrecht, 1893 x x x x x x x x<br />
Sinonimi<br />
a1: sinonimo Acartia josephinae (Crisafi, 1974)<br />
a2: sinonimo Pseudaetideus armatus Wolfenden, 1904; Chiridius<br />
armatus Sars, 1901<br />
a3: sinonimo Undina messinensis Claus, 1863<br />
a4: sinonimo Undina rostrata Claus, 1866<br />
a5: sinonimo Gaetanus kruppii Giesbrecht, 1903<br />
a6: sinonimo Gaidius tenuispinus Brodsky, 1950<br />
a7: sinonimo Chirundina abyssalis With, 1915; Undeuchaeta<br />
obtusa Sars G.O., 1905<br />
a8: sinonimo Hemicalanus longicaudatus Claus, 1863<br />
a9: sinonimo Augaptilus Giesbrecht, 1889<br />
a10: sinonimo Augaptilus filiger (Claus, 1863)<br />
a11: sinonimo Hemicalanus Dana, 1852<br />
a12: sinonimo Eucalanus attenuatus (Dana, 1849)<br />
a13: sinonimo Eucalanus crassus Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
a14: sinonimo Eucalanus monachus Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
a15: sinonimo Paraeuchaeta acuta Bradford et al., 1983<br />
a16: sinonimo Paraeuchaeta spinosa Bradford et al., 1983<br />
a17: sinonimo Leuckartia clausi Giesbrecht, 1889<br />
a18: sinonimo Calocalanus tenuis Farran, 1926<br />
a19: sinonimo Ischnocalanus plumulosus (Claus, 1863)<br />
a20: sinonimo Amallothrix auropecten (Giesbrecht, 1893)<br />
a21: sinonimo Amallothrix lobata (Sars G.O., 1920)<br />
a22: sinonimo Corycella Farran, 1911<br />
a23: sininimo Corycella carinata Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a24: sininimo Corycella rostrata Claus, 1863<br />
a25: sinonimo Oithona Baird, 1843 secondo Boxshall &<br />
Hasley, 2004<br />
a26: sinonimo Oncaea subtilis (Giesbrecht, 1893 ["1892"])<br />
Synonyms<br />
a1: synonym Acartia josephinae (Crisafi, 1974)<br />
a2: synonym Pseudaetideus armatus Wolfenden, 1904;<br />
Chiridius armatus Sars, 1901<br />
a3: synonym Undina messinensis Claus, 1863<br />
a4: synonym Undina rostrata Claus, 1866<br />
a5: synonym Gaetanus kruppii Giesbrecht, 1903<br />
a6: synonym Gaidius tenuispinus Brodsky, 1950<br />
a7: synonym Chirundina abyssalis With, 1915; Undeuchaeta<br />
obtusa Sars G.O., 1905<br />
a8: synonym Hemicalanus longicaudatus Claus, 1863<br />
a9: synonym Augaptilus Giesbrecht, 1889<br />
a10: synonym Augaptilus filiger (Claus, 1863)<br />
a11: synonym Hemicalanus Dana, 1852<br />
a12: synonym Eucalanus attenuatus (Dana, 1849)<br />
a13: synonym Eucalanus crassus Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
a14: synonym Eucalanus monachus Giesbrecht, 1888<br />
a15: synonym Paraeuchaeta acuta Bradford et al., 1983<br />
a16: synonym Paraeuchaeta spinosa Bradford et al., 1983<br />
a17: synonym Leuckartia clausi Giesbrecht, 1889<br />
a18: synonym Calocalanus tenuis Farran, 1926<br />
a19: synonym Ischnocalanus plumulosus (Claus, 1863)<br />
a20: synonym Amallothrix auropecten (Giesbrecht, 1893)<br />
a21: synonym Amallothrix lobata (Sars G.O., 1920)<br />
a22: synonym Corycella Farran, 1911<br />
a23: synonym Corycella carinata Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a24: synonym Corycella rostrata Claus, 1863<br />
a25: synonym Oithona Baird, 1843 according to Boxshall &<br />
Hasley, 2004<br />
a26: synonym Oncaea subtilis (Giesbrecht, 1893 ["1892"])
Copepodi planctonici / Planktonic Copepods 431<br />
a27: sinonimo Oncaea conifera Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a28: sinonimo Oncaea dentipes Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a29: sinonimo Oncaea minuta Giesbrecht, 1892<br />
a30: sinonimo Oncaea similis Sars, 1918<br />
