. Radiography and radio-therapeutics . ssure of Rolando, and below the base hue with theposterior margin of the ascending ramus of the lower jaw. The perpendicular at the two-thirds distance bisects the parietal lobeof the brain. These three lines divide the head into four regions which may be calledA, B, C, D, from before backwards. Region A contains the anterior fossa of the skull with the anterior halfof the frontal lobe, the orbits and the facial bones with the exception of theascending rami of the lower jaws and the palate bones. Region B contains the body of the sphenoid and the greater
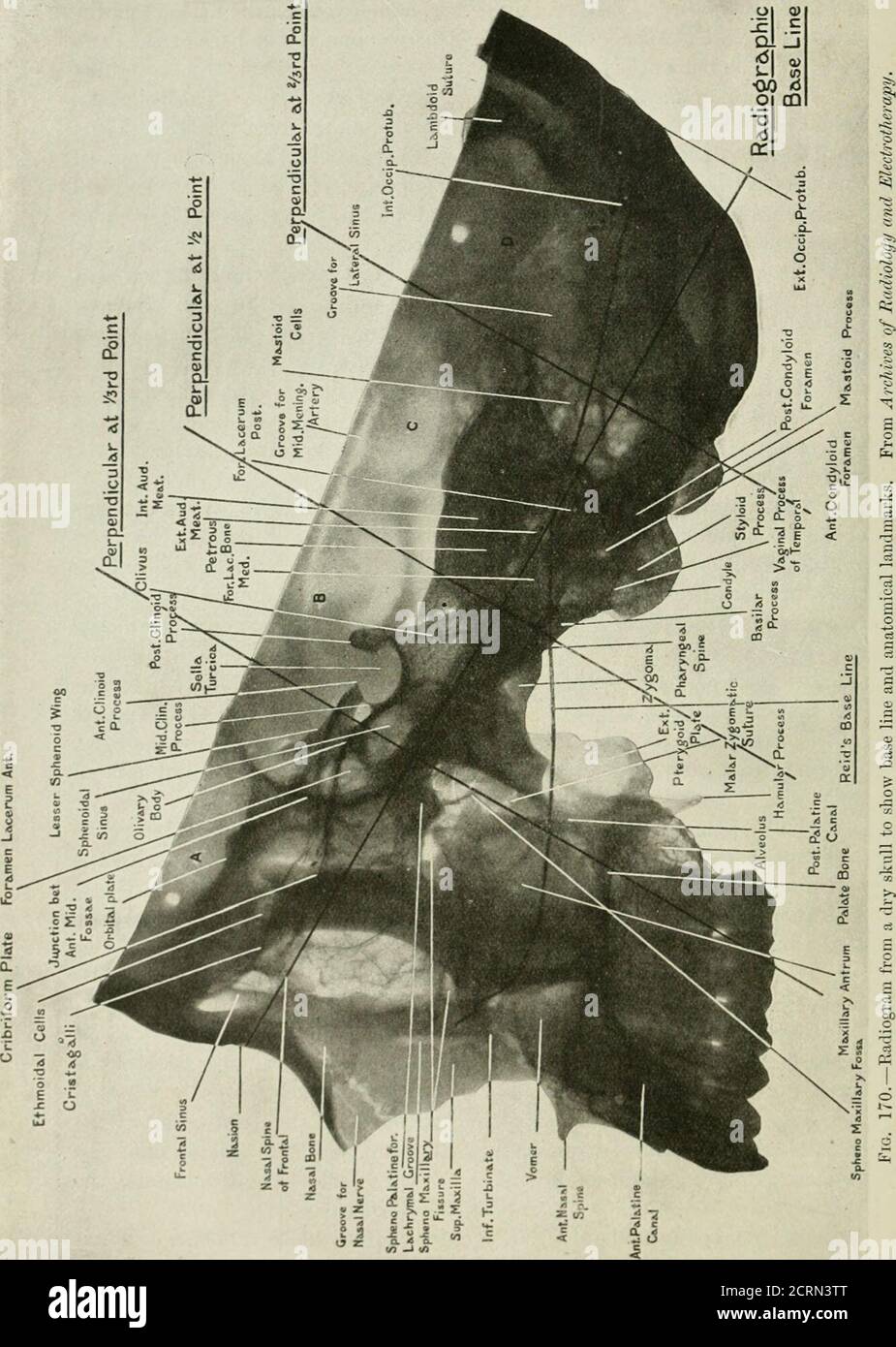
Image details
Contributor:
Reading Room 2020 / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2CRN3TTFile size:
7.2 MB (380.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1334 x 1874 px | 22.6 x 31.7 cm | 8.9 x 12.5 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Radiography and radio-therapeutics . ssure of Rolando, and below the base hue with theposterior margin of the ascending ramus of the lower jaw. The perpendicular at the two-thirds distance bisects the parietal lobeof the brain. These three lines divide the head into four regions which may be calledA, B, C, D, from before backwards. Region A contains the anterior fossa of the skull with the anterior halfof the frontal lobe, the orbits and the facial bones with the exception of theascending rami of the lower jaws and the palate bones. Region B contains the body of the sphenoid and the greater part of thesphenoidal sinus, the sella turcica and pituitary body, the palate bones andascending rami of the lower jaw, the posterior haK of the frontal and theanterior part of the temporo-sphenoidal lobe of the brain. Region C contains the mastoid process, petrous temporal bone, occipitalcondyles, anterior half of the parietal and posterior part of temporal lobesof the cerebrum, the pons, medulla, and anterior part of the cerebellum.. 200 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE SKULL 201 Region D contains the horizontal portion of the lateral sinus, the occipitallobe and posterior half of the parietal lobe of the cerebrum, and the posteriorpart of the cerebellum. As an illustration of the use of the system: To radiograph thesphenoidal sinus laterally. The system shows that the base line runsthrough the sinus, and that it is situated between the intersecting linesat the one-third and one-half distance. The tube is therefore arrangedso that its central rays pass through the base line and between the inter-secting lines. The technique necessary in this system of measurement need be onlybriefly indicated. The patient may be radiographed with the head in either the vertical orhorizontal position, in other words the sagittal suture should be parallelto the plate, a pointof importance in orderthat a region localisedon one side of the skullmay exactly correspondwith the similar regionon the other side; fo