. Biology of the vertebrates : a comparative study of man and his animal allies. Vertebrates; Vertebrates -- Anatomy; Anatomy, Comparative. Centrum of Axis Fig. 440. The human atlas and axis, ventral view. (After Sobotta and McMurrich.) There are four known exceptions to this rule of seven: the three-toed sloth, Brady pus, has nine cervical vertebrae; the ant-bear, Tamandua, eight; while the two-toed sloth, Choloepus, and the American sea cow, Trichechus, each has six. As in reptiles and birds, the first two cervical vertebrae of mammals are further specialized into the so-called atlas and the
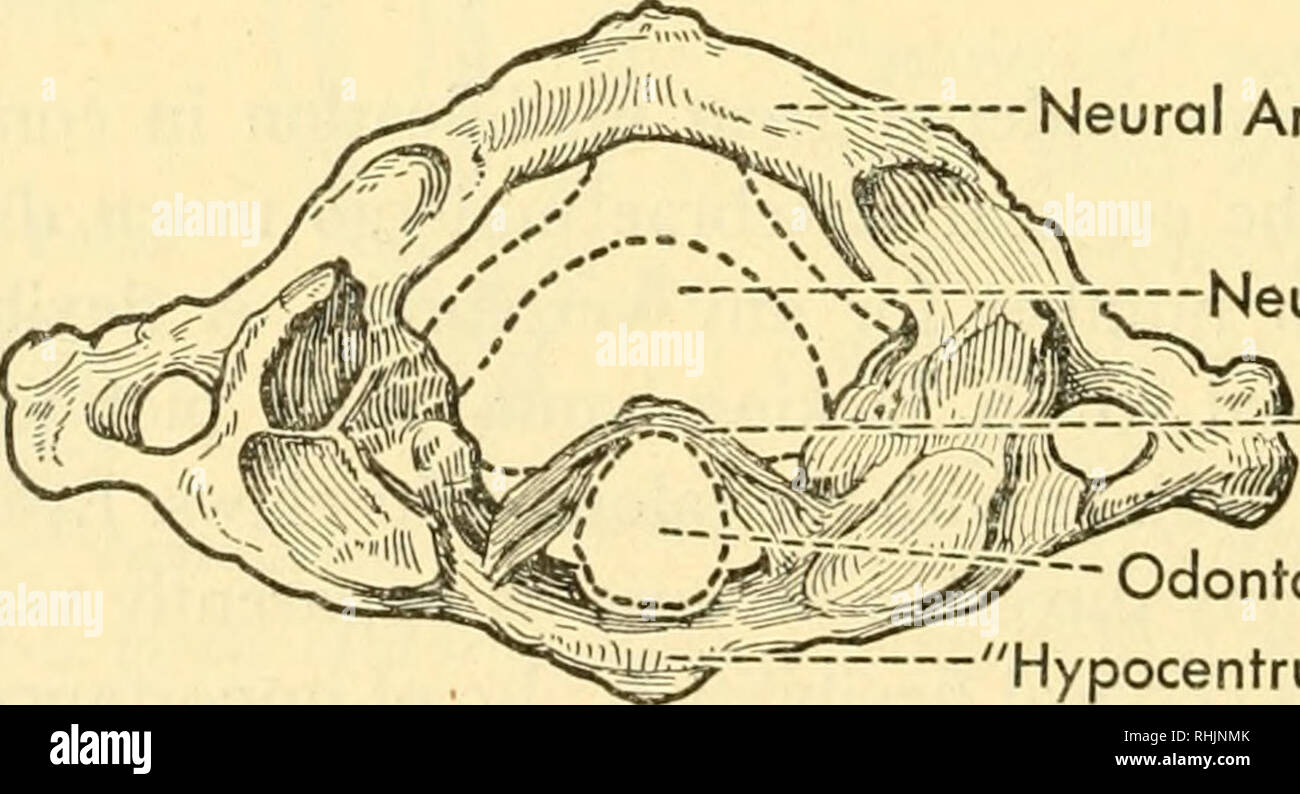
Image details
Contributor:
Library Book Collection / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RHJNMKFile size:
7.2 MB (282.6 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
2147 x 1164 px | 36.4 x 19.7 cm | 14.3 x 7.8 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Biology of the vertebrates : a comparative study of man and his animal allies. Vertebrates; Vertebrates -- Anatomy; Anatomy, Comparative. Centrum of Axis Fig. 440. The human atlas and axis, ventral view. (After Sobotta and McMurrich.) There are four known exceptions to this rule of seven: the three-toed sloth, Brady pus, has nine cervical vertebrae; the ant-bear, Tamandua, eight; while the two-toed sloth, Choloepus, and the American sea cow, Trichechus, each has six. As in reptiles and birds, the first two cervical vertebrae of mammals are further specialized into the so-called atlas and the axis (Fig. 440). The atlas, according to Vesalius, takes its name from human anatomy, since in man it "bears the weight of the world" upon its shoulders in the form of the head, -Neural Arch. Neural Canal ^/W-'r"Tra nsverse Ligament ~~ Odontoid Process 'Hypocentrum" Fig. 441. Relation of odontoid process to atlas in man, as seen from the anterior (superior, of human anatomical terminology) side. (After Gray.) after the fashion of its classical prototype. Two articular surfaces at the base of the skull in mammals, the occipital Condyles, are in frictional contact with two corresponding surfaces on the atlas, thus forming a joint that allows for the nodding movements of the head. The atlas is virtually without the. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Walter, Herbert Eugene, b. 1867; Sayles, Leonard Perkins, 1902-. New York : Macmillan Co.