a31: sinonimo Mormonilla minor Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a27: synonym Oncaea conifera Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a28: synonym Oncaea dentipes Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
a29: synonym Oncaea minuta Giesbrecht, 1892<br />
a30: synonym Oncaea similis Sars, 1918<br />
a31: synonym Mormonilla minor Giesbrecht, 1891<br />
Note<br />
A1: il genere è stato diviso in 6 sotto-generi: Acartia (Planktacartia),<br />
Acanthacartia, Acartiura, Euacartia, Hypoacartia,<br />
Odontacartia, questa divisione non è accettata da Barthélémy<br />
(1999) e Boxshall & Halsey (2004)<br />
A2: il genere non è ancora accettato da molti autori<br />
A3: per Markhaseva (1996) questa famiglia comprende solo<br />
26 generi, è stata seguita la sua revisione<br />
A4: Bradford-Grieve (1999) segue le considerazioni di Matthews<br />
(1972) sulle sinonime di questo genere. Questo<br />
genere è essenzialmente batipelagico<br />
A5: per la famiglia Eucalanidae è stata seguita la revisione<br />
di Geletin (1976), come riportato da Boxshall & Halsey<br />
(2004)<br />
A6: per la famiglia Euchaetidae è stata seguita la revisione<br />
di Park (1995)<br />
A7: il genere Mecynocera viene qui posizionato nella famiglia<br />
Mecynoceriidae secondo quanto riportato da Boxshall &<br />
Halsey (2004). È da segnalare che recentemete è stato<br />
posizionato nei Paracalanidae da Bradford-Grieve, 2008<br />
A8: per questa specie è stata seguita la classificazione riportata da<br />
Walter & Boxshall (2008) nel World of Copepods database.<br />
Disponibile in http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda<br />
A9: il genere Calocalanus, precedentemente allocato nella<br />
famiglia Calocalanidae, è attualmenete incluso nella<br />
famiglia Paracalanidae (Boxshall & Halsey, 2004)<br />
A10: Bowman & Abele (1982) hanno corretto lo spelling di<br />
Scolecithricidae in Scolecitrichidae<br />
A11: si tratta di copepodi riportati come iperbentonici in<br />
acque costiere<br />
A12: Boxshall & Halsey (2004) considerano sei sub-generi:<br />
Agetus, Corycaeus, Ditrichocorycaeus, Monocorycaeus,<br />
Onychocorycaeus, Urocorycaeusas. Il genere Corycaeus<br />
necessita di una revisione filogenetica<br />
A13: la famiglia Lubbockiidae è stata istituita da Huys &<br />
Böttger-Schnack nel 1996/97<br />
A14: attualmente sono riportati sette generi: Archioncaea,<br />
Conaea, Epicalymma, Monothula, Oncaea, Spinoncaea,<br />
Triconia<br />
A15: l’anno di pubblicazione della monografia di W. Giesbrecht<br />
sui copepodi pelagici del Golfo di Napoli deve<br />
essere citato come Giesbrecht 1893 ["1892"] (G.A.<br />
Boxshall, comunicazione personale, 2005; Holthuis &<br />
Vervoort, 2006). La data effettiva di pubblicazione<br />
(1893) è diversa da quella indicata nella monografia<br />
stessa (1892). Ai sensi dell'articolo 22A.2.3. del Codice<br />
Internazionale di Nomenclatura Zoologica, si raccomanda<br />
di citare entrambe le date (per ulteriori dettagli, si<br />
veda la nota di Ruth Böttger-Schnack relativa alla famiglia<br />
Oncaeidae nel database World Register of Marine<br />
Species nel sito http://www.marinespecies.org/)<br />
A16: Boxshall & Halsey (2004) riconoscono il genere Triconia,<br />
nonostante le argomentazioni riportate da Heron &<br />
Frost (2000)<br />
A17: per la sistemazione del genere Pachos abbiamo seguito<br />
Boxshall & Halsey (2004). Per vari autori questo genere<br />
