Human anatomy, including structure and development and practical considerations . and theblunted point tlirected downwartl and forward (Fig. 978J. Hehind, it communicateswith the Sylvian aqueduct, and through this canal indirectly with the fourth entricle;anteriorly it connects with the two lateral ventricles by means of the foramina ofMonro. Its sagittal diameter, measured between the anterior commissure and thebase of the pineal body, is approximately 2.5 cm. The lateral wall of the ventricle(Fig. 976) is formed chiefly by that part of the thalamus which lies below the levelof the taenia th
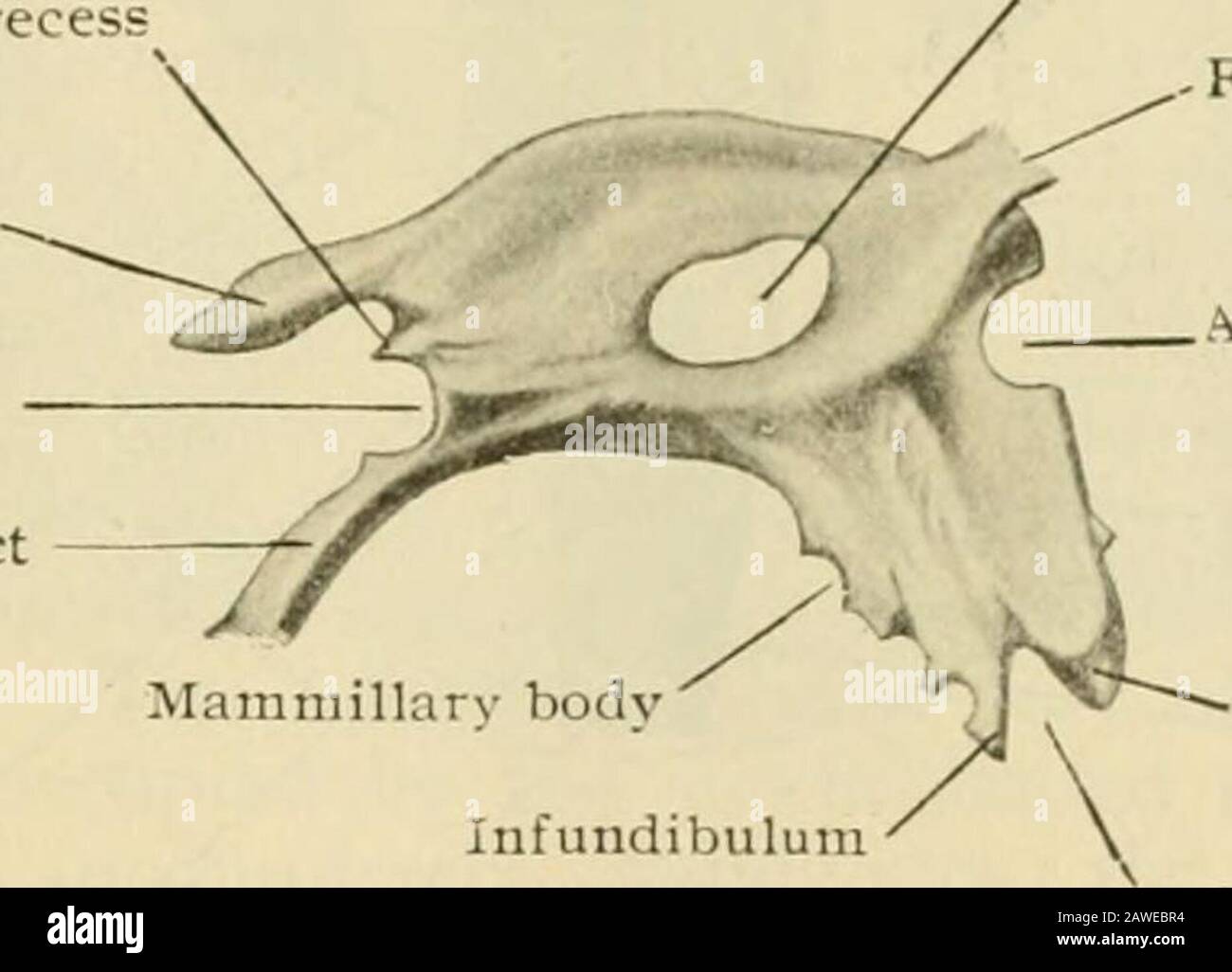
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AWEBR4File size:
7.1 MB (142.9 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1862 x 1342 px | 31.5 x 22.7 cm | 12.4 x 8.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Human anatomy, including structure and development and practical considerations . and theblunted point tlirected downwartl and forward (Fig. 978J. Hehind, it communicateswith the Sylvian aqueduct, and through this canal indirectly with the fourth entricle;anteriorly it connects with the two lateral ventricles by means of the foramina ofMonro. Its sagittal diameter, measured between the anterior commissure and thebase of the pineal body, is approximately 2.5 cm. The lateral wall of the ventricle(Fig. 976) is formed chiefly by that part of the thalamus which lies below the levelof the taenia thalami. On this surface, slightly in advance of the middle, is seen thesmall oval field of the middle commissure^ and in front of this the downward curvingelevation produced by the anterior pillar of the fornix. Between the latter and theprominent anterior tubercle of the thalamus lies the foramen of Monro (lorameniiiterveiitricularc), which establishes communication between the third and the cor- Pineal recess Suprapineal recess Posterior commissure Sylvian aqueduct Fig. 978.. Middle commissure/ -Foramen of Monro Anterior commissure Optic recess Infundibulum • Optic chiasm Cast of third ventricle, viewed from the side. X %? {Retziiis.) responding lateral ventricle, and transmits the trunk formed by the union of thevein of the corpus striatum and the choroid vein. A shallow furrow on the ventric-ular wall, the sulcus hypothalamicus leads from the foramen backward and some-what downward (Fig. 976). It is of importance as indicating, even in the adultbrain, the demarcation between the thalamencephalon and the hypothalamus—partsderived respectively from the dorsal and -entral zones of the embryonic brain-esicle.The roof of the ventricle extends from the foramina of Monro, bounded aboveand in front by the arching pillars of the fornix, to the pineal body behind, * overwhich it pouches out into the suprapineal recess, as the little diverticulum o-erlyingthe body is termed. The