resta tuttora di incerta collocazione<br />
A18: la famiglia Euterpinidae Brian, 1921 è stata qui considerata<br />
come in Boxshall & Halsey (2004)<br />
A19: Ivanenko & Defaye (2006) hanno introdotto questo<br />
nuovo genere sulla base del carattere del P1 della<br />
femmina con 3-segmenti dell'endopodite<br />
Remarks<br />
A1: the genus divides into 6 sub-genera: Acartia<br />
(Planktacartia), Acanthacartia, Acartiura, Euacartia,<br />
Hypoacartia, Odontacartia, this division is not accepted<br />
by Barthélémy (1999) or by Boxshall & Halsey (2004)<br />
A2: the genus is not yet accepted by all the authors<br />
A3: for Markhaseva (1996) this family comprises only 26<br />
genera. We have followed her revision<br />
A4: Bradford-Grieve (1999 ) follows the position of Matthews<br />
(1972) concerning the synonymy of this genus. This<br />
genus is essentially bathypelagic.<br />
A5: for the Eucalanidae family we have followed the revision<br />
proposed by Geletin (1976), as also repoted by Boxshall<br />
& Halsey (2004)<br />
A6: for the Euchaetidae family we have followed the revision<br />
proposed by Park (1995)<br />
A7: we have included the genus Mecynocera in<br />
Mecynoceriidae, following Boxshall & Halsey (2004).<br />
The genus has recently been moved to Paracalanidae by<br />
Bradford-Grieve 2008<br />
A8: this species has been named according to Walter & Boxshall<br />
(2008) in the World of Copepods database. Available<br />
online at http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda<br />
A9: the genus Calocalanus, previously assigned to the<br />
Calocalanidae family, is now included in Paracalanidae<br />
(Boxshall & Halsey, 2004)<br />
A10: Bowman & Abele (1982) correct the spelling of<br />
Scolecithricidae now Scolecitrichidae<br />
A11: the copepods belonging to thi genus are reported as<br />
hyperbenthic in coastal waters<br />
A12: Boxshall & Halsey (2004) considered six sub-genera:<br />
Agetus, Corycaeus, Ditrichocorycaeus, Monocorycaeus,<br />
Onychocorycaeus, Urocorycaeusas. The genus Corycaeus<br />
needes a phylogenetic revision<br />
A13: the Lubbockiidae family was instituted by Huys &<br />
Böttger-Schnack in 1996/97<br />
A14: at present the family includes seven genera: Archioncaea,<br />
Conaea, Epicalymma, Monothula, Oncaea, Spinoncaea,<br />
Triconia<br />
A15: the publication year of Giesbrecht´s monograph on the<br />
pelagic copepods of the Gulf of Naples as to be cited as<br />
1893 ["1892"] (G.A. Boxshall pers. comm., 2005; Holthuis<br />
& Vervoort, 2006). Article 22.AS.2.3. of the International<br />
Code of Zoological Nomenclature recommends citing<br />
both dates with the actual date cited first, followed by the<br />
imprint date for information and enclosed in parentheses<br />
or other brackets and quotation marks (for details, see<br />
Ruth Böttger-Schnack’s notes on the Oncaeidae family<br />
in the World Register of Marine Species database on the<br />
web site http://www.marinespecies.org/)<br />
A16: Boxshall & Halsey (2004) acknowledged the genus<br />
Triconia, although it had been questioned by Heron &<br />
Frost (2000)<br />
A17: the genus Pachos as been assigned following the<br />
suggestion of Boxshall & Halsey (2004). This genus is<br />
given as incertae sedis by many authors<br />
A18: for Euterpinidae Brian, 1921 we have followed Boxshall<br />
& Halsey (2004)<br />
A19: Ivanenko & Defaye (2006) created this new genus based on<br />
the characteristic of female P1 with 3 segmented endopodids